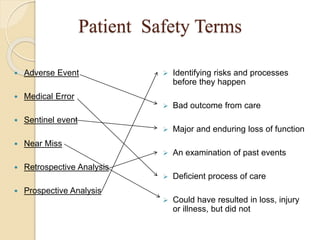
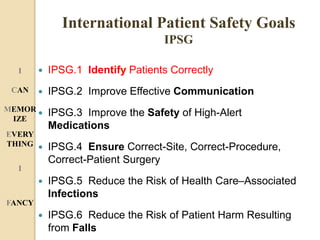
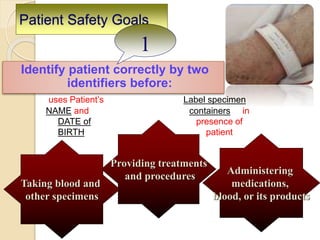
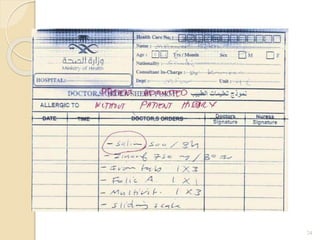
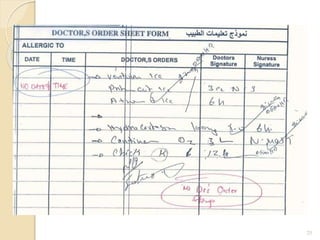
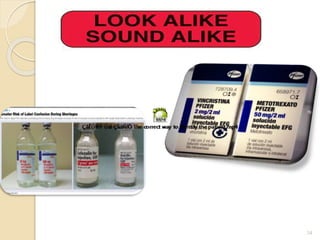
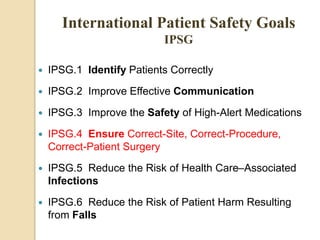
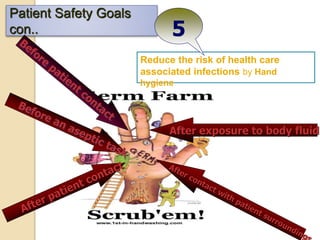
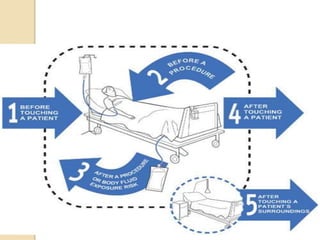
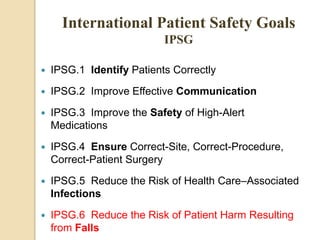
The document discusses patient safety definitions, goals, and best practices. It defines patient safety as working to avoid, manage, and treat unsafe acts in healthcare through the use of best practices leading to optimal patient outcomes. The goals are to provide a safe environment for all individuals by promoting a proactive, non-punitive culture that facilitates reporting of hazards, errors, near-misses, and other unsafe conditions. Key aspects that should be reported include unanticipated outcomes, infections, errors, near misses, and safety concerns. Effective communication, identifying patients correctly, improving medication safety, ensuring correct procedures, reducing infections, and mitigating fall risks are emphasized as important areas of focus.