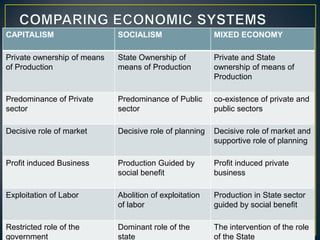
The document discusses three main economic systems - capitalism, socialism, and mixed economies. Capitalism relies on private ownership and market forces, while socialism involves state ownership and central planning. Most countries have mixed economies that incorporate aspects of both systems, with private and public sectors operating side by side. The US and Canada are provided as examples of capitalist economies, while India has established a mixed economy with strategic industries controlled by the government and others left to private enterprise.