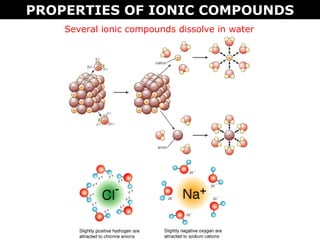
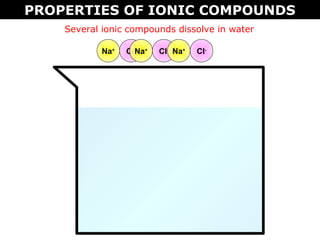
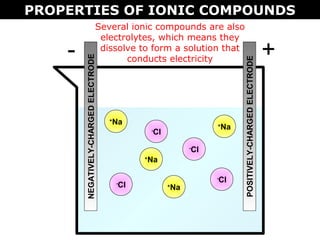
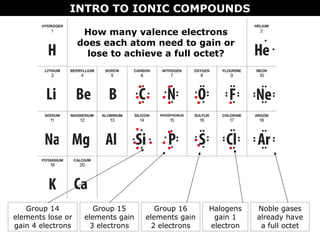
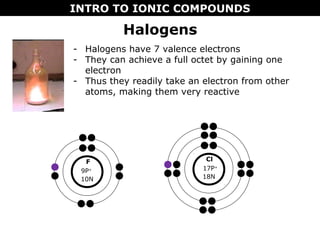
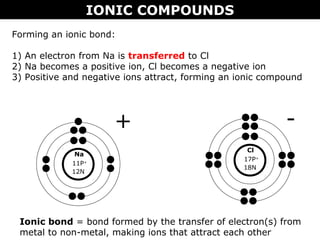
1) Ionic compounds form when a metal transfers electrons to a nonmetal, creating oppositely charged ions that are attracted to each other. This results in properties like being hard, brittle, and dissolving in water to conduct electricity.
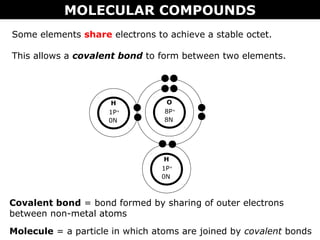
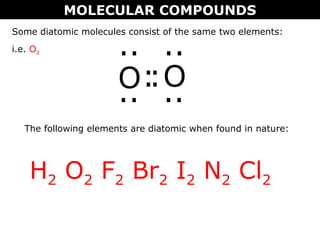
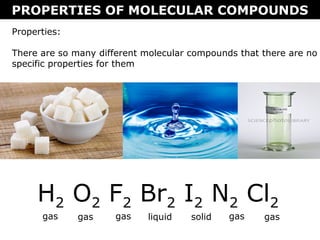
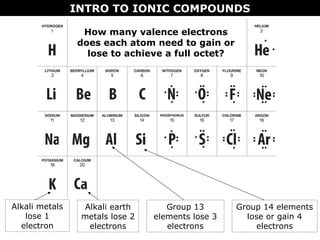
2) Molecular compounds form when nonmetals share electrons in covalent bonds. Molecular compounds have more varied properties depending on the atoms involved.
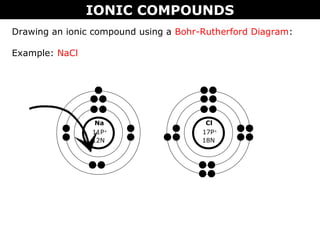
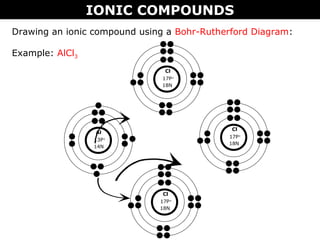
3) The document provides instructions on drawing Lewis dot and Bohr-Rutherford diagrams to represent ionic and molecular compounds.


![IONIC COMPOUNDS
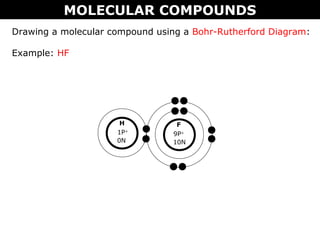
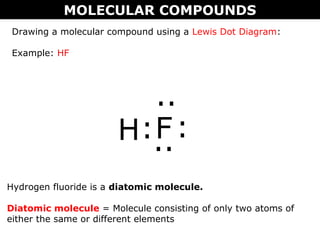
Drawing an ionic compound using a Lewis Dot Diagram:
Example: NaCl
Na[ ]
+
Cl
..
:: ..[ ]
-
Rule: Square brackets must appear around ions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02bionicvs-150908161045-lva1-app6892/85/02-b-ionic-vs-molecular-compounds-bohr-rutherford-and-lewis-9-320.jpg)
![IONIC COMPOUNDS
Drawing an ionic compound using a Lewis Dot Diagram:
Example: AlCl3
Al
.
.
.[ ]
3+
Cl
..
:: ..[ ]
-
Cl
..
:: ..[ ]
-
Cl
..
:: ..[ ]
-
Rule: Square brackets must appear around ions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02bionicvs-150908161045-lva1-app6892/85/02-b-ionic-vs-molecular-compounds-bohr-rutherford-and-lewis-11-320.jpg)