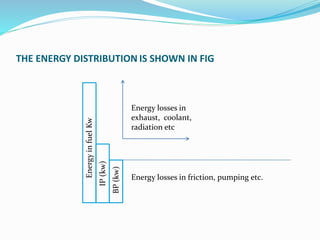
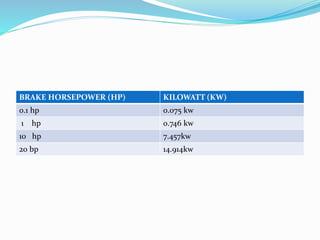
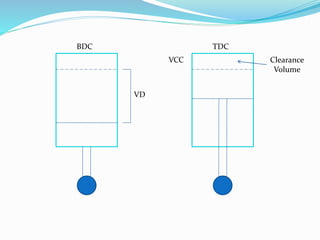
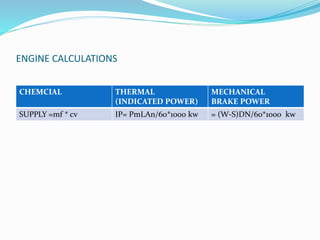
The document discusses the performance testing of internal combustion (i.c.) engines, focusing on key parameters like indicated power, brake power, and mechanical efficiency. It outlines methods to calculate these parameters and their significance in evaluating engine performance, including specific fuel consumption, thermal efficiency, and factors affecting losses. The document also includes practical examples and calculations for a four-stroke single-cylinder engine.