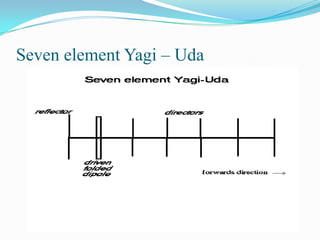
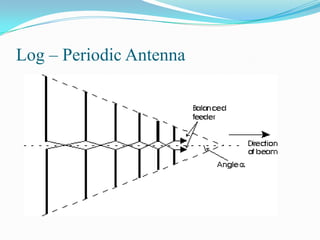
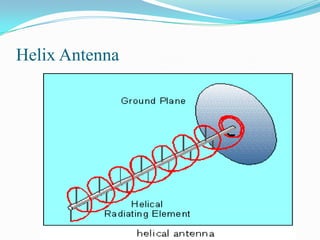
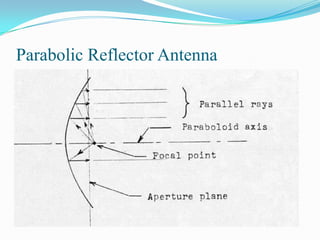
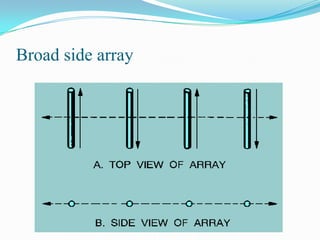
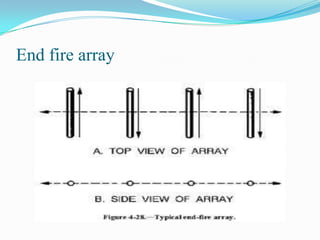
This document describes different types of antennas used for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves. It discusses transmitter and receiver antennas. Specific antenna types covered include Yagi-Uda antennas, log-periodic antennas, helix antennas, parabolic antennas, loop antennas, and antenna arrays. Each antenna type has distinct characteristics that make it suitable for different frequency ranges and applications.