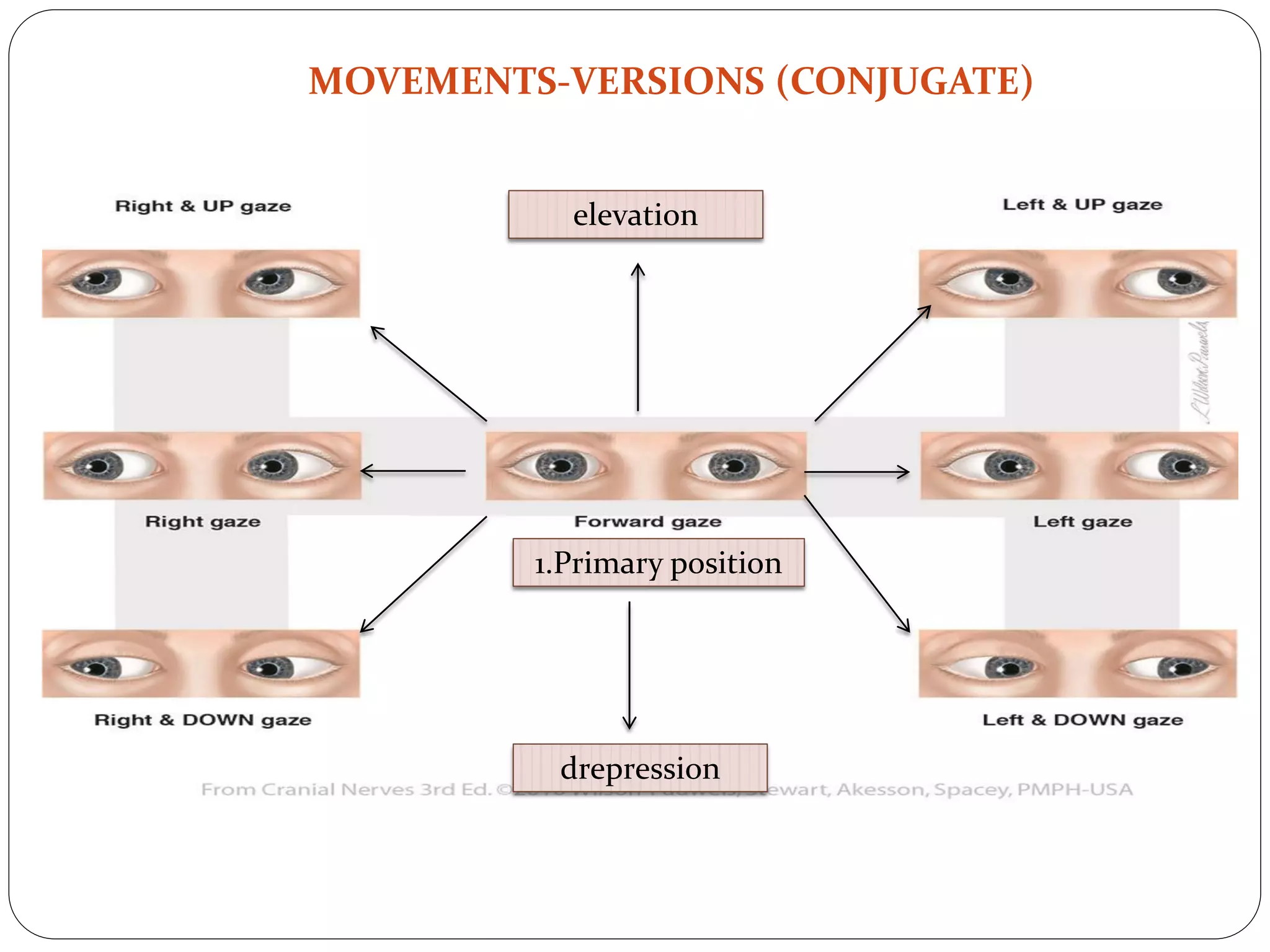
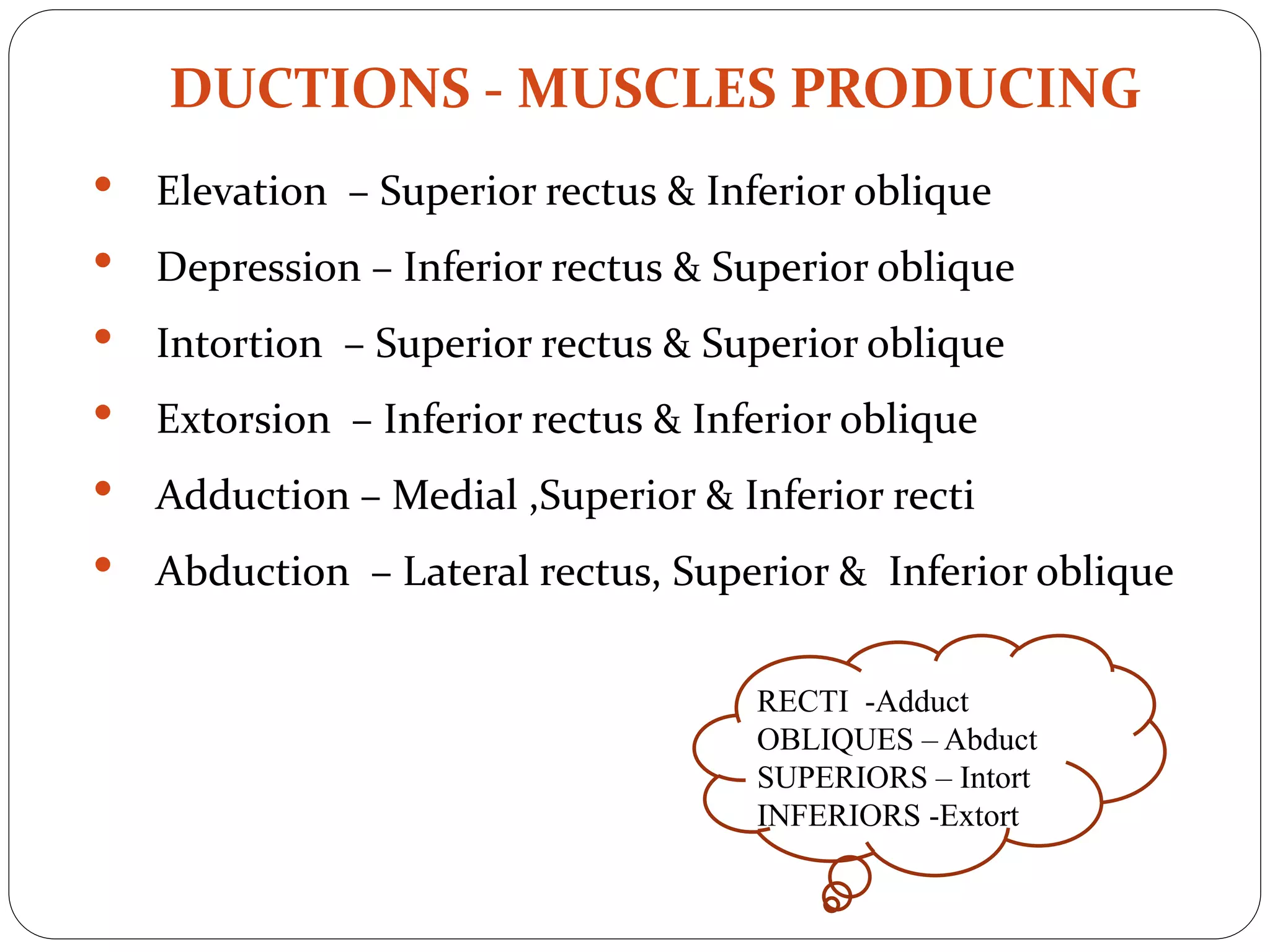
The document discusses the extraocular muscles of the eye. It describes the six extraocular muscles - the four rectus muscles (medial, lateral, superior, inferior) and two oblique muscles (superior, inferior) that control eye movement. It details the origin, insertion, nerve supply and action of each individual muscle. Collectively, these muscles enable movements like elevation, depression, adduction, abduction, intorsion and extorsion of the eyeball. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle is also described, which is responsible for elevating the upper eyelid. Various clinical tests and conditions involving these muscles like strabismus, ptosis and nerve palsies are mentioned.