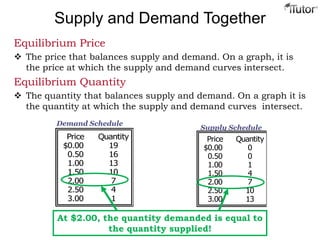
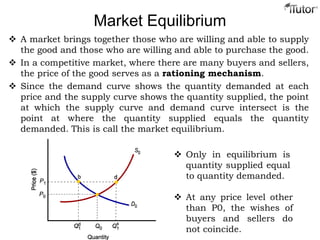
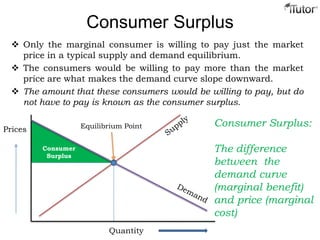
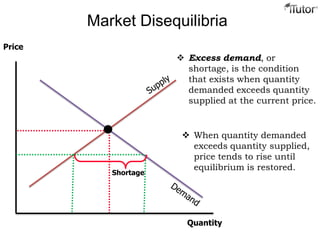
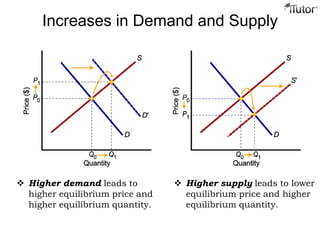
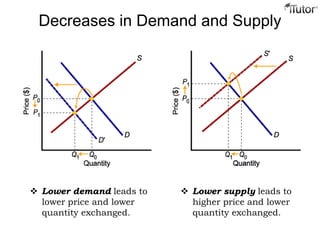
The document discusses market equilibrium, which occurs at the price where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. This equilibrium price is found at the intersection of the supply and demand curves. At the equilibrium point, the market is balanced, with no excess supply or demand. Disequilibrium can occur if there is a shortage when demand exceeds supply, or a surplus when supply exceeds demand. The document also discusses how changes in supply or demand affect the equilibrium price and quantity, and introduces the concepts of consumer surplus and producer surplus.