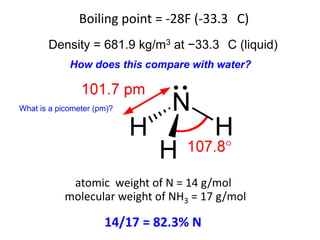
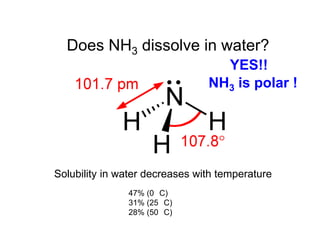
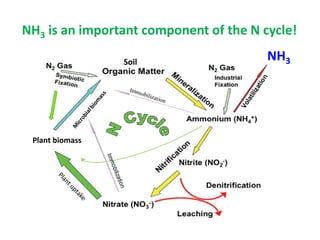
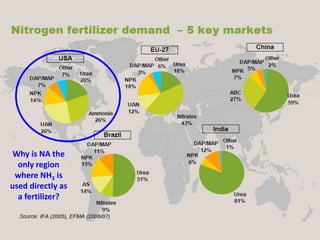
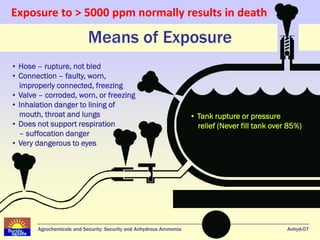
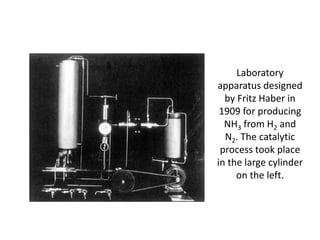
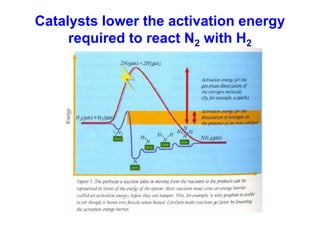
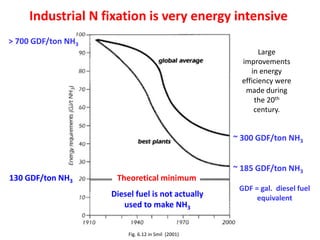
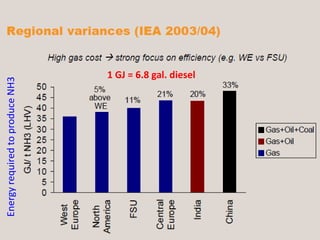
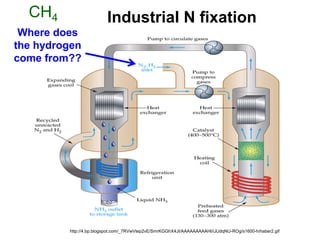
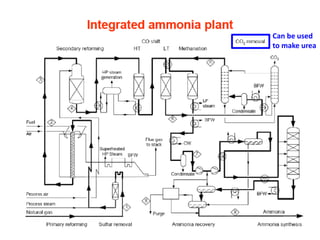
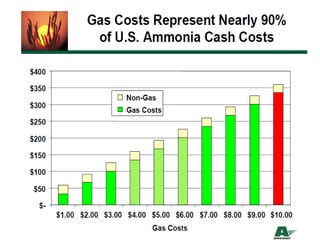
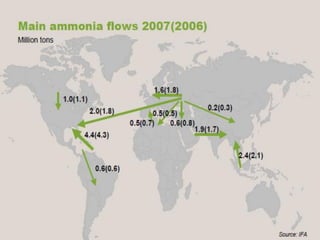
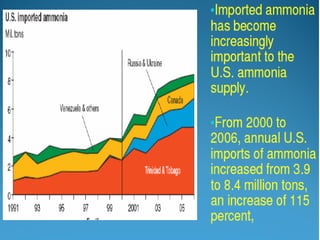
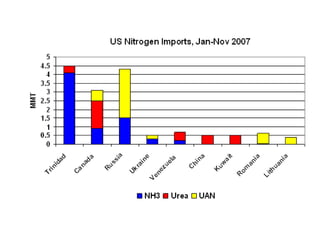
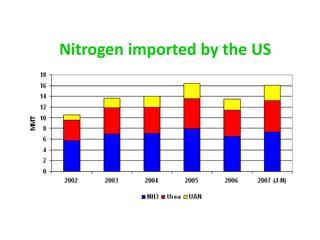
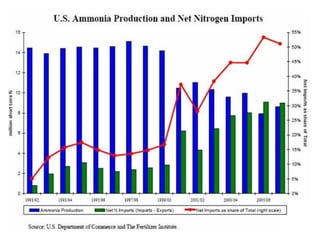
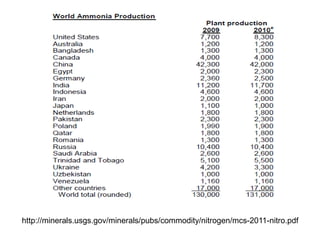
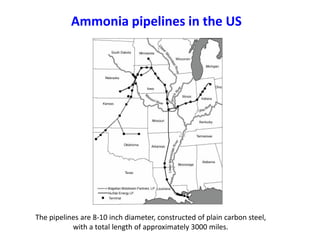
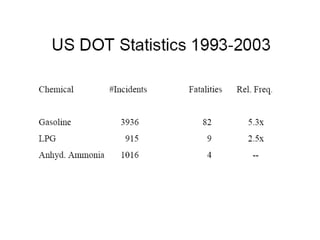
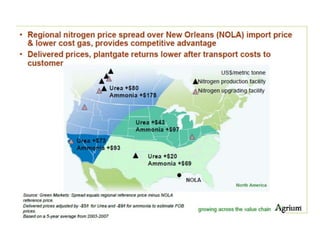
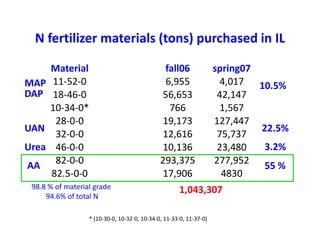
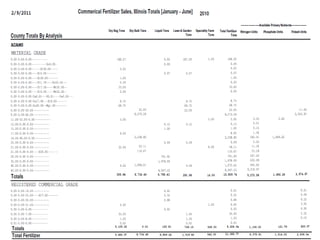
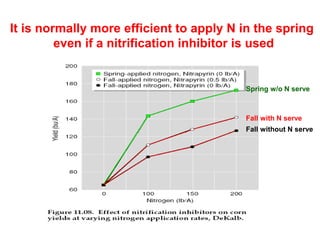
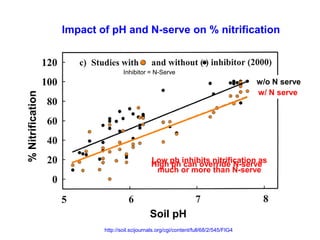
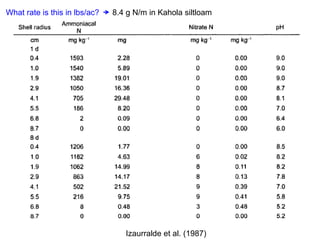
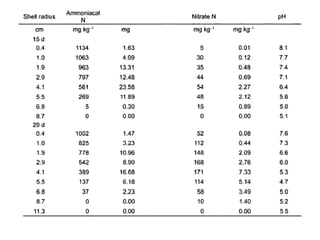
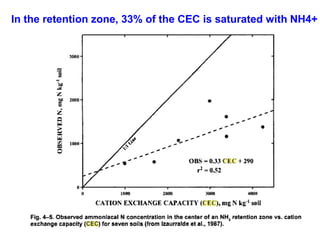
Anhydrous ammonia is a colorless gas that is stored as a liquid under pressure. It is commonly used as an agricultural fertilizer. When the pressure is released, the liquid vaporizes into a pungent smelling gas. Exposure to ammonia can cause injuries to the eyes, throat, and lungs. It is a polar molecule that readily dissolves in water. The Haber-Bosch process allows industrial fixation of nitrogen from air into ammonia through use of high pressures and temperatures with an iron catalyst. This process is very energy intensive. Fritz Haber's development of this process was important for increasing food production but also enabled Germany to produce explosives and chemical weapons during WWI.