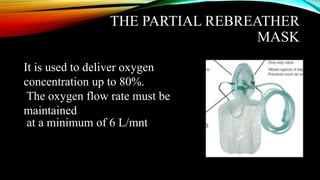
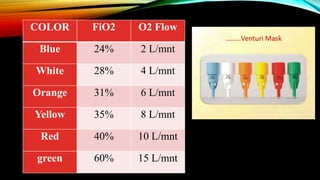
The document discusses various methods of oxygen administration. It defines oxygen administration as providing oxygen at a higher concentration than atmospheric air. Various sources of oxygen are described including wall outlets and cylinders. Signs of hypoxemia that indicate the need for oxygen therapy are provided. Common indications for oxygen therapy include cyanosis, dyspnea, and hypoxemia. Different devices for oxygen delivery are outlined like nasal cannulas, masks, hoods, and tracheostomy collars along with their advantages and disadvantages.