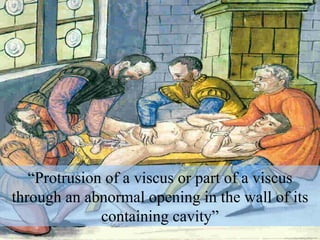
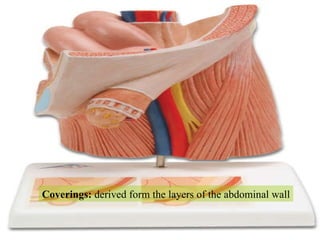
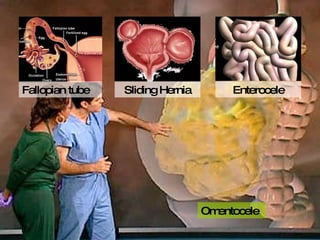
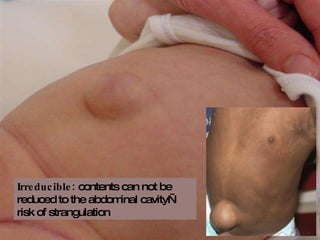
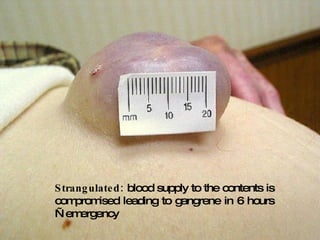
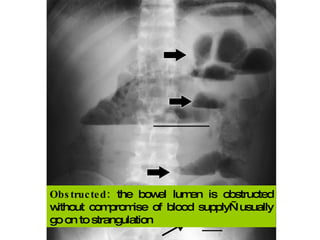
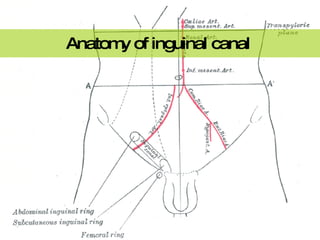
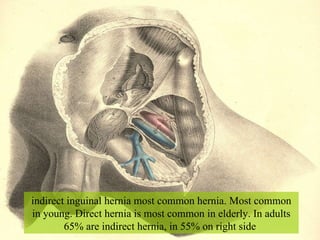
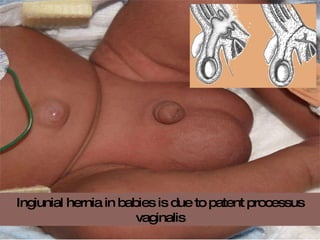
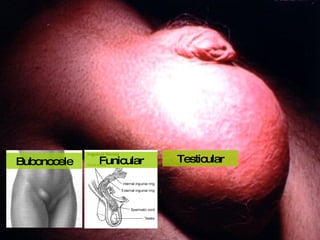
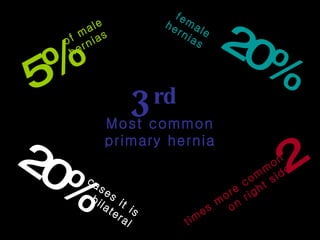
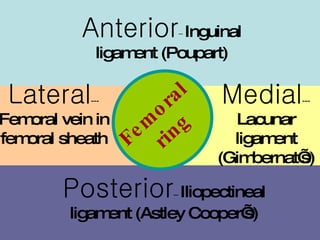
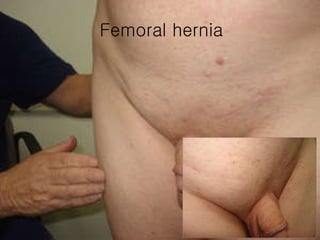
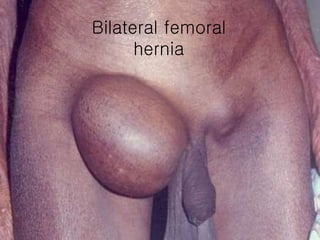
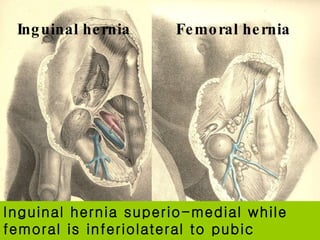
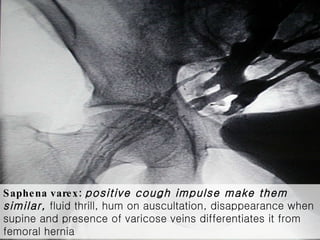
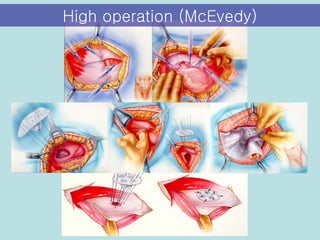
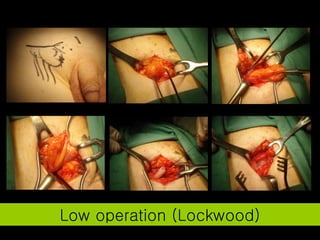
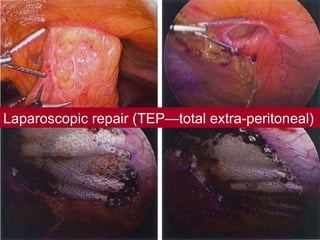
The document discusses different types of femoral hernias, including Laugier's femoral hernia, Narath's femoral hernia, and Cloquet's hernia. It provides details on the anatomy of the femoral canal and ring, noting the narrowness of the canal that results in femoral hernias presenting with strangulation in 40% of cases. When treating femoral hernia, the document advises operating as soon as diagnosed due to the risk of strangulation, and that truss is contraindicated for femoral hernia.