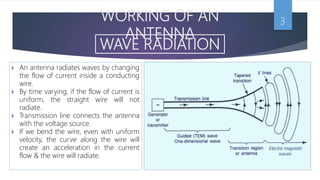
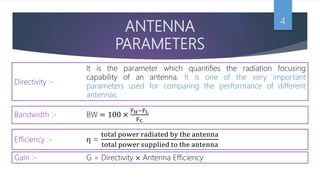
An antenna converts alternating current into radio frequency fields and vice versa. It radiates waves by changing the flow of current inside a conducting wire. The efficiency, gain, directivity, and bandwidth are important antenna parameters used to compare performance. There are different types of antennas including dipole, loop, monopole, and array antennas which are used for applications like radio, radar, and satellite communication.