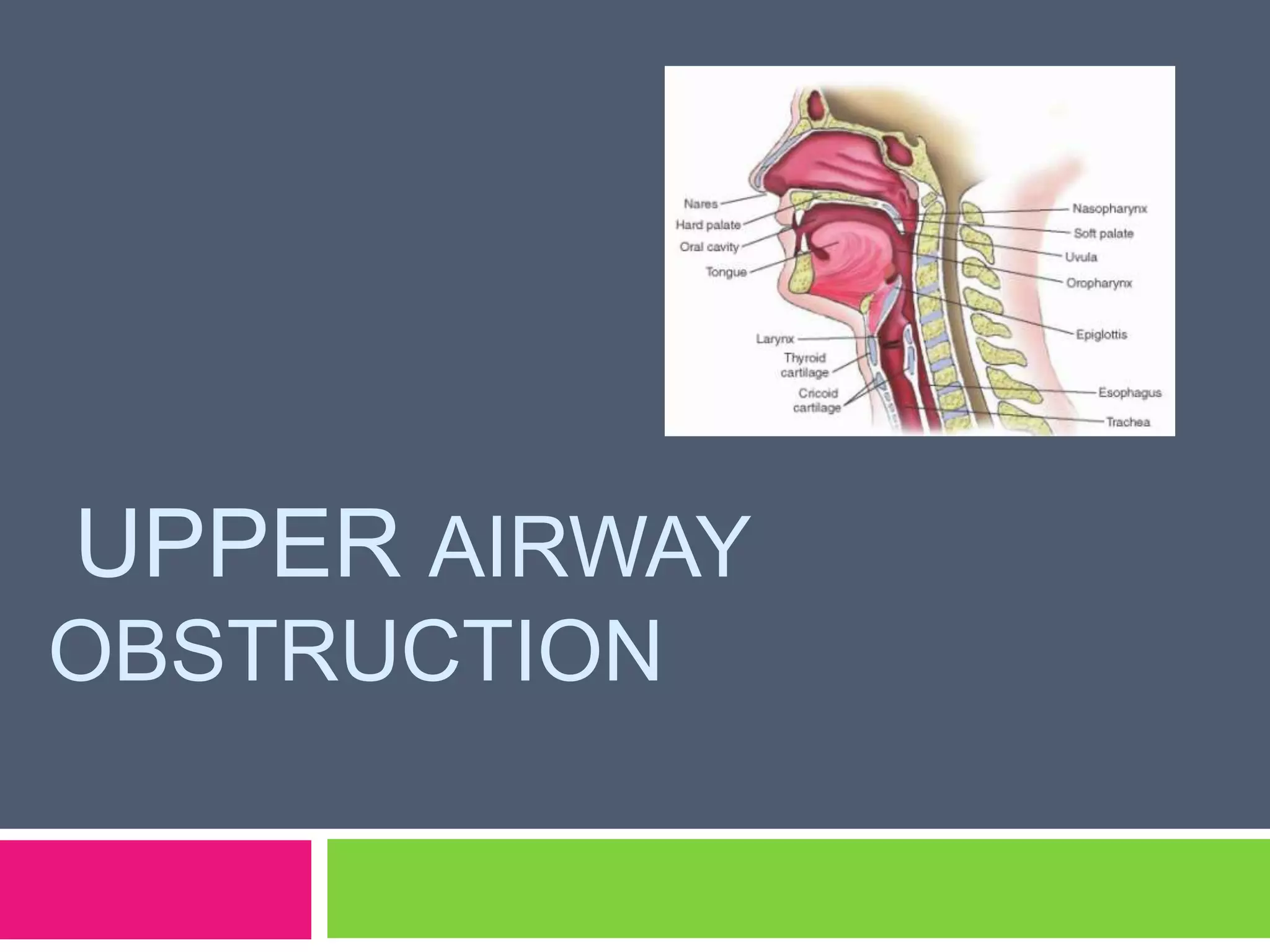
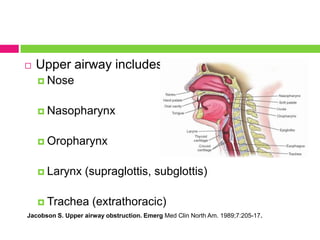
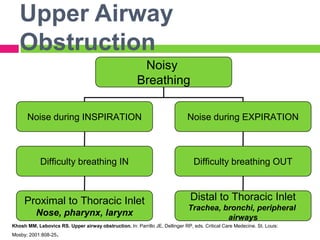
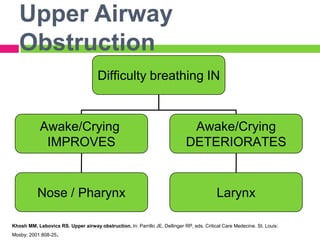
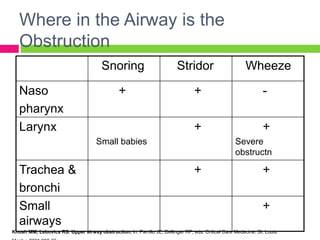
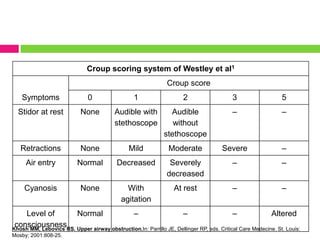
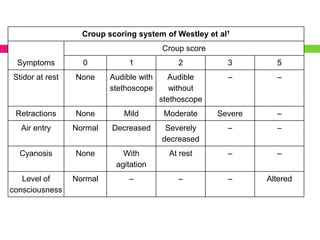
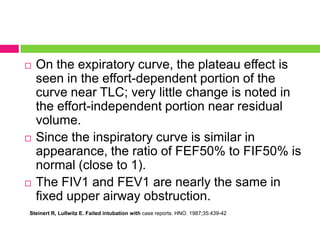
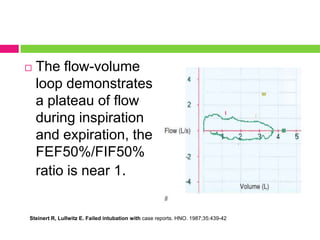
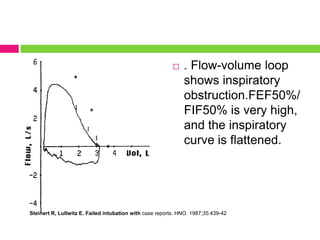
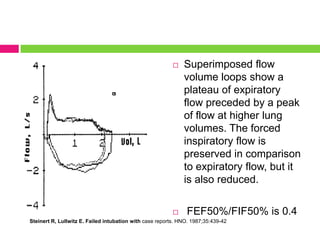
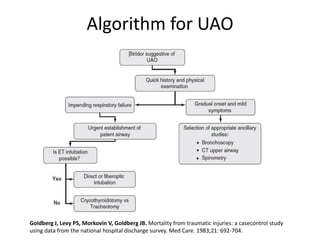
This document discusses upper airway obstruction, including its location, signs and symptoms, causes, and types. The upper airway extends from the nose or mouth to the main carina. Common causes of obstruction include infections, tumors, and trauma. Signs include noisy breathing, dyspnea, and hypoxemia. Obstructions can be fixed or variable. Fixed obstructions do not change size during breathing and result in flattened flow-volume loops. Variable obstructions change size during breathing, most commonly seen in vocal cord paralysis. Proper diagnosis relies on patient history and examination of flow-volume loops.