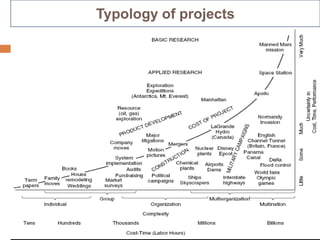
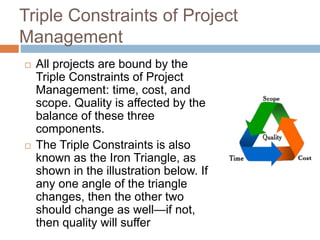
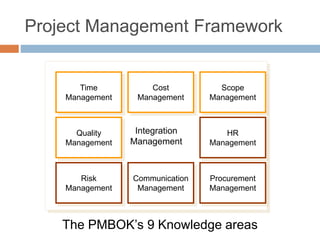
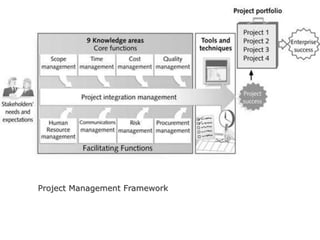
The document defines key project management concepts including what constitutes a project, project characteristics, the differences between project and program management, the six basic project functions, common pitfalls, and the triple constraints of time, cost and scope. It also outlines the nine knowledge areas that comprise the project management framework: integration management, scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, human resource management, communications management, risk management, and procurement management.