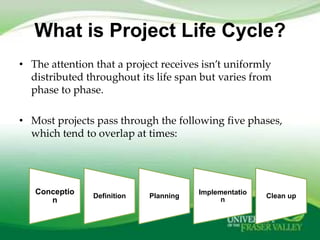
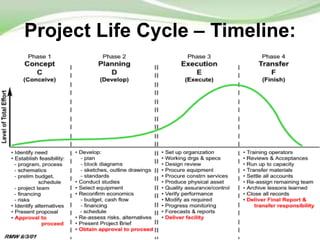
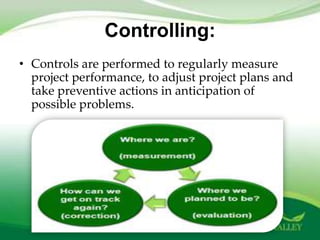
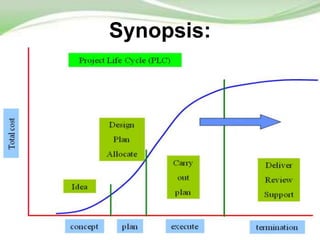
The document outlines project management as a systematic approach to planning, executing, and controlling projects to achieve specific goals within constraints such as scope, time, and budget. It describes the project life cycle, which includes phases of conception, definition, planning, implementation, and clean-up, detailing key activities and functions required in each phase. Additionally, it highlights the roles of a project manager and measures of project success and failure.