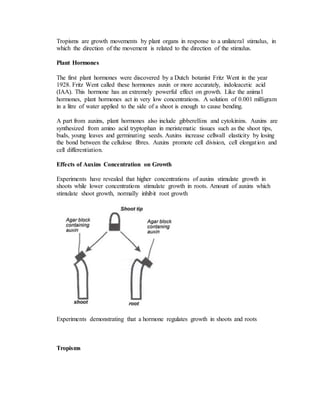
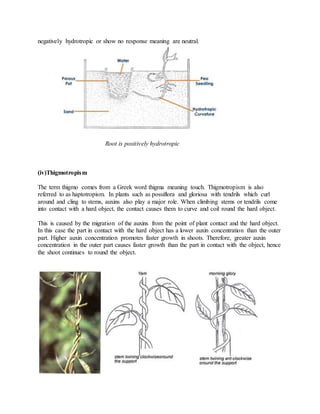
Plants can move in response to stimuli through growth movements and turgor movements. Growth movements include autonomic movements controlled by the plant itself and paratonic movements induced by external stimuli like light, moisture, gravity, chemicals, and touch. Paratonic movements include tropic movements where the plant grows toward or away from a stimulus, as well as nastic movements resulting from changes in turgor pressure. Tropic movements are mediated by plant hormones like auxins, which promote cell growth and cause plants to bend toward or away from a stimulus depending on its concentration. Auxins also influence other growth processes like apical dominance, adventitious root growth, fruit development and ripening, and weed control.