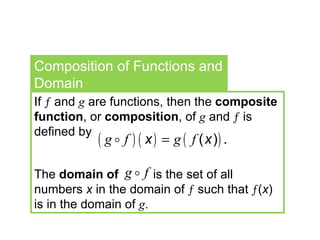
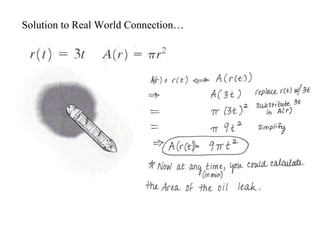
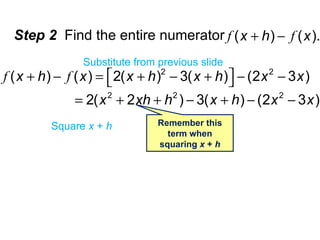
The document discusses composition of functions and the difference quotient. It provides an example of using the composition of functions to determine the area of an oil patch given the increasing radius over time. It then defines the difference quotient as a formula to compute the slope of a secant line and uses an example function to demonstrate finding the difference quotient through simplifying the expression.