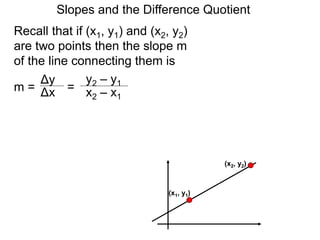
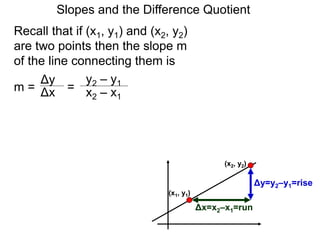
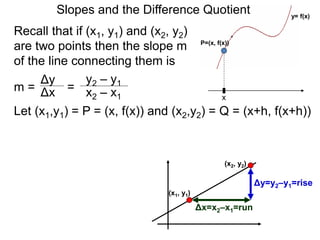
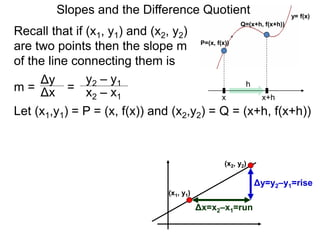
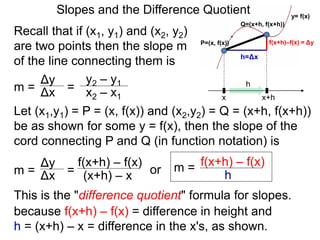
The document discusses the difference quotient formula for calculating the slope between two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) on a function y=f(x). It shows that the slope m is equal to (f(x+h)-f(x))/h, where h is the difference between x1 and x2. This "difference quotient" formula allows slopes to be calculated from the values of a function at two nearby points. Examples are given of simplifying the difference quotient for quadratic and rational functions.






![x
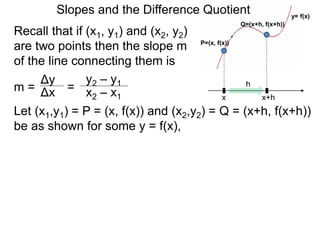
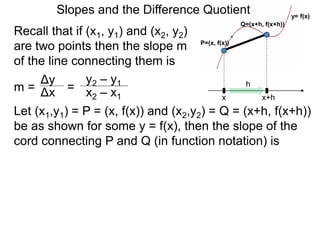
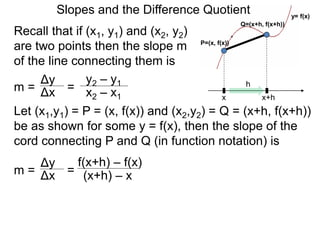
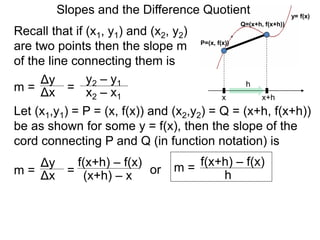
P=(x, f(x))
x+h
Q=(x+h, f(x+h))
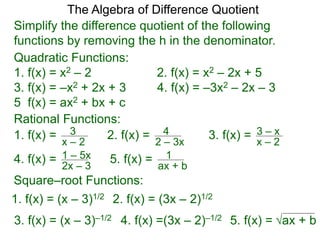
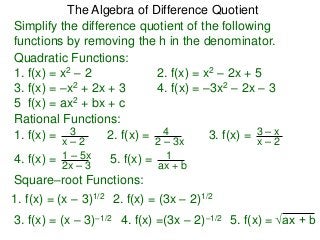
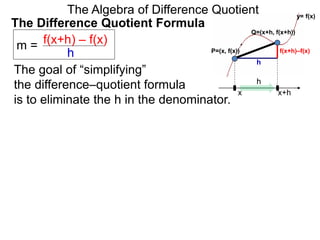
The goal of “simplifying”
the difference–quotient formula
is to eliminate the h in the denominator.
Examples of the algebra for manipulating this formula
are given below.
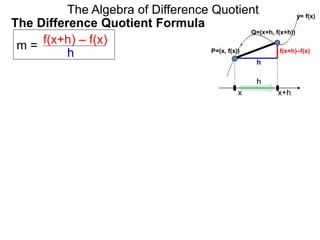
m = f(x+h) – f(x)
h
h
f(x+h)–f(x)
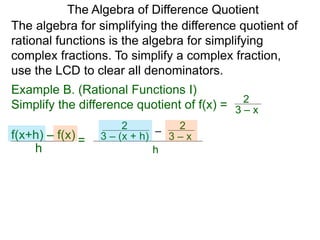
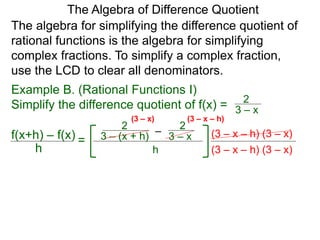
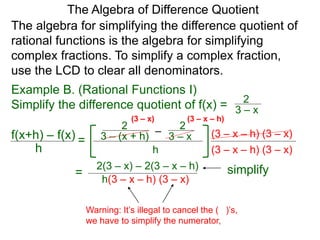
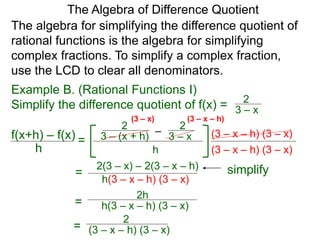
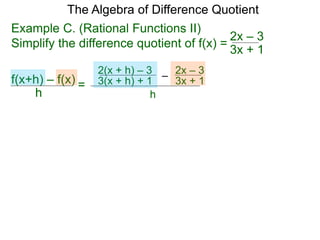
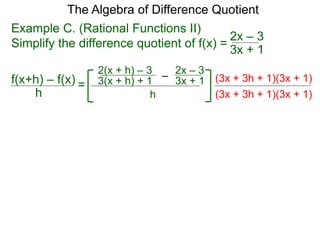
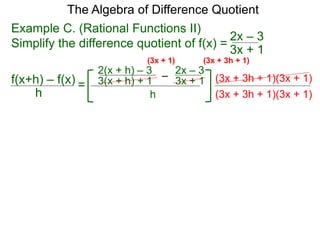
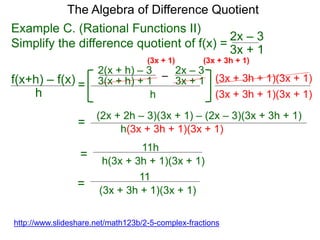
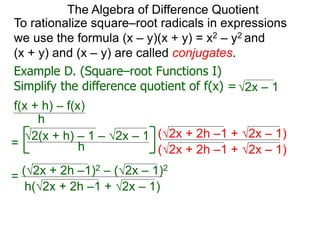
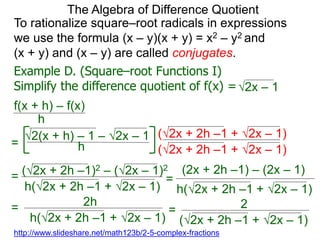
The Algebra of Difference Quotient
The Difference Quotient Formula
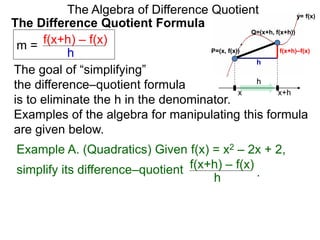
Example A. (Quadratics) Given f(x) = x2 – 2x + 2,
f(x+h) – f(x)
h =
(x+h)2 – 2(x+h) + 2 – [ x2 – 2x + 2]
h
f(x+h) – f(x)
h .simplify its difference–quotient
y= f(x)
h](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/difference-quotientalgebra-150420231148-conversion-gate01/85/Difference-quotient-algebra-19-320.jpg)
![x
P=(x, f(x))
x+h
Q=(x+h, f(x+h))
The goal of “simplifying”
the difference–quotient formula
is to eliminate the h in the denominator.
Examples of the algebra for manipulating this formula
are given below.
m = f(x+h) – f(x)
h
h
f(x+h)–f(x)
The Algebra of Difference Quotient
The Difference Quotient Formula
Example A. (Quadratics) Given f(x) = x2 – 2x + 2,
f(x+h) – f(x)
h =
(x+h)2 – 2(x+h) + 2 – [ x2 – 2x + 2]
h
2xh – 2h + h2
h
= 2x – 2 + h.=
f(x+h) – f(x)
h .simplify its difference–quotient
y= f(x)
http://www.slideshare.net/math123
a/4-7polynomial-operationsvertical
h](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/difference-quotientalgebra-150420231148-conversion-gate01/85/Difference-quotient-algebra-20-320.jpg)