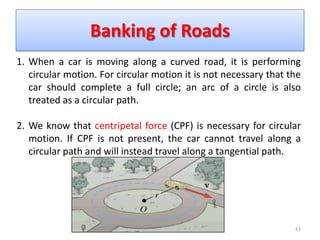
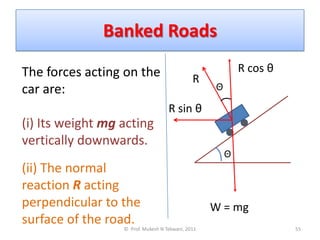
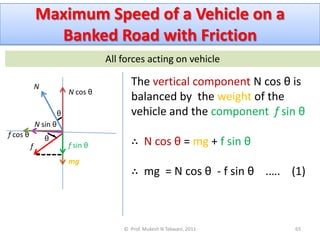
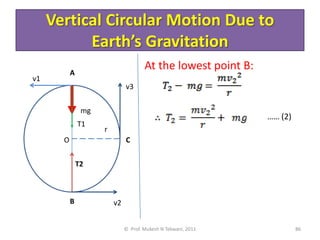
This document discusses circular motion and provides examples and explanations of key concepts related to circular motion, including:
1) Circular motion is defined as motion along a complete or partial circle. Centripetal force is required to produce the acceleration needed for circular motion.
2) Examples of centripetal force include tension in a string for a body whirled in a circle, friction for a car rounding a turn, and gravitational attraction for objects like moons orbiting planets.
3) Centripetal acceleration always points toward the center of the circular path and has a magnitude of v^2/r, where v is the object's speed and r is the radius of the path. Radial acceleration equals the






















![Radial Acceleration
The velocity of particle at any instant (any time) is called its
instantaneous velocity.
The instantaneous velocity is given by
v = dr / dt
∴ v = d/dt [ ir cos wt + jr sin wt]
∴ v = - i r w sin wt + j r w cos wt
© Prof. Mukesh N Tekwani, 2011 36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/circularmotion-120902002951-phpapp02/85/Circular-motion-23-320.jpg)