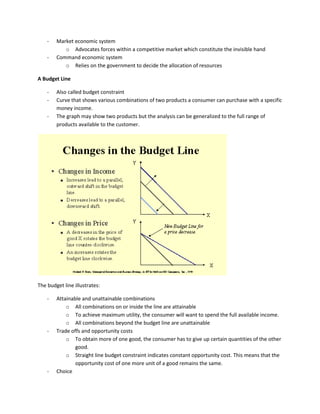
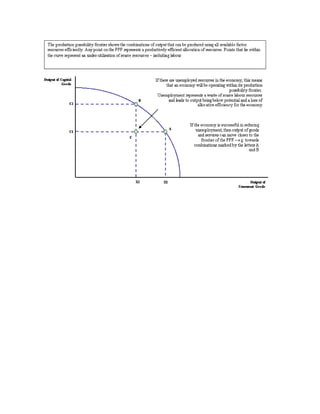
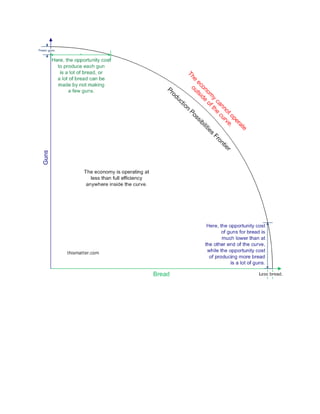
Economics studies how individuals and societies make decisions regarding scarce resources. It analyzes human behavior as purposeful and rational, seeking to maximize utility given costs and benefits. Microeconomics examines individual and firm decision-making while macroeconomics analyzes total output, resource allocation, and trade at a national level. The market economic system relies on competitive forces while command systems involve centralized government planning. Individuals and societies must choose how to allocate limited resources to maximize production and promote growth.