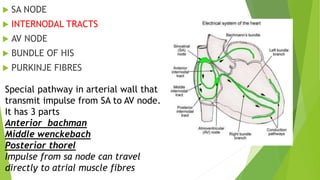
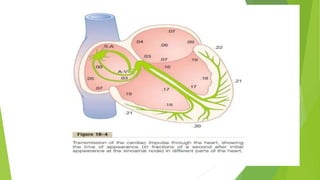
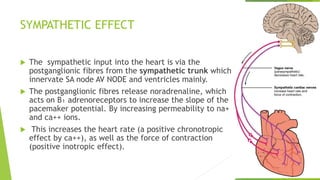
The document summarizes cardiac impulse conduction and innervation. It discusses the electrical conduction system of the heart including the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers which generate and transmit electrical impulses to allow for coordinated heart contraction. The conduction velocities and pathways of the different conduction fibers are described. The document also outlines the innervation of the heart by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, noting their opposing effects on heart rate and contractility.