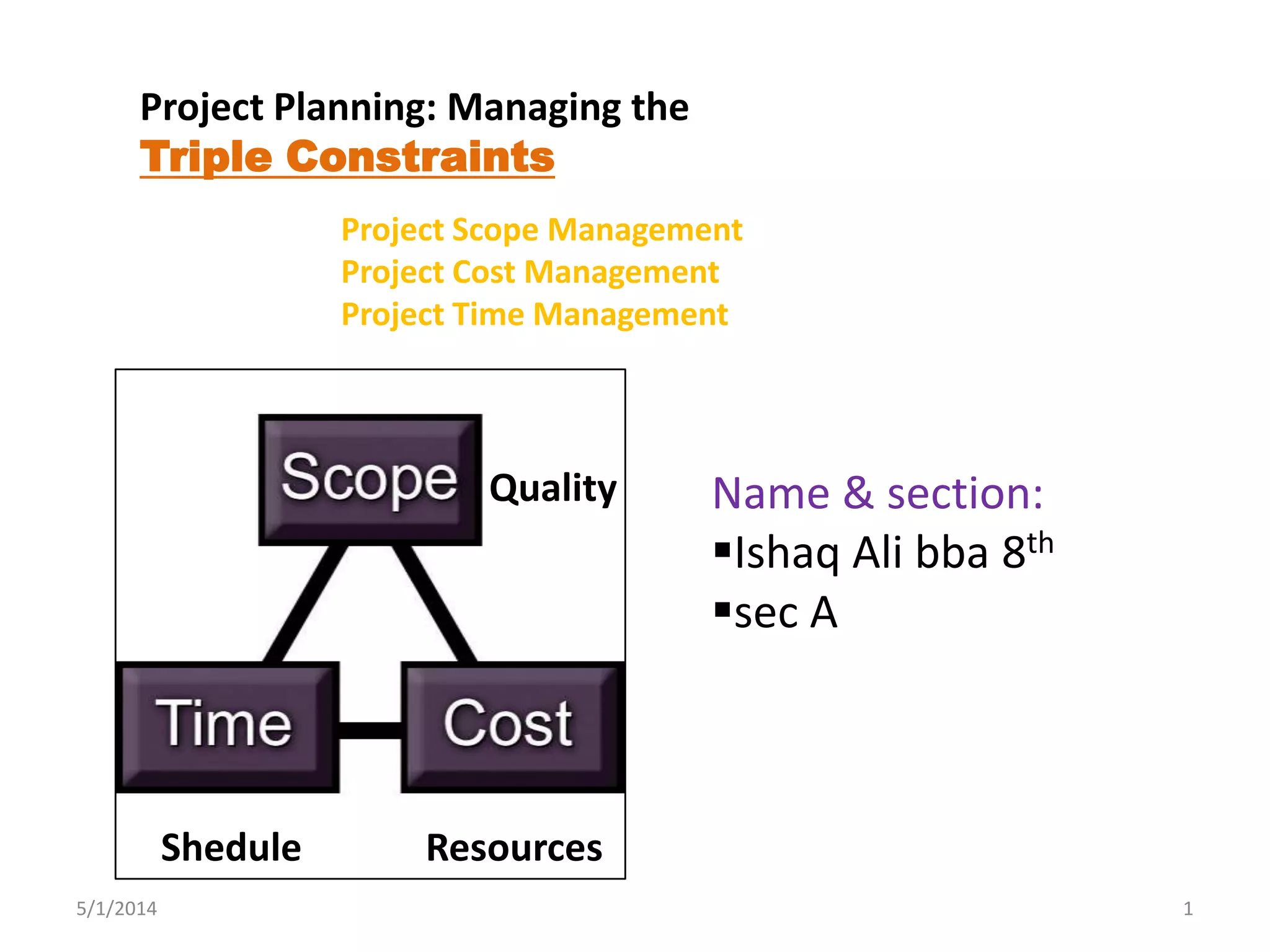
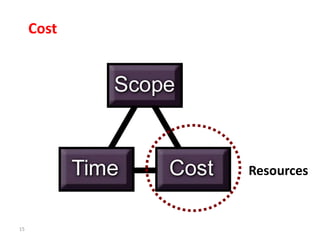
This document discusses project management techniques for managing the triple constraints of scope, time, and cost on projects. It defines key terms for scope, time, and cost management and describes tools and techniques for planning, controlling, and completing each area successfully. These include work breakdown structures, Gantt charts, estimating techniques like analogous and parametric estimating, variance analysis, and change control systems. The goal is to incorporate these techniques to deliver projects on budget, on schedule, and according to defined objectives and requirements.