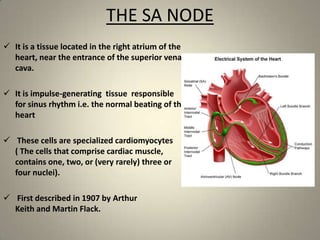
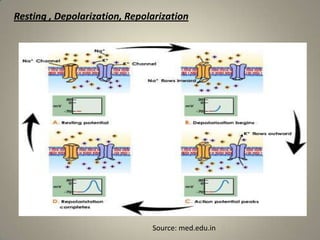
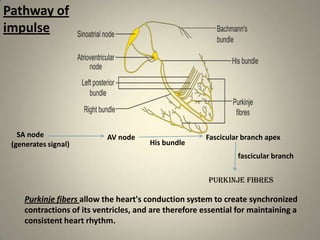
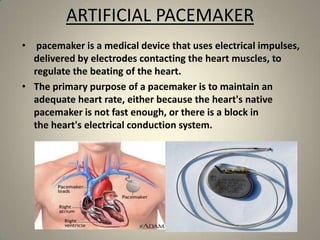
This document summarizes the sinoatrial node, which acts as the heart's natural pacemaker by generating electrical impulses that trigger contractions. It is located in the right atrium and contains specialized cardiomyocytes. These cells use resting potential, depolarization, and repolarization to generate action potentials that conduct through the heart's conduction system and cause coordinated contractions of the atria and ventricles. If the sinoatrial node fails, secondary pacemakers in the atrioventricular node or bundle of His can maintain a slower heart rate. An artificial pacemaker can also regulate heart rate electrically if the natural pacemaker is insufficient.