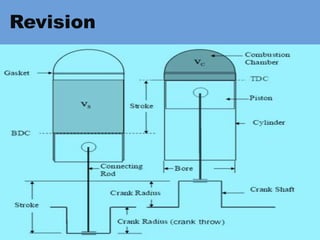
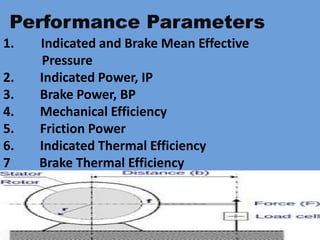
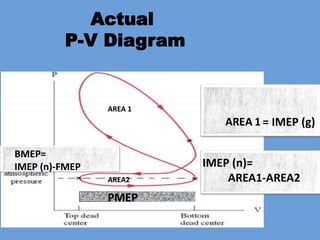
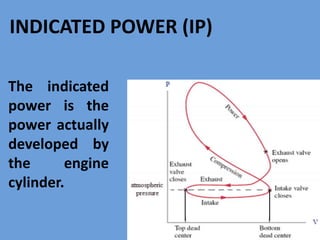
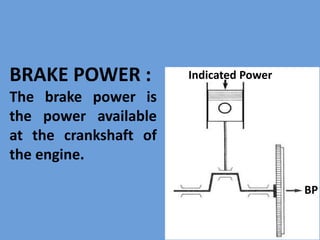
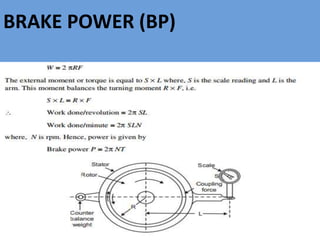
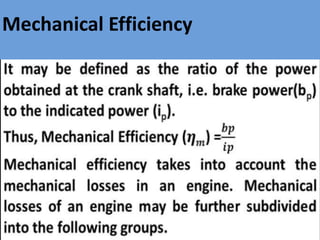
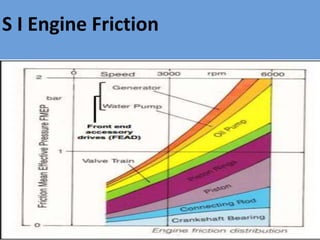
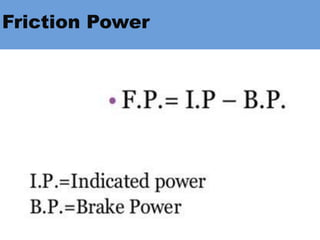
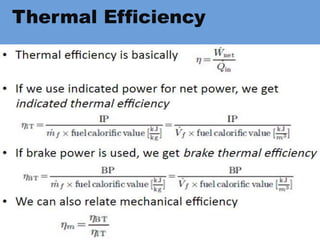
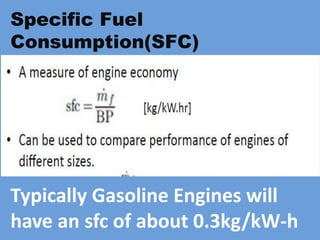
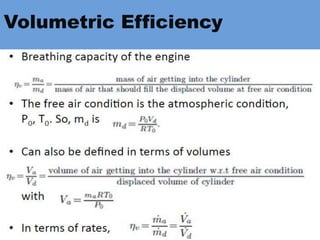
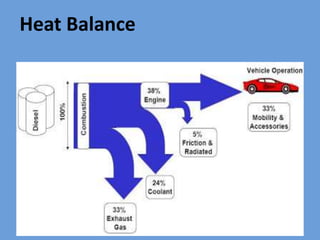
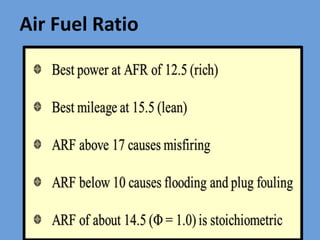
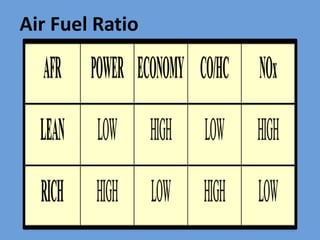
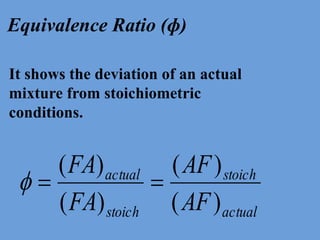
The document outlines key concepts related to engine efficiency, including indicated power, brake power, mechanical efficiency, and thermal efficiency. It discusses performance parameters such as specific fuel consumption and volumetric efficiency, as well as the importance of the air-fuel ratio and equivalence ratio in engine operation. Additionally, it addresses factors affecting volumetric efficiency and includes a quiz section to assess understanding of these concepts.