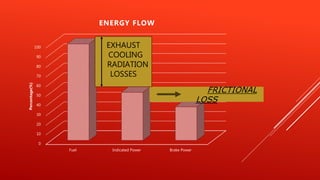
This document discusses various engine performance parameters such as indicated power, brake power, thermal efficiencies, mechanical efficiency, volumetric efficiency, mean effective pressure, mean piston speed, specific fuel consumption, air-fuel ratio, and calorific value. It provides definitions and equations for calculating these parameters including indicated thermal efficiency, brake thermal efficiency, mechanical efficiency, volumetric efficiency, indicated mean effective pressure, brake mean effective pressure, piston speed, brake specific fuel consumption, indicated specific fuel consumption, stoichiometric air-fuel ratio, equivalence ratio, and calorific value. The document was designed by Bhawesh Prajapati and references additional sources.