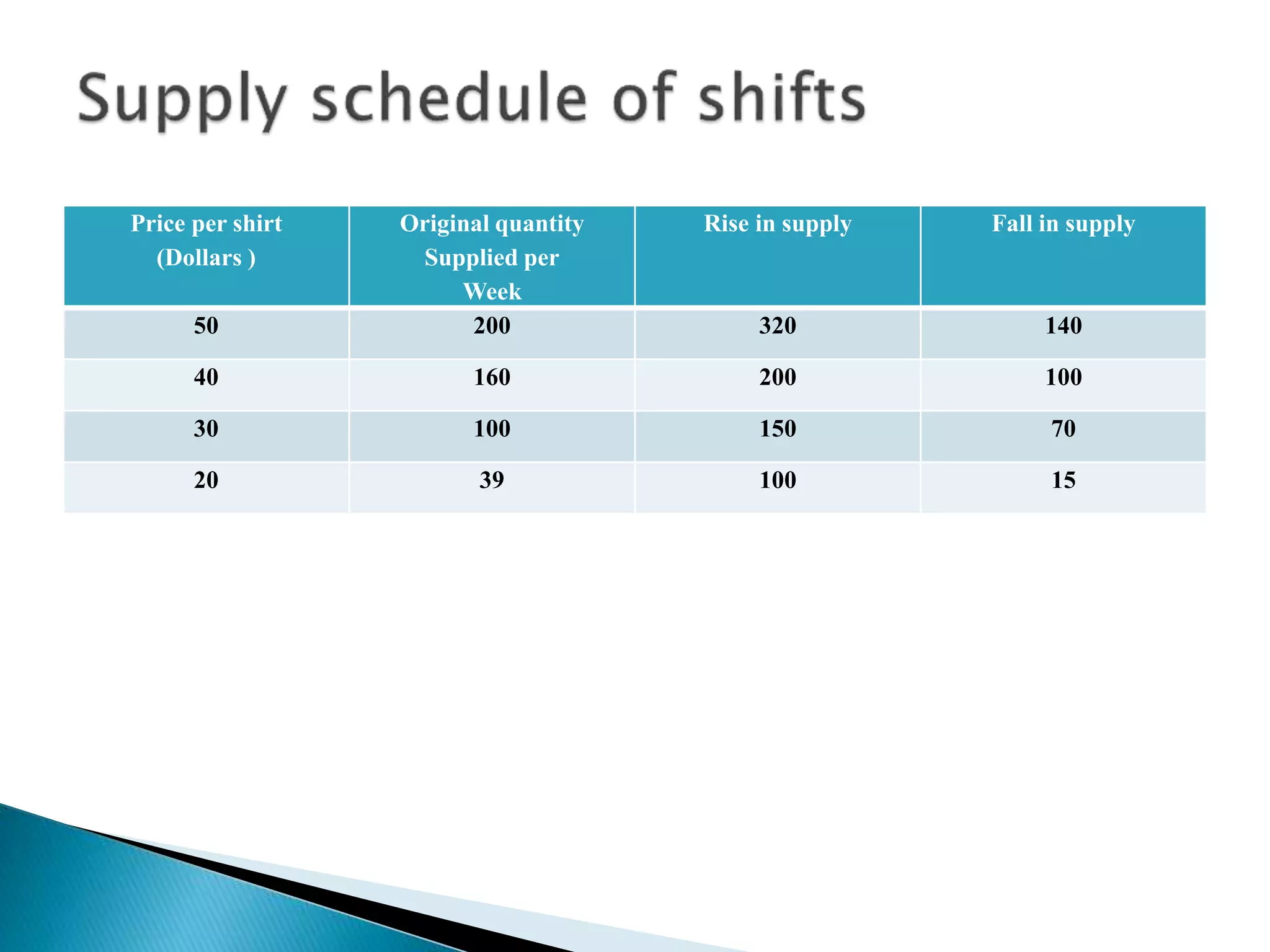
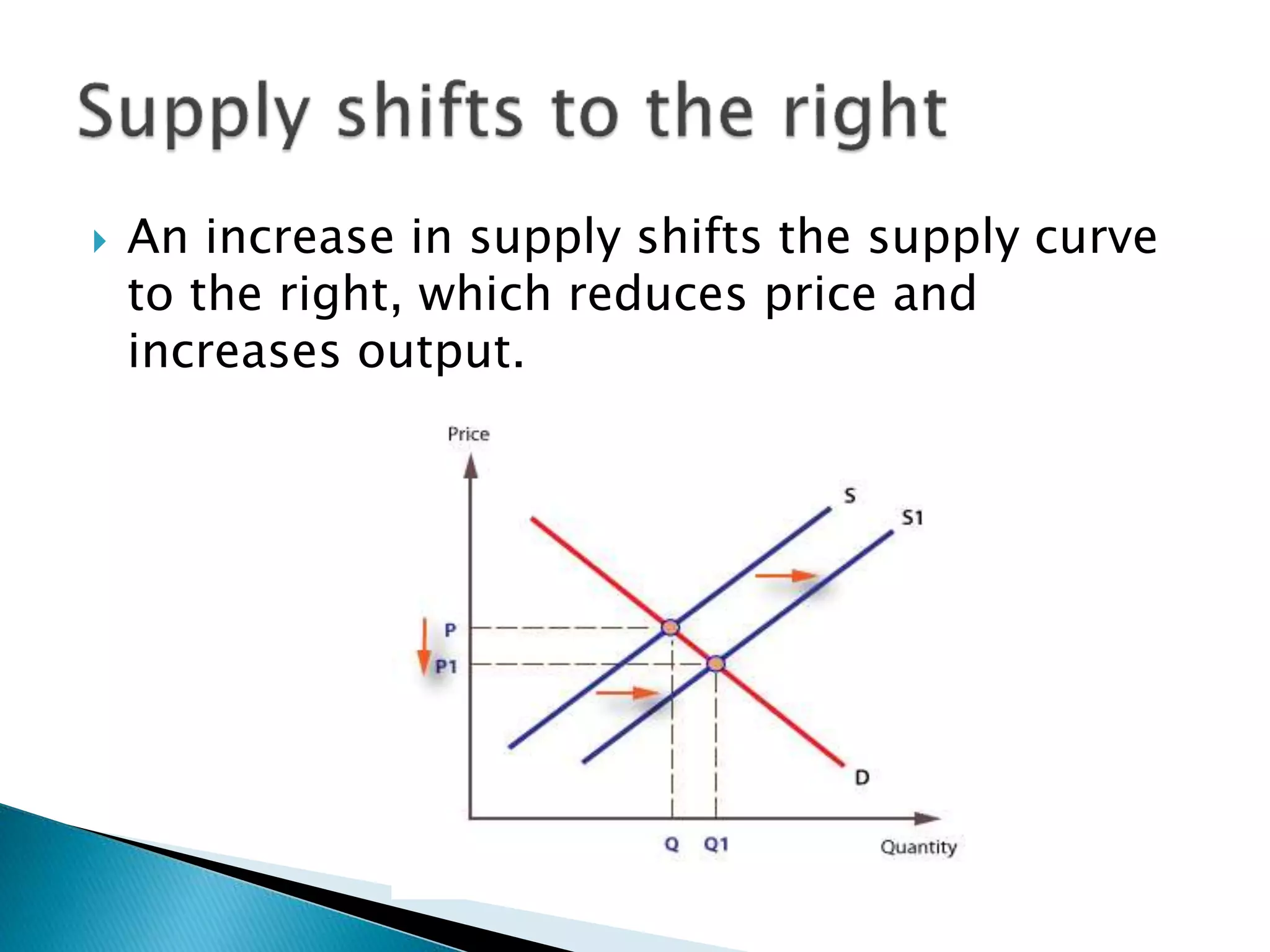
The document discusses the concept of supply in economics, defining it as the quantities of goods and services available for sale at fixed prices over specified periods. It outlines the relationship between price and quantity supplied, the law of supply, and factors that can lead to shifts in the supply curve. Additionally, it examines market equilibrium, surplus, and shortage scenarios, explaining how changes in supply and demand affect equilibrium price and quantity.