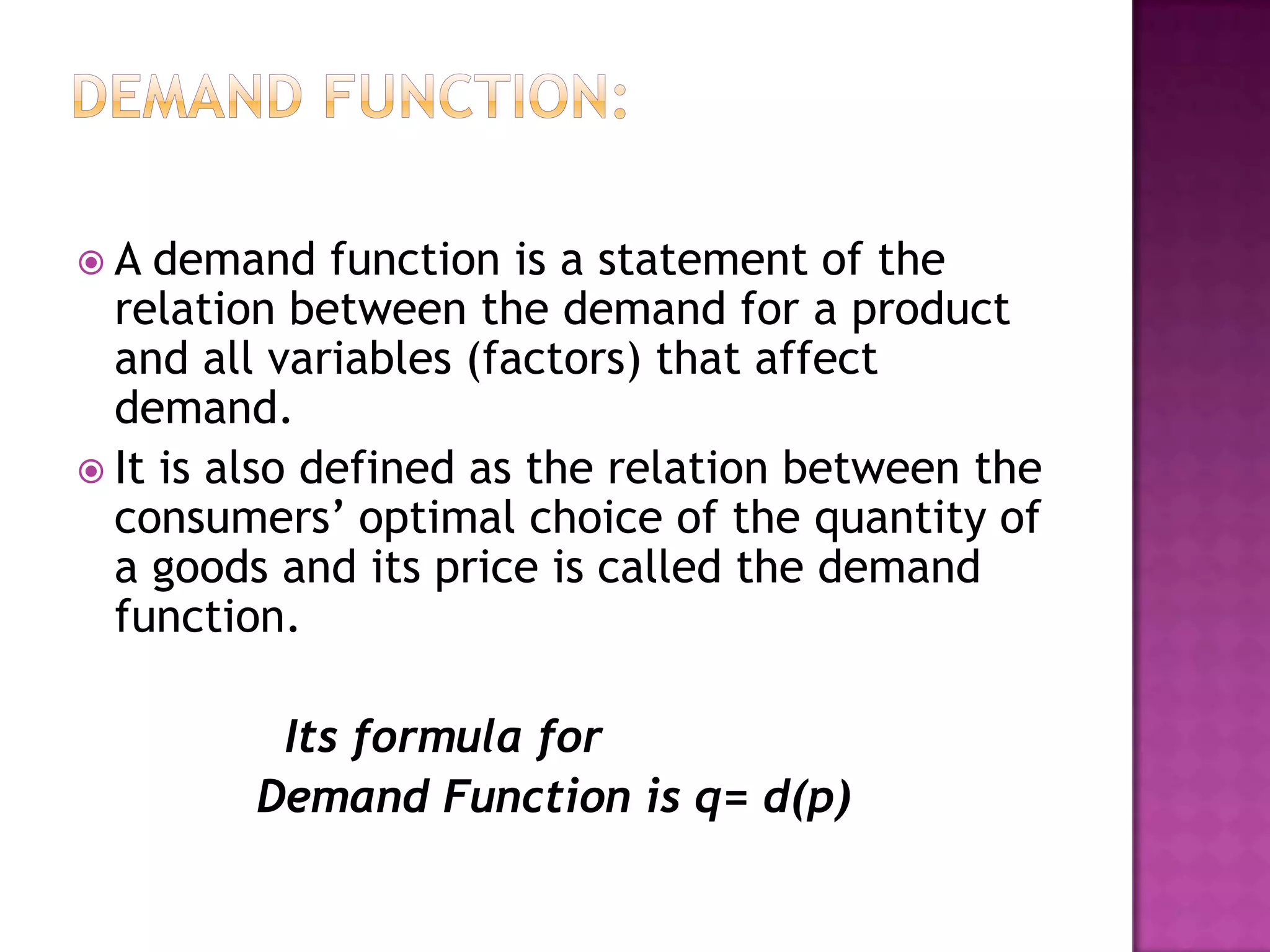
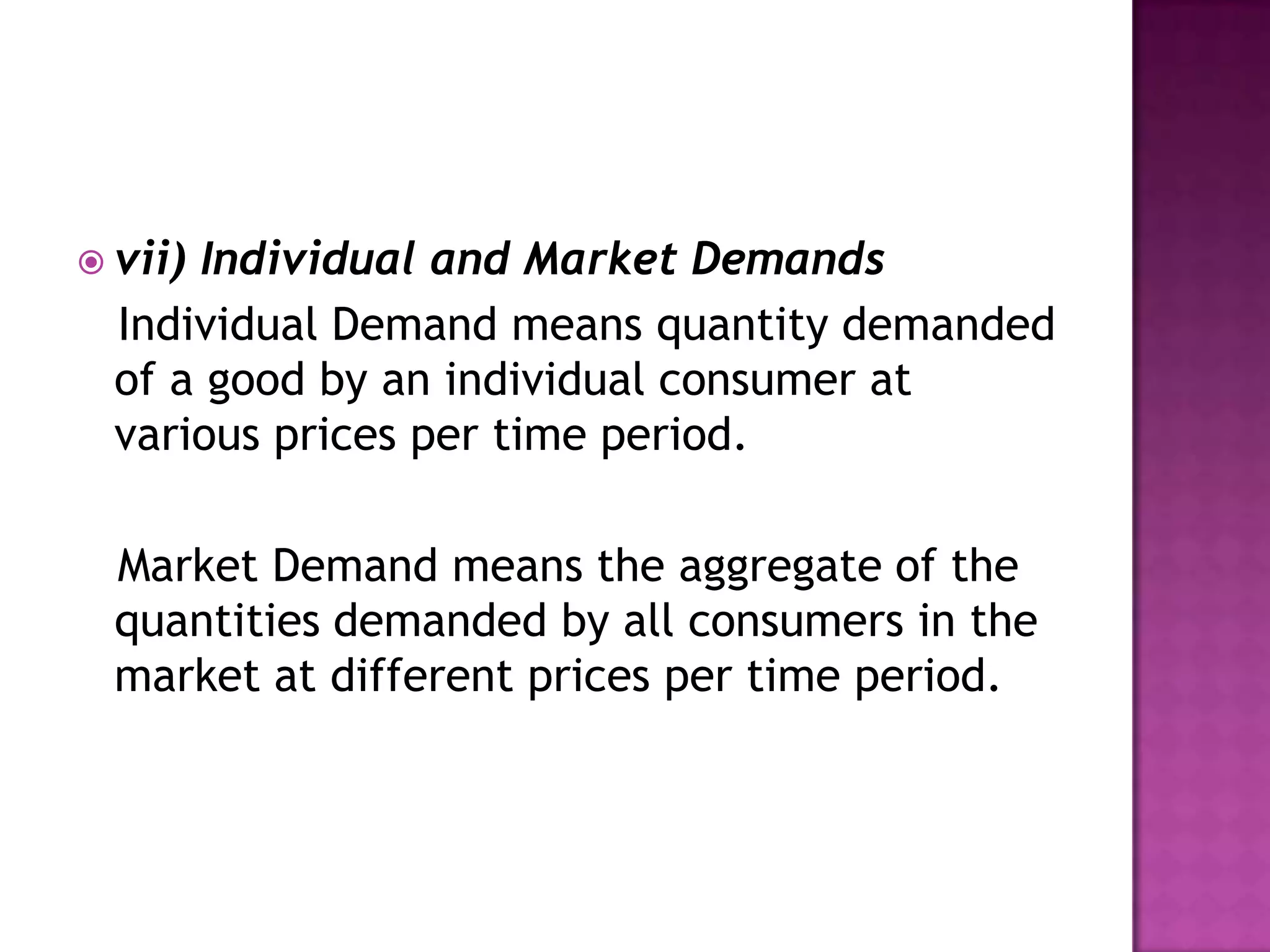The document discusses demand functions and different types of demand. It defines individual and market demand functions. Individual demand function shows how demand for a commodity relates to its price, income of the consumer, tastes and other factors. Market demand function adds population size and income distribution as additional factors. The document also outlines seven types of demand: direct vs derived, domestic vs industrial, autonomous vs induced, perishable vs durable goods, new vs replacement, final vs intermediate, and individual vs market demands.