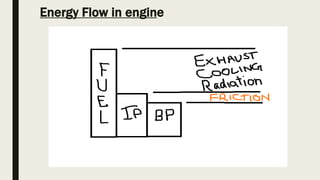
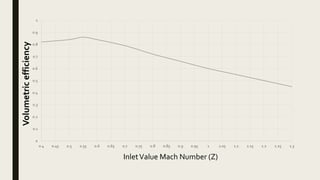
The document discusses key performance parameters of engines including thermal efficiencies, power outputs, specific fuel consumption, air-fuel ratios, and volumetric efficiency. It defines indicated thermal efficiency as the ratio of indicated power to fuel energy, and brake thermal efficiency as the ratio of brake power to fuel energy. Mechanical efficiency is the ratio of brake power to indicated power. Volumetric efficiency is the ratio of actual to theoretical air intake. Mean effective pressures and specific power input are also discussed.