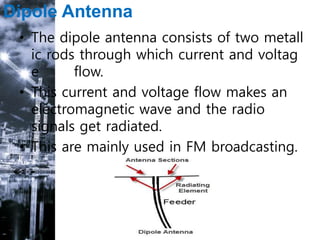
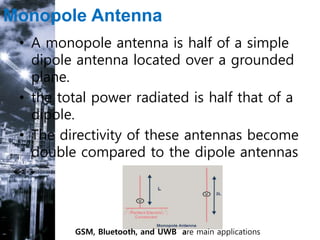
This document discusses different types of antennas used for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves. It describes log-periodic antennas, which work over a wide frequency range using a logarithmic size progression of elements. Specific types are described, including bow-tie antennas and log-periodic dipole arrays. Wire antennas like dipoles, monopoles, and loops are also covered. Travelling wave antennas transmit signals along their length, represented by helical and Yagi-Uda antennas. Microwave antennas and reflector antennas are used at higher frequencies for applications like communication and radar. Key antenna properties and a variety of applications are also summarized.