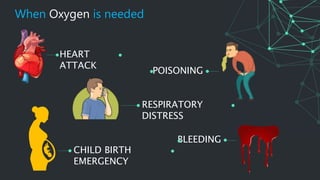
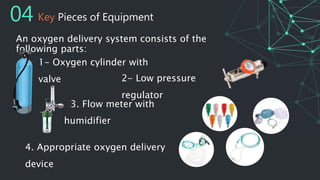
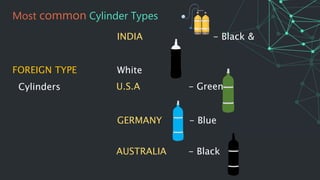
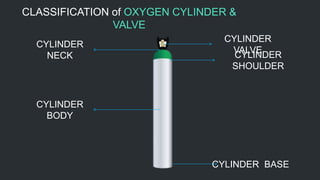
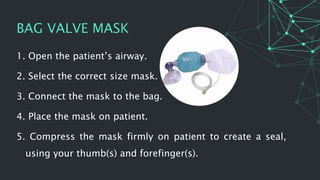
This document provides information on oxygen therapy equipment and procedures. It describes five situations where oxygen is needed, including heart attacks and respiratory distress. The key equipment for oxygen delivery includes oxygen cylinders, regulators to reduce pressure, flow meters, and various masks. Proper safety precautions must be followed when using oxygen, such as not smoking near cylinders. The document explains how to assemble the equipment and administer oxygen using different masks and attachments like nasal cannulas and venturi masks.