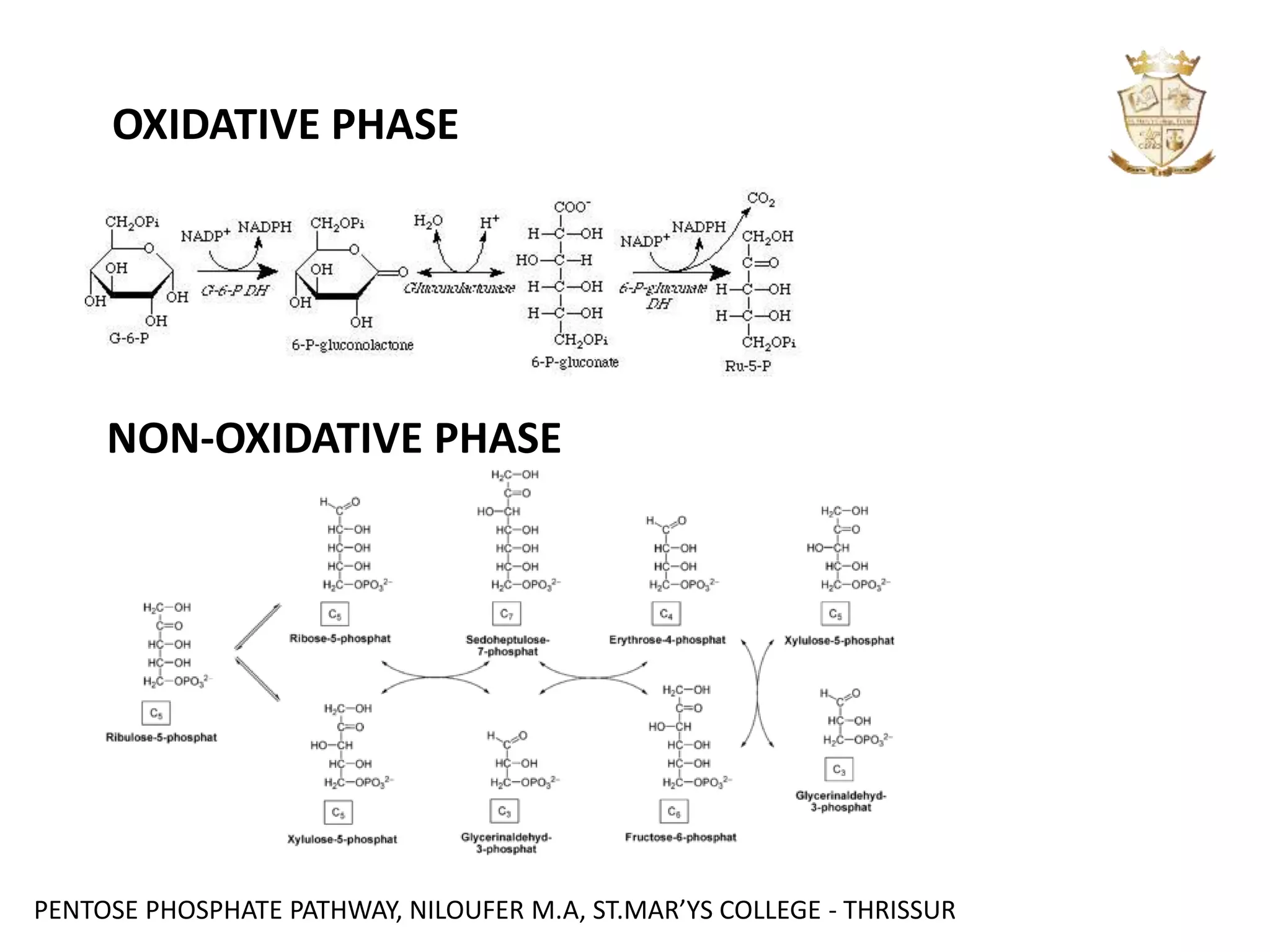
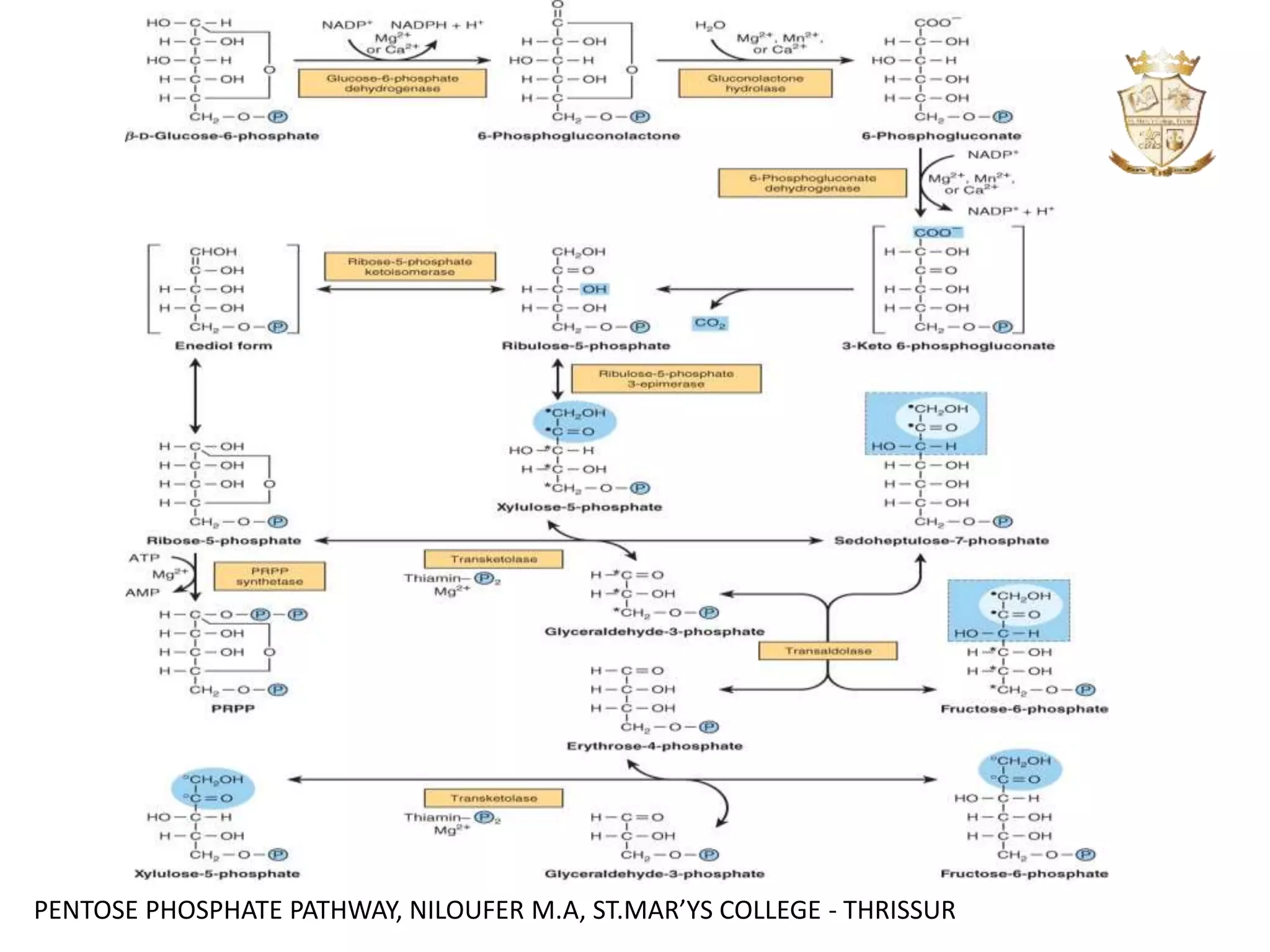
The document summarizes the pentose phosphate pathway. It consists of an oxidative phase and a non-oxidative phase. The oxidative phase generates NADPH and ribulose 5-phosphate through oxidation reactions. The non-oxidative phase converts ribulose 5-phosphate into other 5-carbon sugars, regenerating glucose 6-phosphate while producing ribose 5-phosphate. The pathway provides reducing power in the form of NADPH for biosynthesis and maintains levels of the antioxidant glutathione.