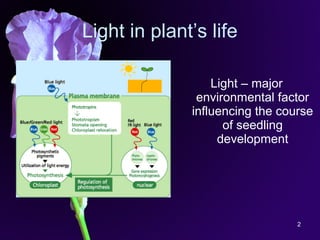
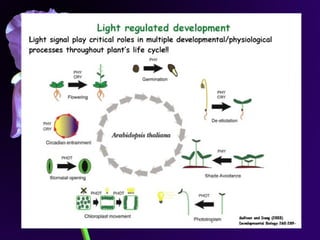
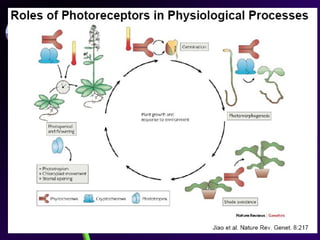
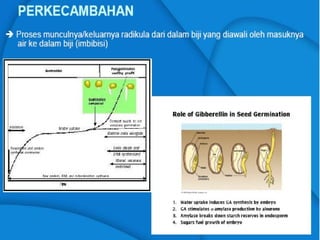
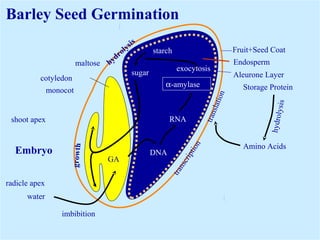
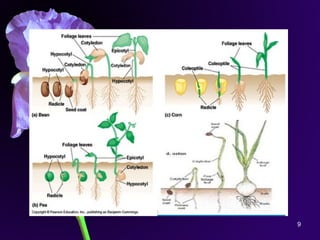
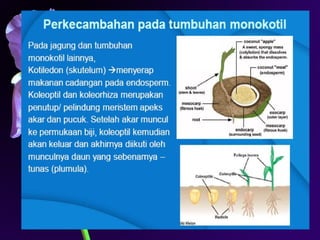
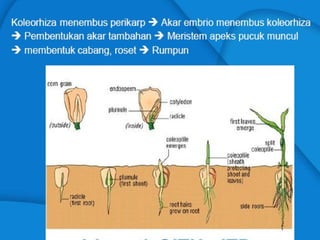
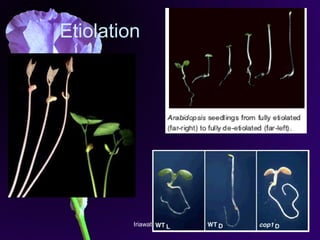
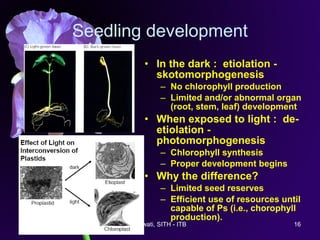
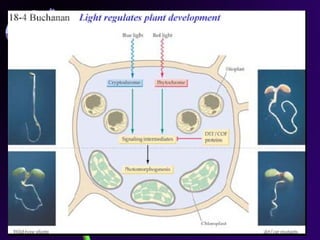
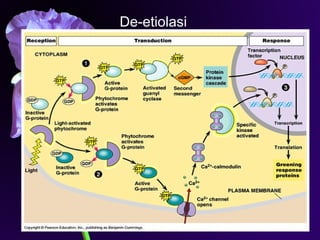
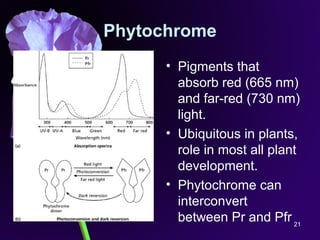
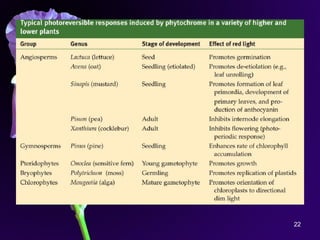
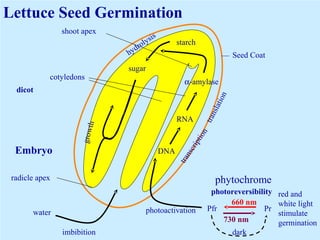
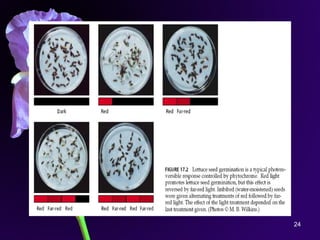
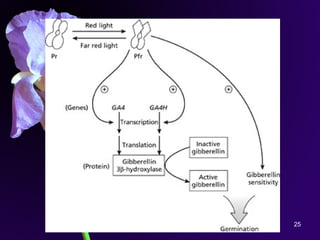
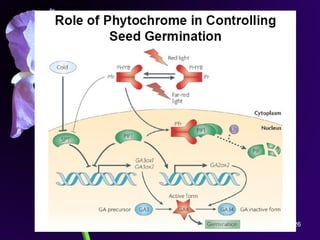
Light is a major environmental factor that influences seedling development. During seed germination, light controls whether seedlings develop normally (de-etiolation) or abnormally in the dark (etiolation). In the dark, seedlings undergo etiolation with limited organ development and no chlorophyll production. When exposed to light, seedlings undergo de-etiolation where they develop properly with chlorophyll synthesis and organ development. This process of de-etiolation from the etiolated state to normal growth is triggered by light and involves photoreceptors such as phytochromes that detect light and induce changes in seedling development.