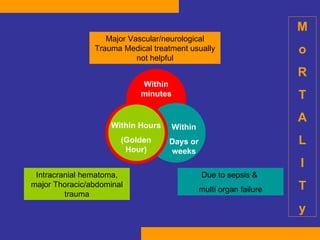
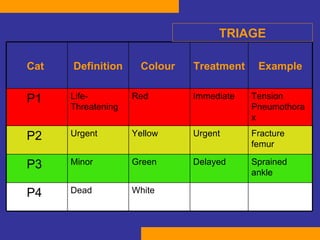
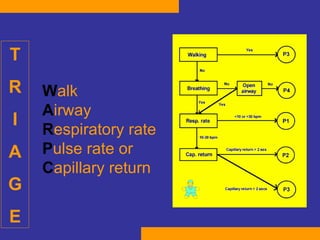
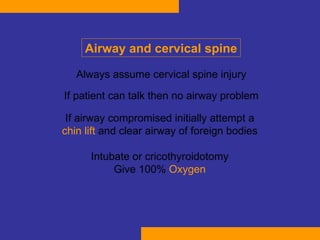
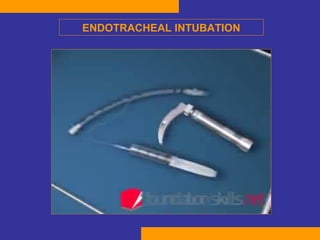
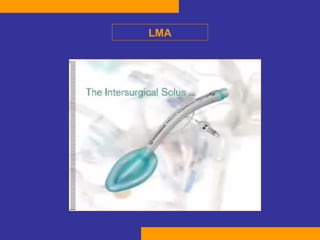
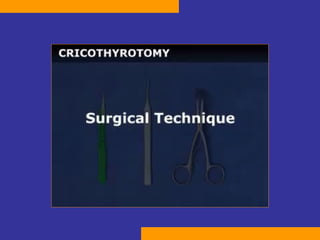
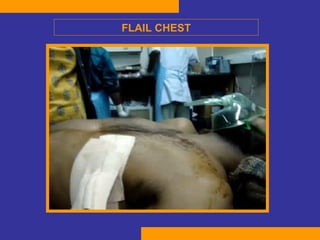
This document discusses the treatment of polytrauma patients with airway and circulatory problems. It defines polytrauma as trauma to two or more body systems. It notes that mortality from major vascular or neurological trauma can occur within minutes or hours. The document outlines the ABCDE approach to assessment and treatment - Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure. It provides examples of treatments for different injuries including tension pneumothorax, chest trauma, hemorrhage control, and neurological assessment.