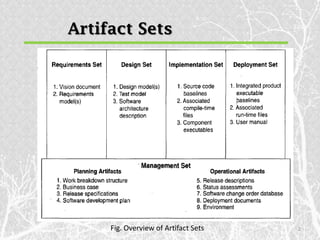
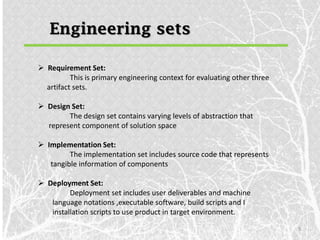
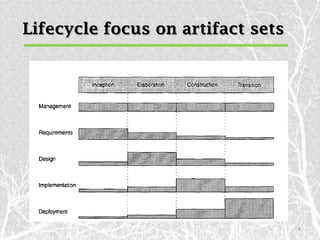
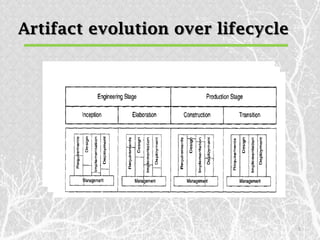
This document outlines various artifact sets produced during the software engineering process, including requirement, design, implementation, deployment, test, and management artifacts. It discusses the artifacts in each set and how they evolve over the software lifecycle. The key artifact sets are the requirement set containing the engineering context, the design set representing different abstraction levels, the implementation set with source code, and the deployment set for delivering the software to users. Test artifacts must also be developed concurrently and documented similarly. Management artifacts include documents for planning, tracking status and releases, and defining the development environment.