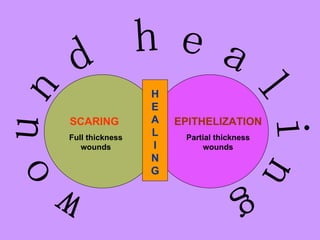
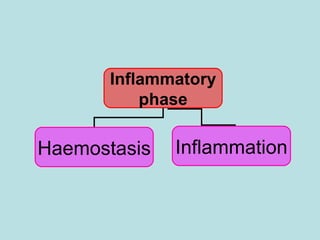
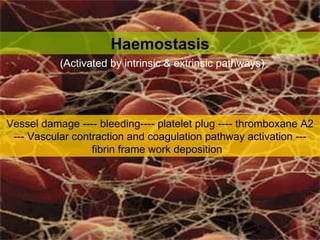
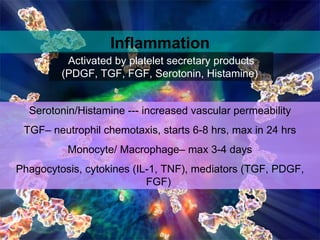
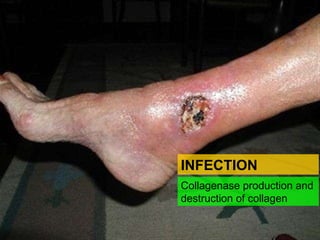
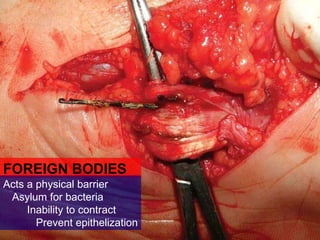
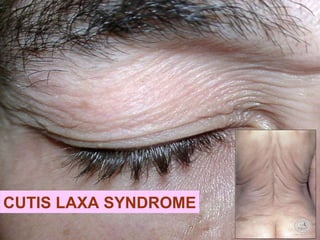
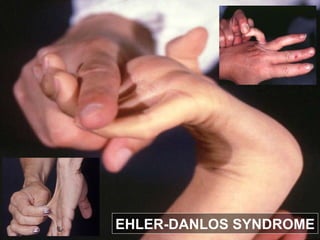
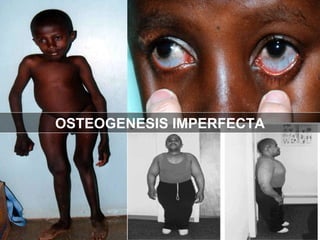
Wound healing is a complex, dynamic process involving several phases: inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling. The inflammatory phase involves hemostasis and inflammation to limit blood loss and seal the wound. The proliferative phase fills the wound gap with granulation tissue through fibroplasia, angiogenesis, and re-epithelialization. The remodeling phase involves regression of vessels and granulation tissue, wound contraction, and collagen remodeling to strengthen the scar. Successful wound healing depends on factors like adequate blood supply, infection control, and avoiding risks such as smoking, which can impair healing.