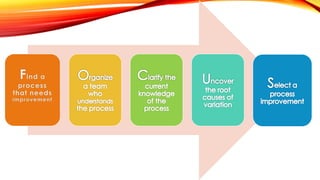
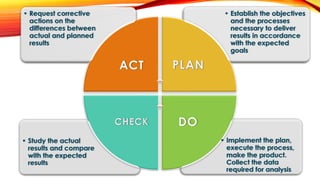
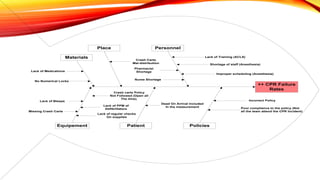
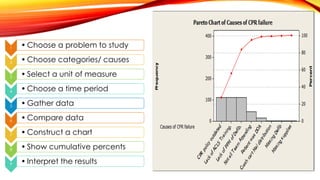
The document outlines the Focus PDCA strategy for continuous process improvement, detailing a nine-step process that involves finding improvement projects, organizing teams, clarifying current processes, and identifying root causes. It emphasizes the use of tools such as cause-and-effect diagrams and Pareto charts to focus on key issues and solutions. The process concludes with implementing solutions and monitoring outcomes to ensure the desired results are achieved and sustained.