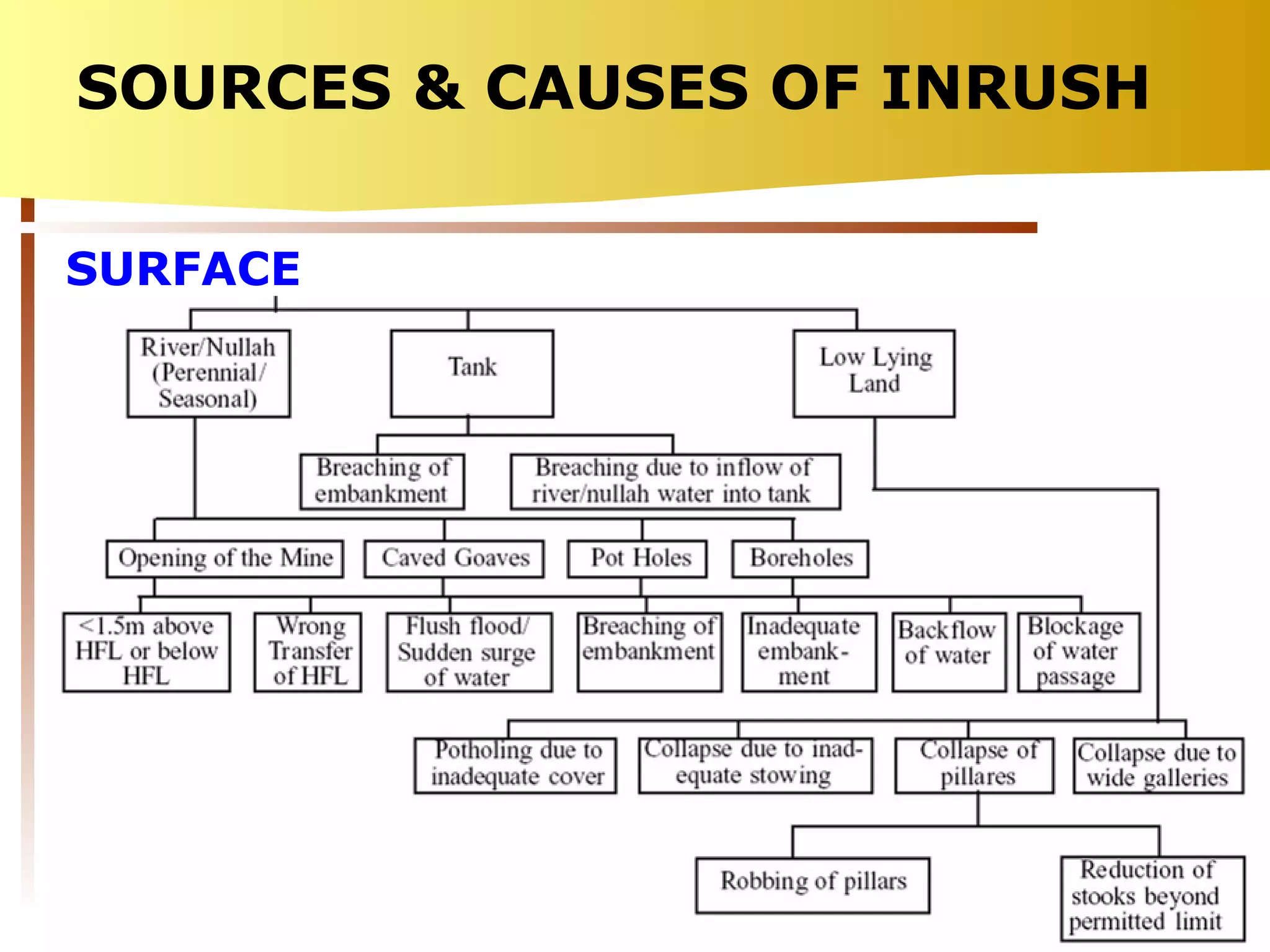
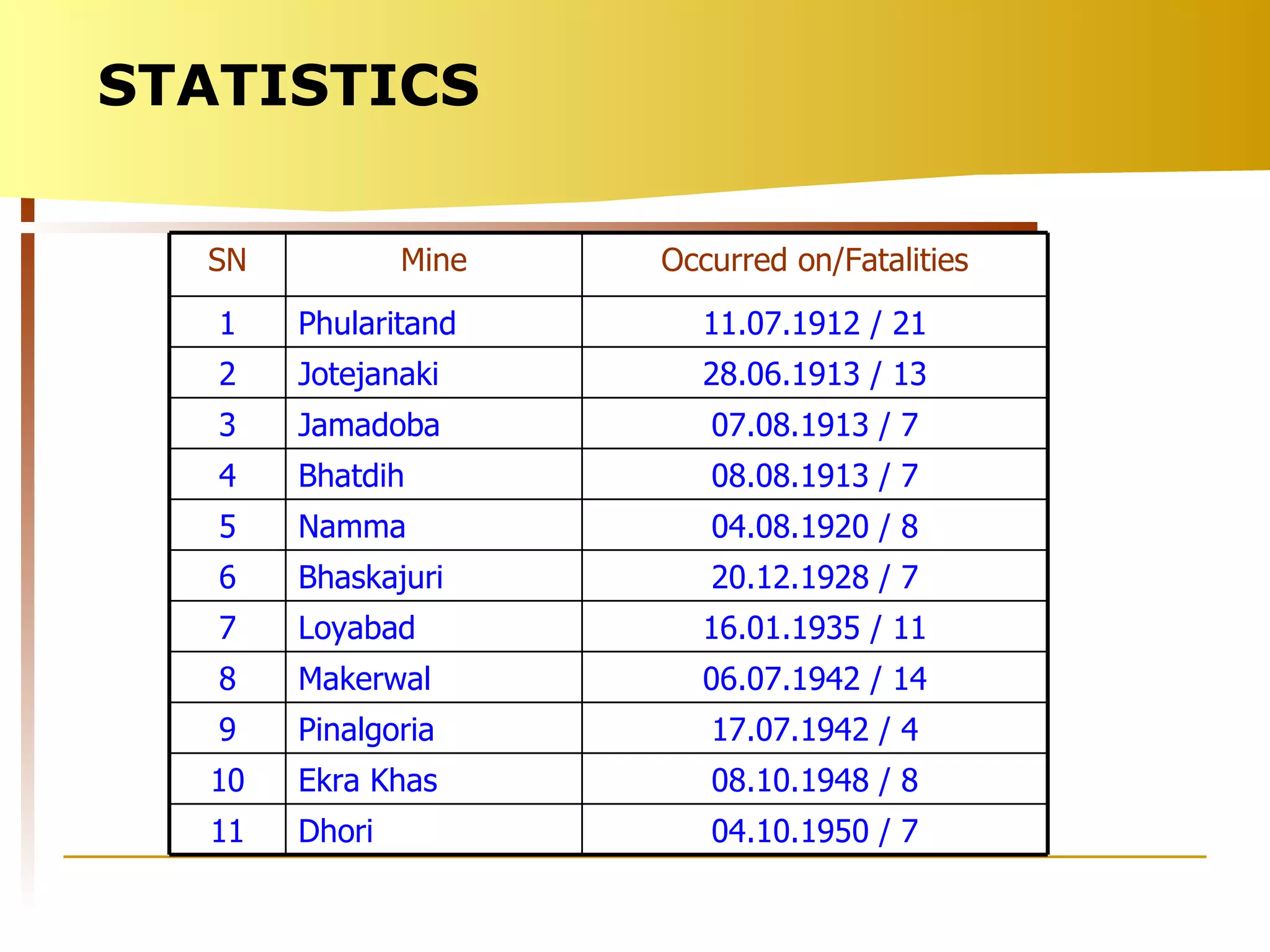
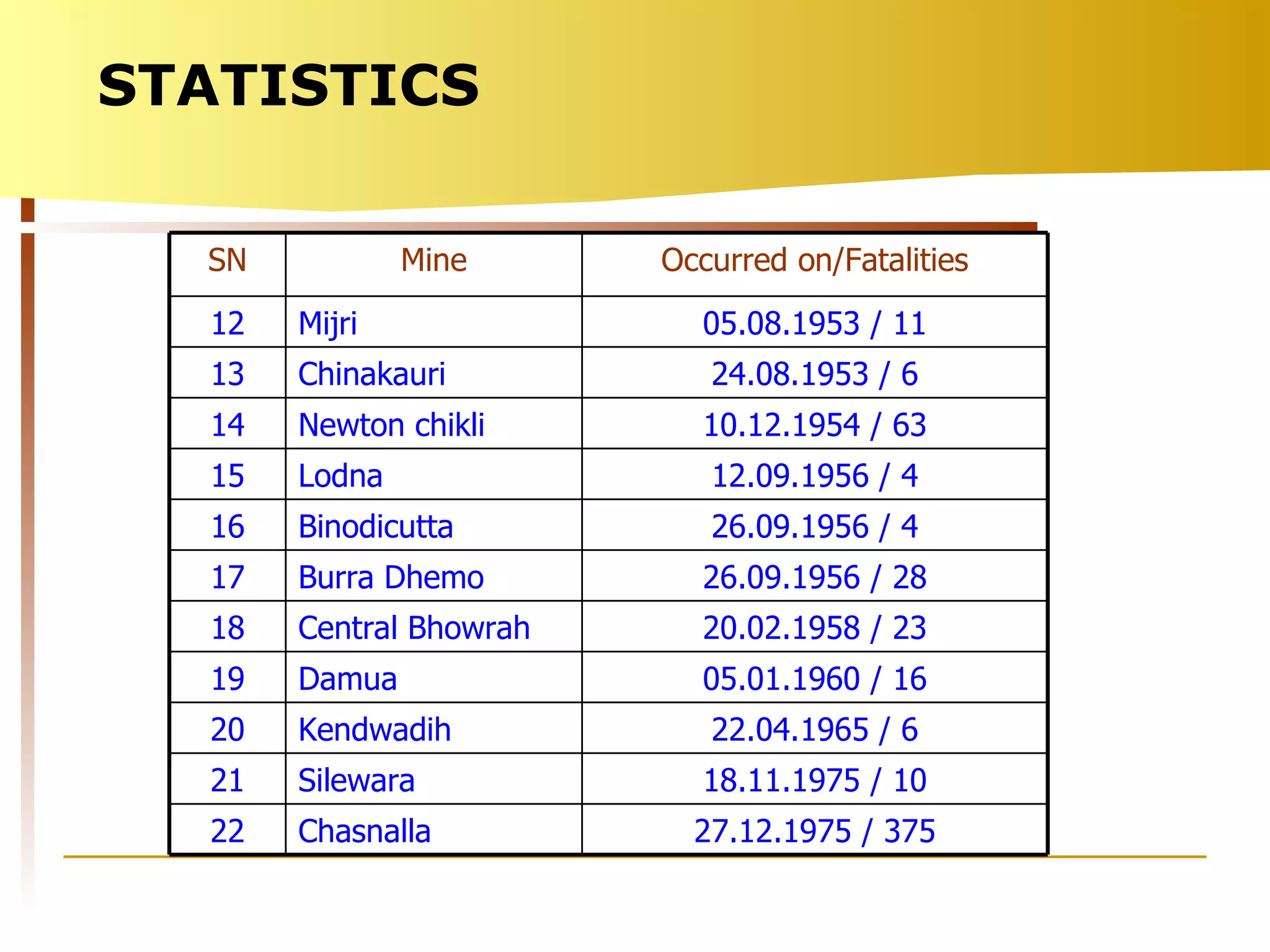
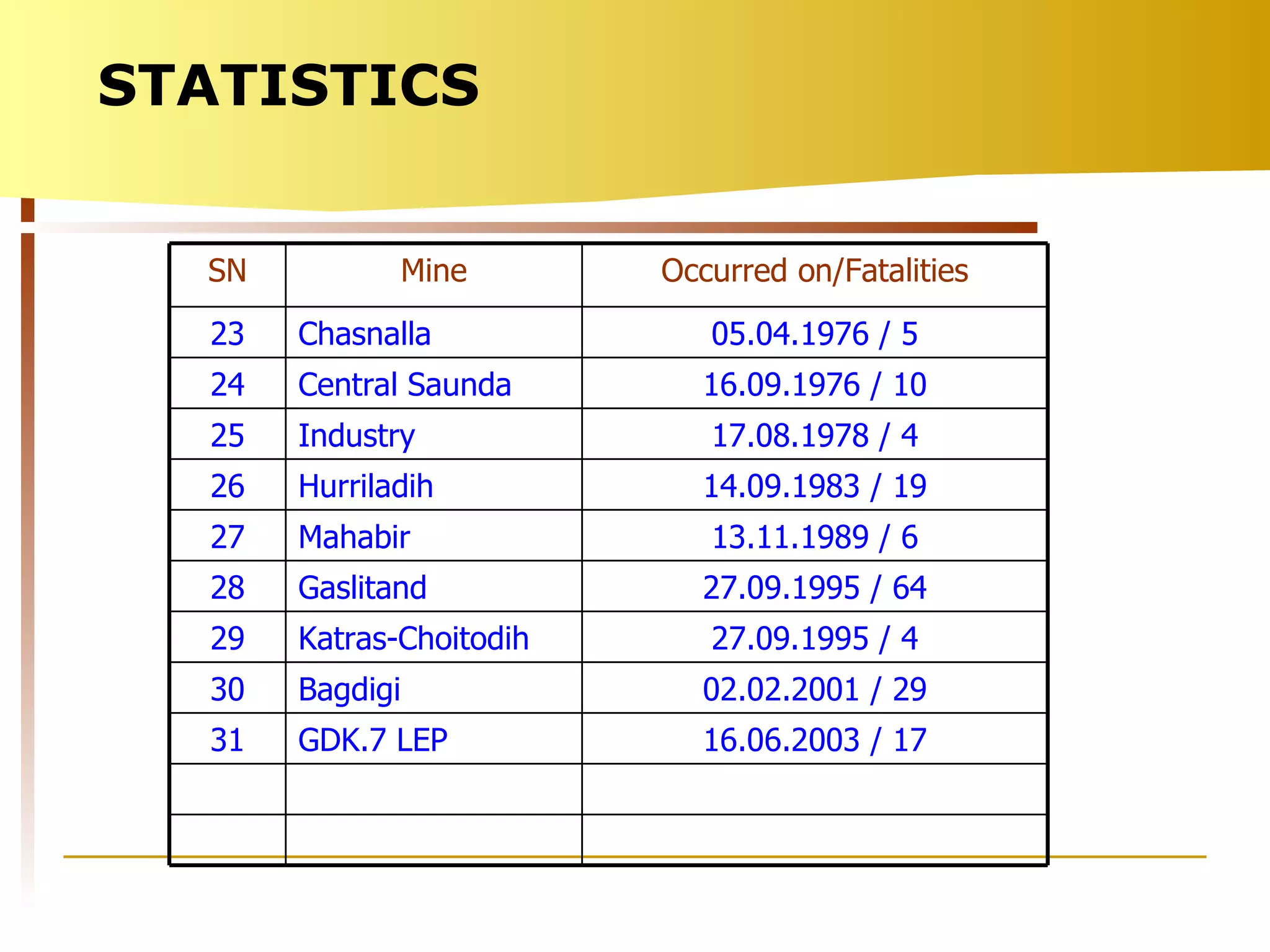
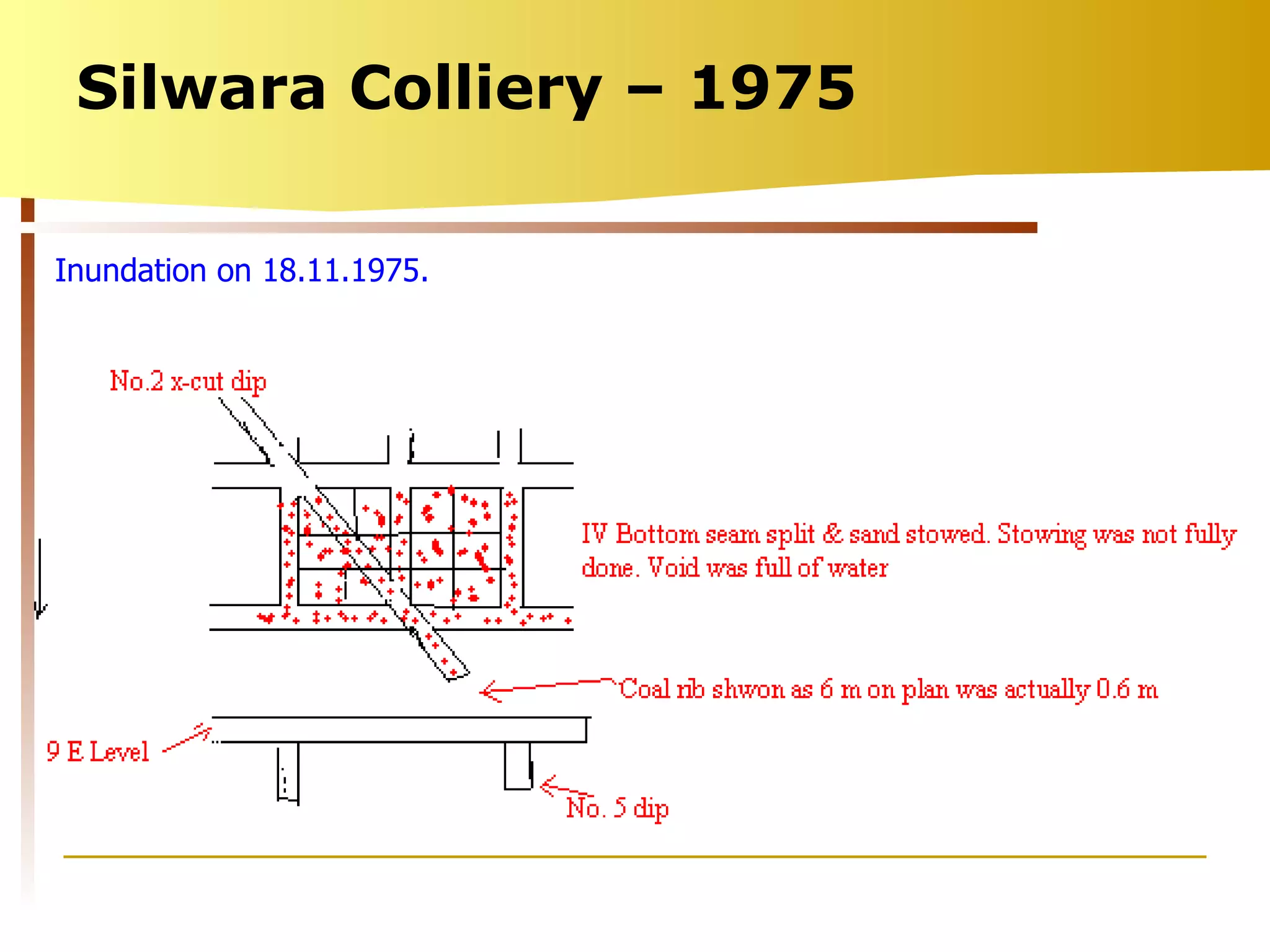
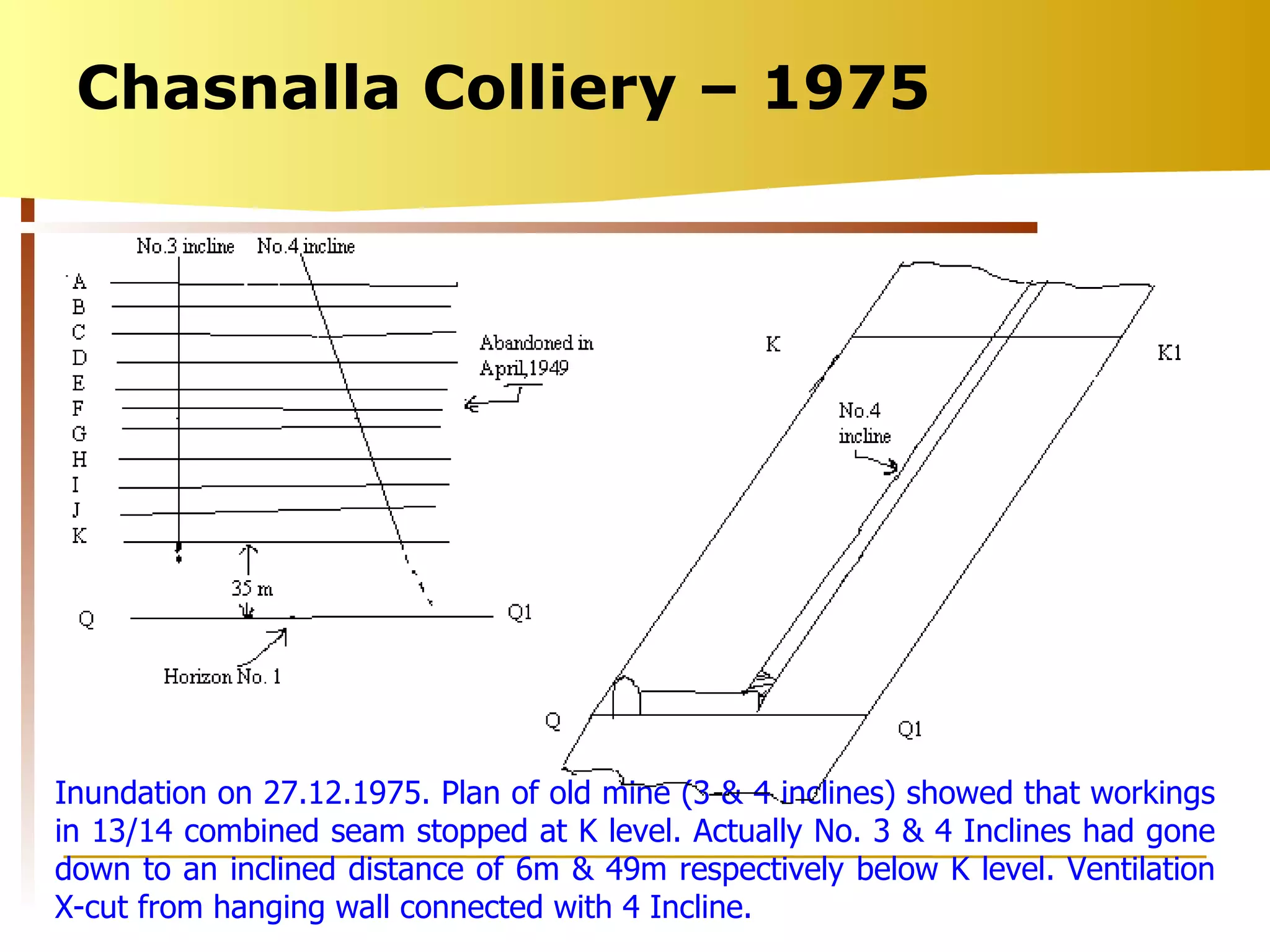
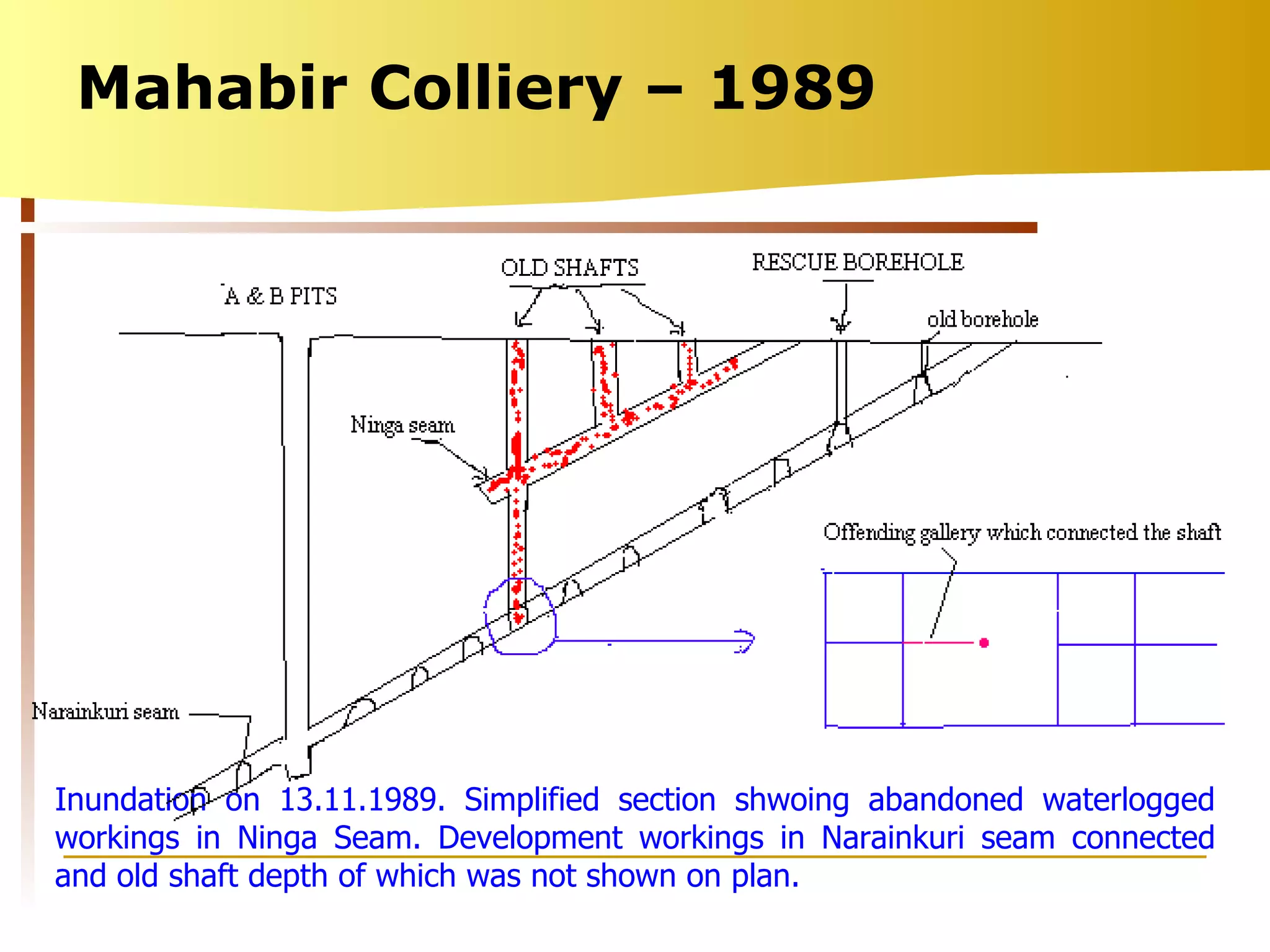
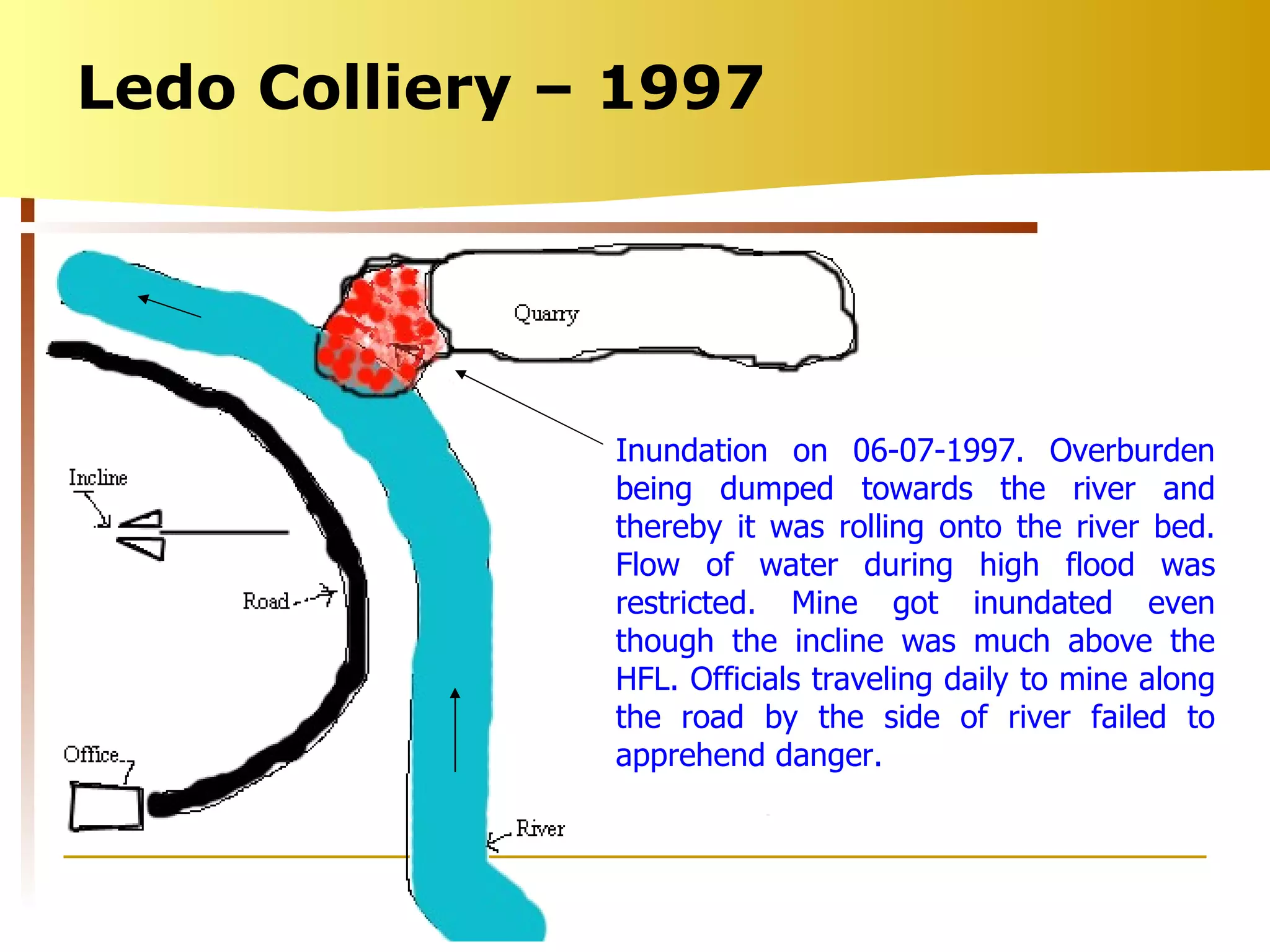
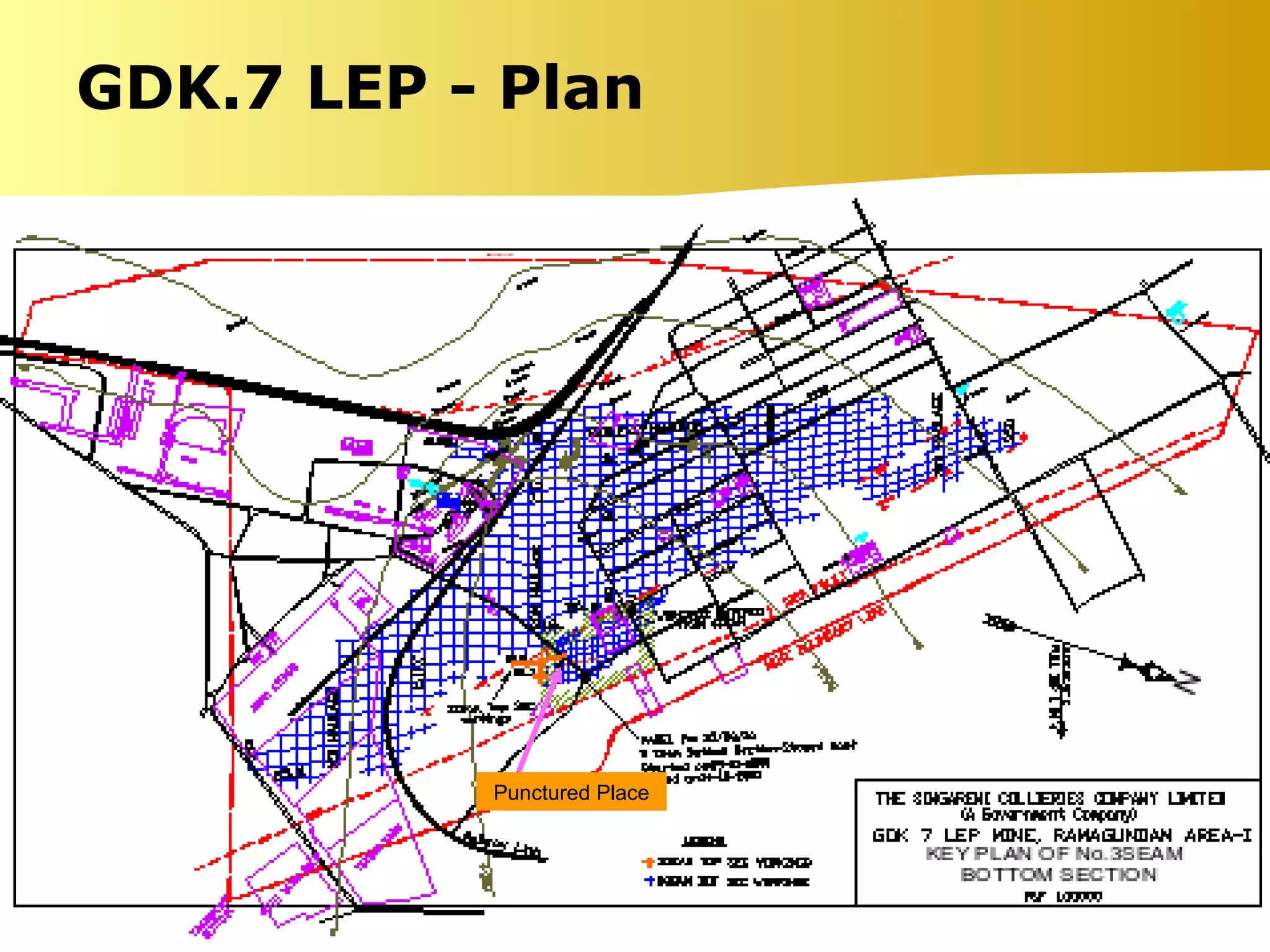
The document summarizes causes and statistics of mine inundation incidents in India. It discusses dangers from surface water sources like rivers and from underground water sources like abandoned mine workings. Case studies of past incidents at various mines are provided, highlighting factors like not dewatering old workings before extending new drifts. Statistics from 1913 to 2003 of over 30 mine inundation incidents in India are listed, with location and fatality details. Measures taken by DGMS like guidelines, inspections and monitoring are outlined to prevent future inundation accidents.