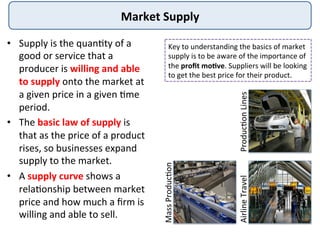
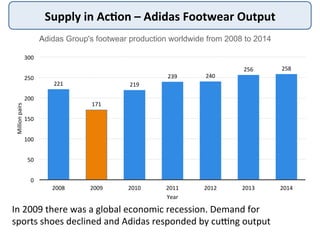
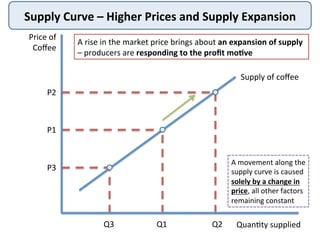
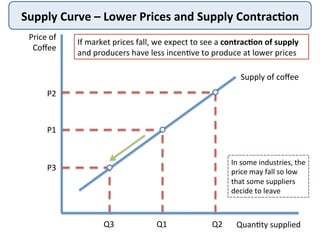
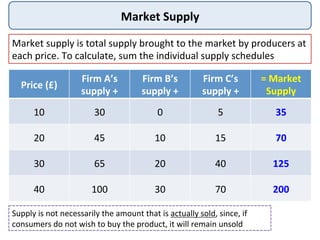
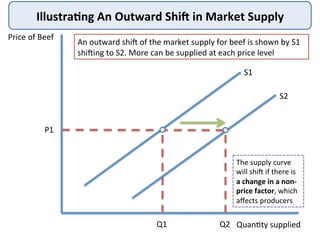
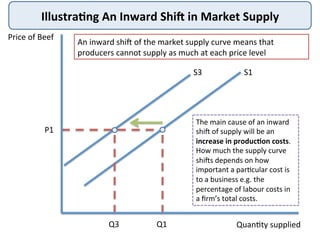
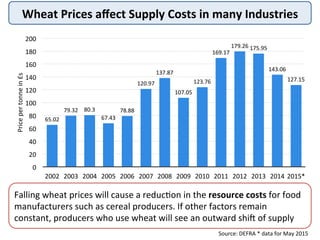
The document discusses the theory of market supply in economics. It defines supply as the quantity of a good or service producers are willing and able to provide at a given price in a given time period. The basic law of supply is that supply increases as price rises, as shown by a positively-sloped supply curve. The reasons for the upward-sloping supply curve are the profit motive, increasing production costs as output expands, and new producers entering the market at higher prices. The document provides examples and illustrations of how supply responds to changes in price and other factors.