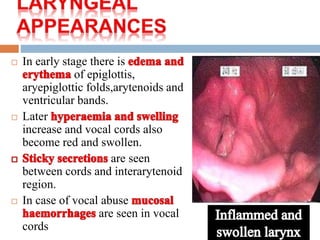
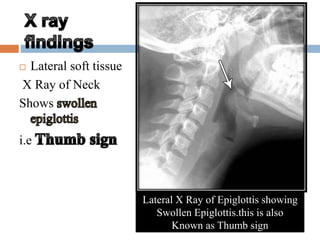
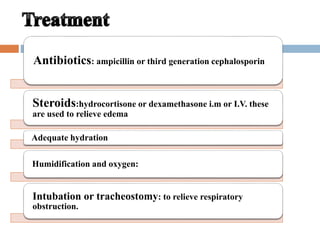
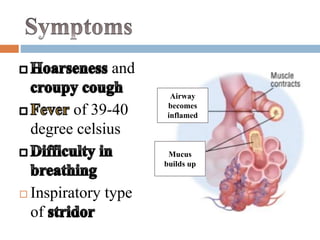
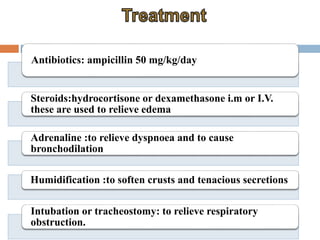
Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx which can lead to loss of voice. Symptoms are worse at night. In early stages, there is redness of structures like the epiglottis and vocal cords. Later, swelling increases and vocal cords become red and swollen with fluid seen between cords. Treatment includes vocal rest, avoiding smoking/alcohol, steam inhalation, cough suppressants, antibiotics, and steroids. Croup is an inflammatory condition of the larynx and trachea mostly caused by viruses in children aged 6 months to 3 years, causing swelling in the subglottic region and obstructing the airway.