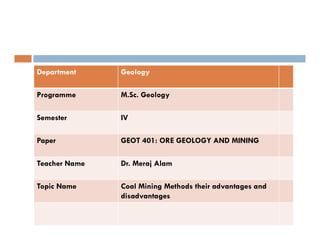
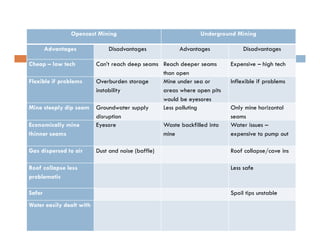
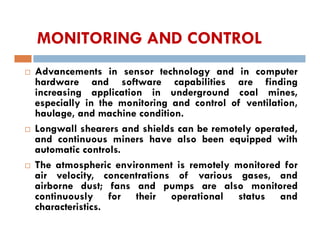
This document discusses coal mining methods, including their advantages and disadvantages. It describes surface mining methods like opencast mining and underground mining techniques. Surface mining is cheaper but has disadvantages like disturbing overburden and creating unstable spoil tips. Underground mining can access deeper seams but is more expensive, inflexible, and dangerous due to risks of gas, dust, fires and roof collapses. The document also outlines the history of coal mining and various techniques used over time.