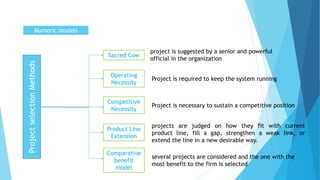
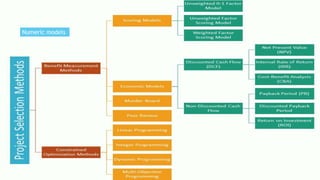
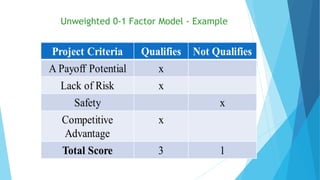
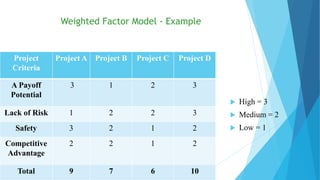
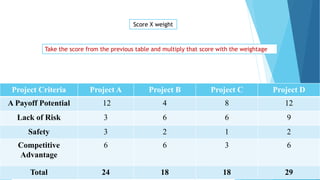
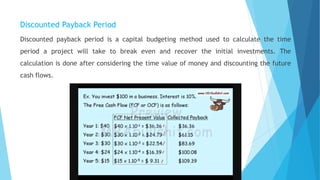
The document discusses the critical process of project selection, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right projects for an organization's long-term survival. It outlines various project selection models and methods, including multi-criteria analysis, unweighted and weighted factor scoring models, and financial metrics like net present value and return on investment. Additionally, it describes review processes like murder boards and peer reviews to ensure thorough evaluation and validation of potential projects.