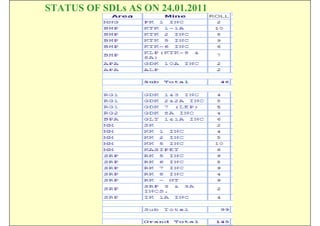
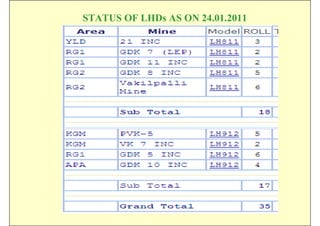
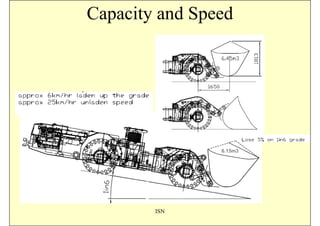
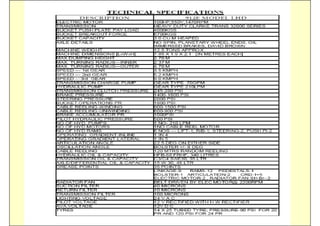
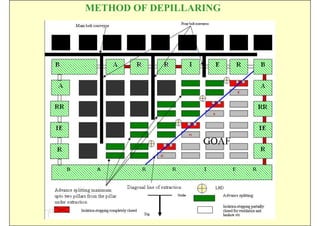
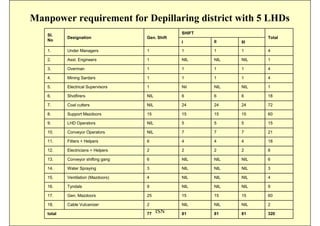
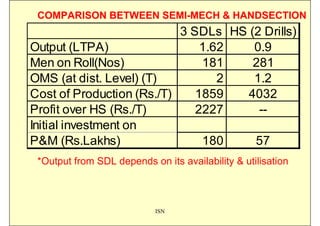
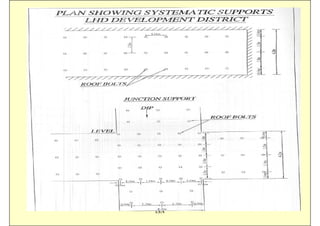
This document discusses the semi-mechanization of coal mining in India using Side Discharge Loaders (SDLs) and Load Haul Dumpers (LHDs). It provides background on the introduction of mechanization in coal mining in India. SDLs and LHDs have become important tools for intermediate technology in coal mining. The document describes the operations, capacities, advantages and safety features of SDLs and LHDs. It also discusses best practices, operating problems and the code of practice for operators.