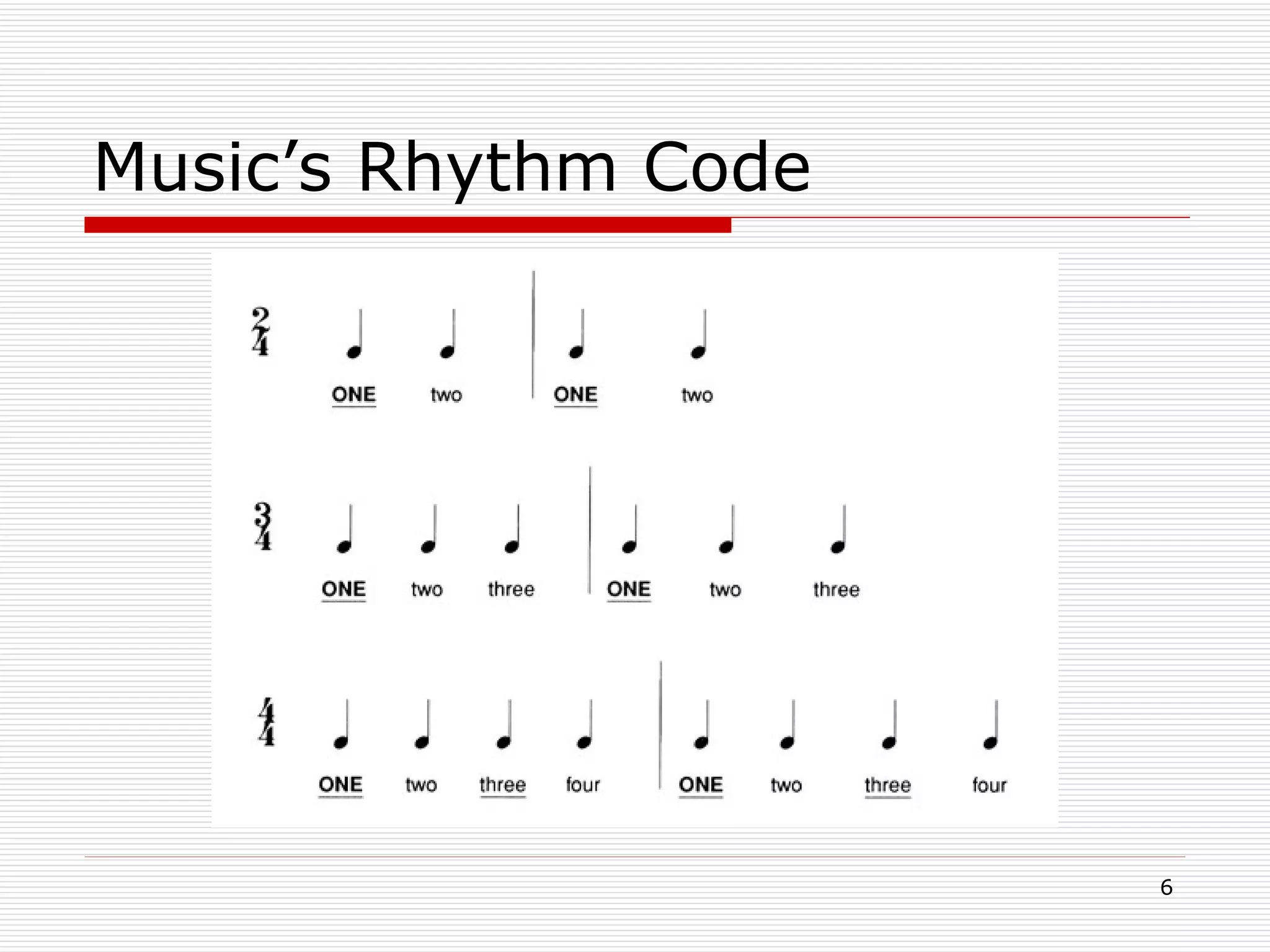
The document summarizes some of the fundamental elements of music, including rhythm, pitch, timbre, texture, and dynamics. It defines each element and provides some key details about each one. Rhythm is defined as the organization of time in music and discusses elements like tempo, meter, accent, and notation. Pitch discusses the highness or lowness of tones, notes, melody, harmony, scales, keys, and clefs. Timbre describes the characteristics of sounds. Texture refers to the consistency of musical sounds from monophonic to polyphonic. Dynamics describes the volume or loudness of music.