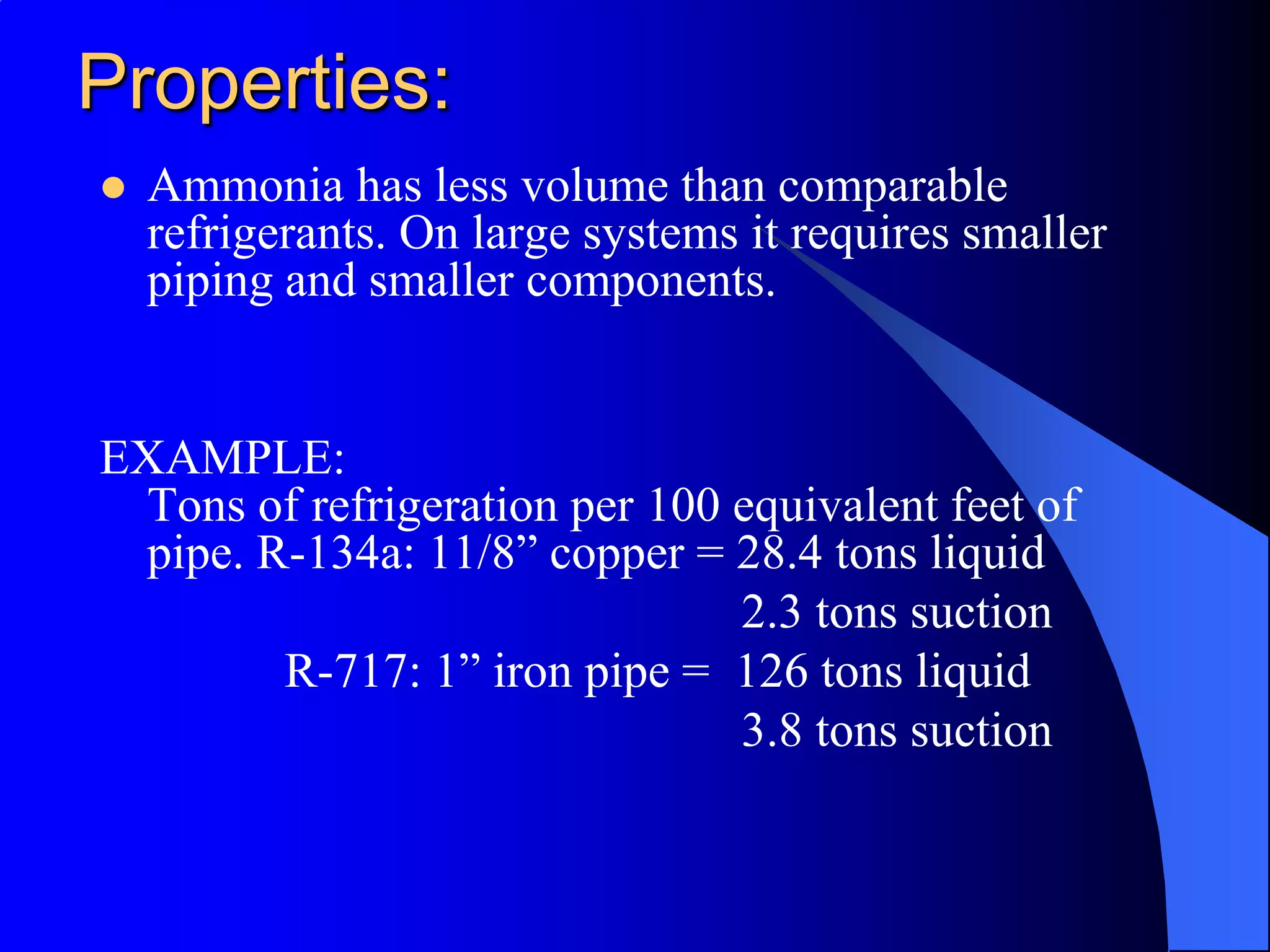
Anhydrous ammonia (NH3), or R-717, is an efficient refrigerant that has environmental advantages, including non-ozone depleting properties and low climate impact. While ammonia is effective and requires smaller components than other refrigerants, it is also toxic and corrosive, necessitating safety precautions during use. Systems containing ammonia must adhere to strict regulations based on their size, and personal protective equipment is essential for those working in environments with ammonia.