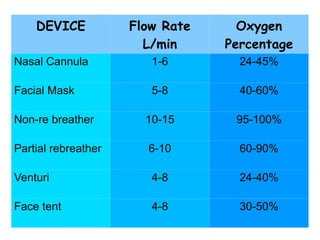
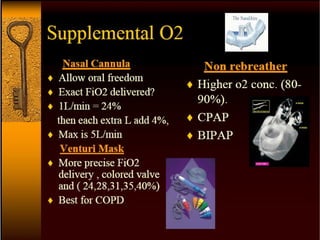
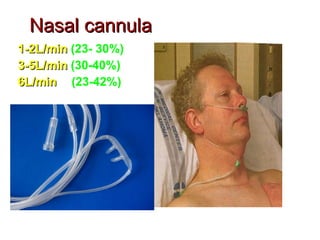
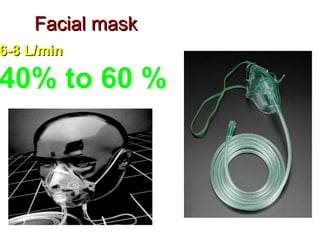
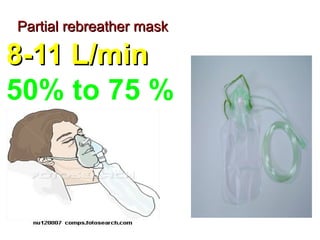
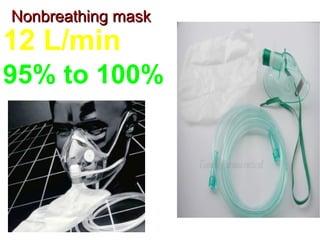
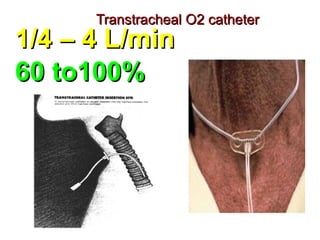
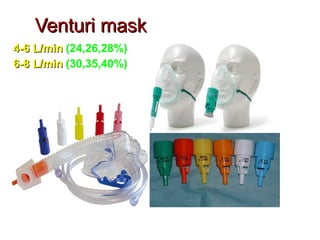
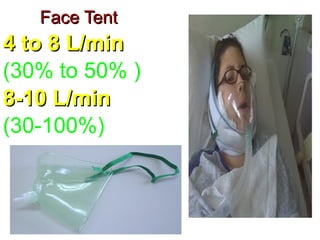
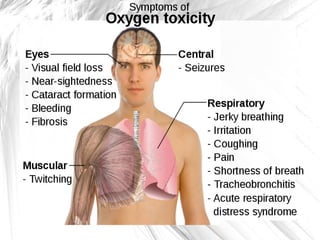
Oxygen therapy involves administering oxygen at concentrations higher than in room air to treat hypoxemia. It is commonly used as part of pulmonary rehabilitation to correct low oxygen levels in the blood and tissues. The main indication for oxygen therapy is a resting blood oxygen level of 55 mm Hg or lower. Tests like oximetry and blood gas analysis can determine if a patient needs oxygen therapy. Different devices like nasal cannulas, masks, and venturi masks can deliver oxygen at varying concentrations depending on the flow rate. Prolonged high-dose oxygen therapy can cause oxygen toxicity, resulting in lung damage.