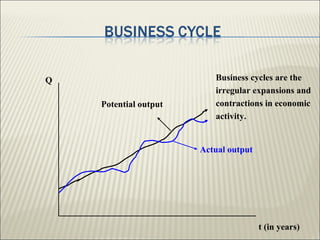
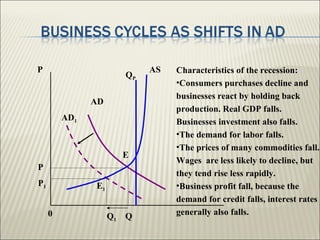
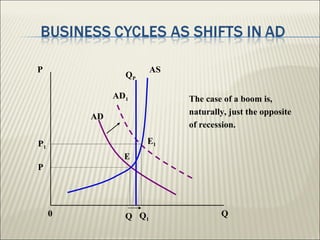
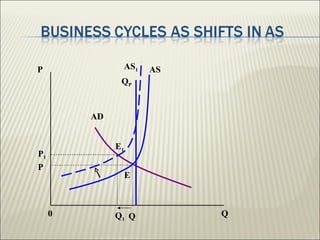
The document discusses the business cycle, which encompasses the fluctuations in national output, income, and employment that typically last between 2 to 10 years. It defines three types of business cycles: short-term, medium-term, and long-term, and outlines the four major phases of the business cycle: recession, trough, expansion, and peak. Additionally, it touches on government roles in the economy through public distribution systems, taxation, and expenditure.