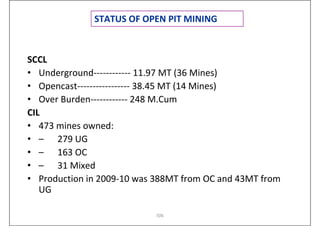
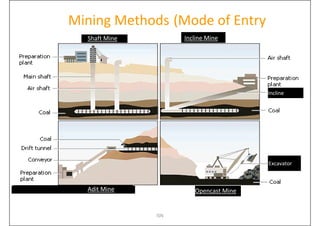
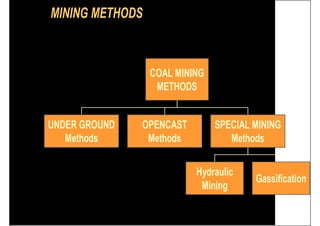
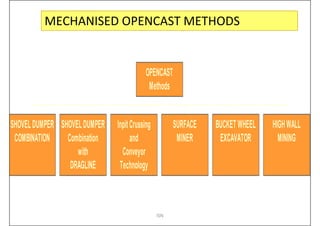
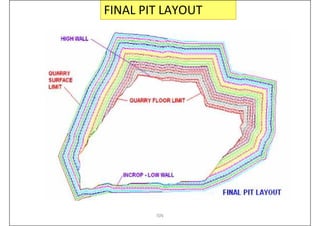
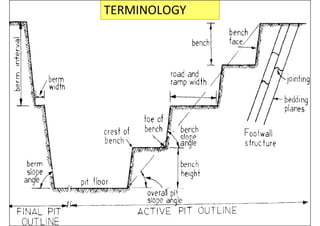
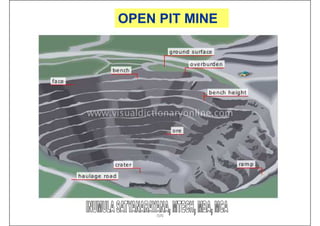
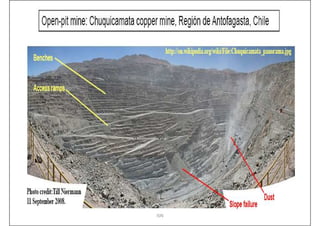
This document provides an overview of open-pit mining basics. It discusses that open-pit mining, also called surface mining, extracts ore or minerals from the ground without tunneling underground. The document outlines the two main types of mining as surface mining and subsurface mining. It also provides details on open-pit mining methods, factors for selecting mining methods, advantages and disadvantages of open-pit mining, and the key operations involved in open-pit mining.