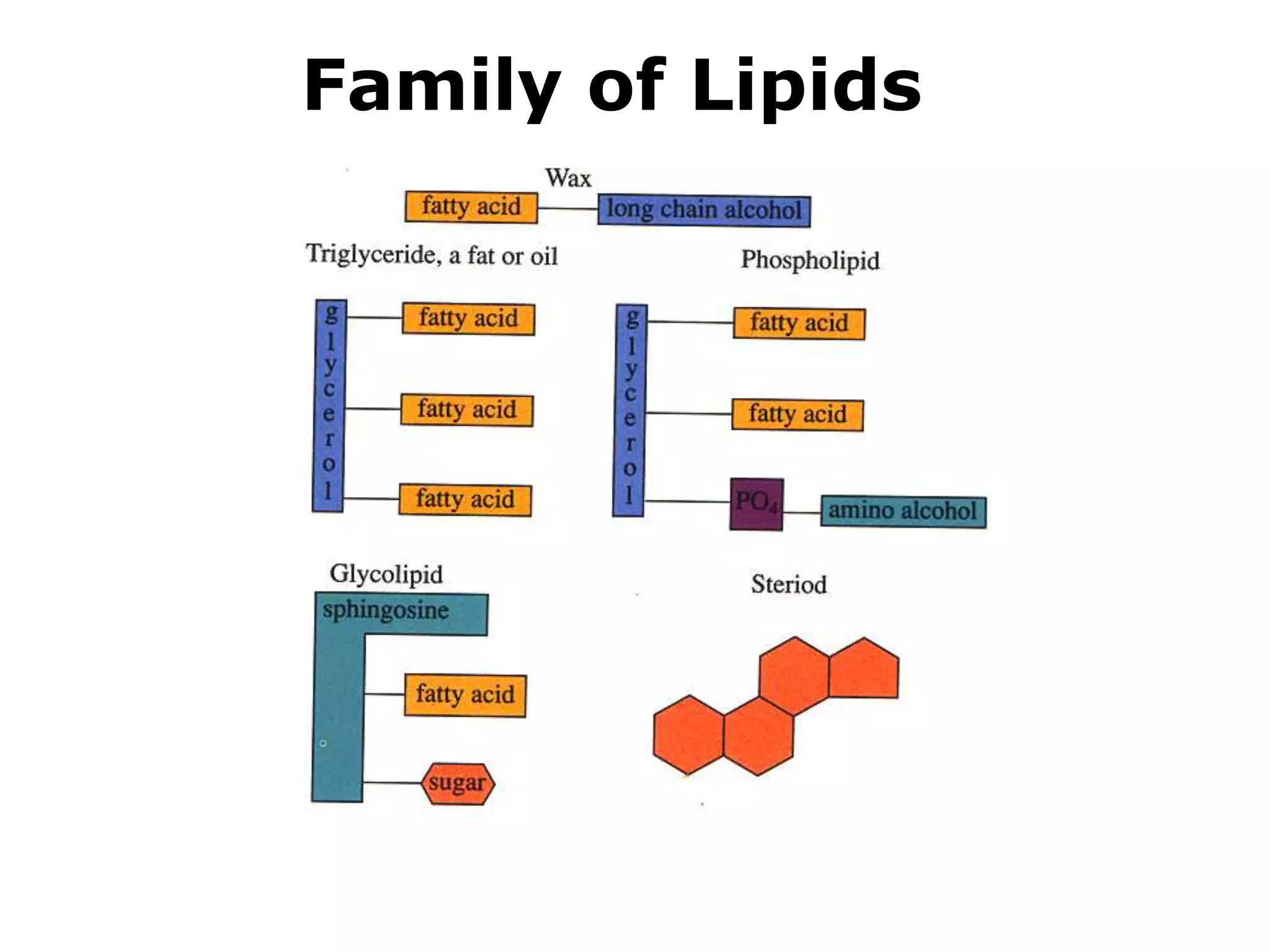
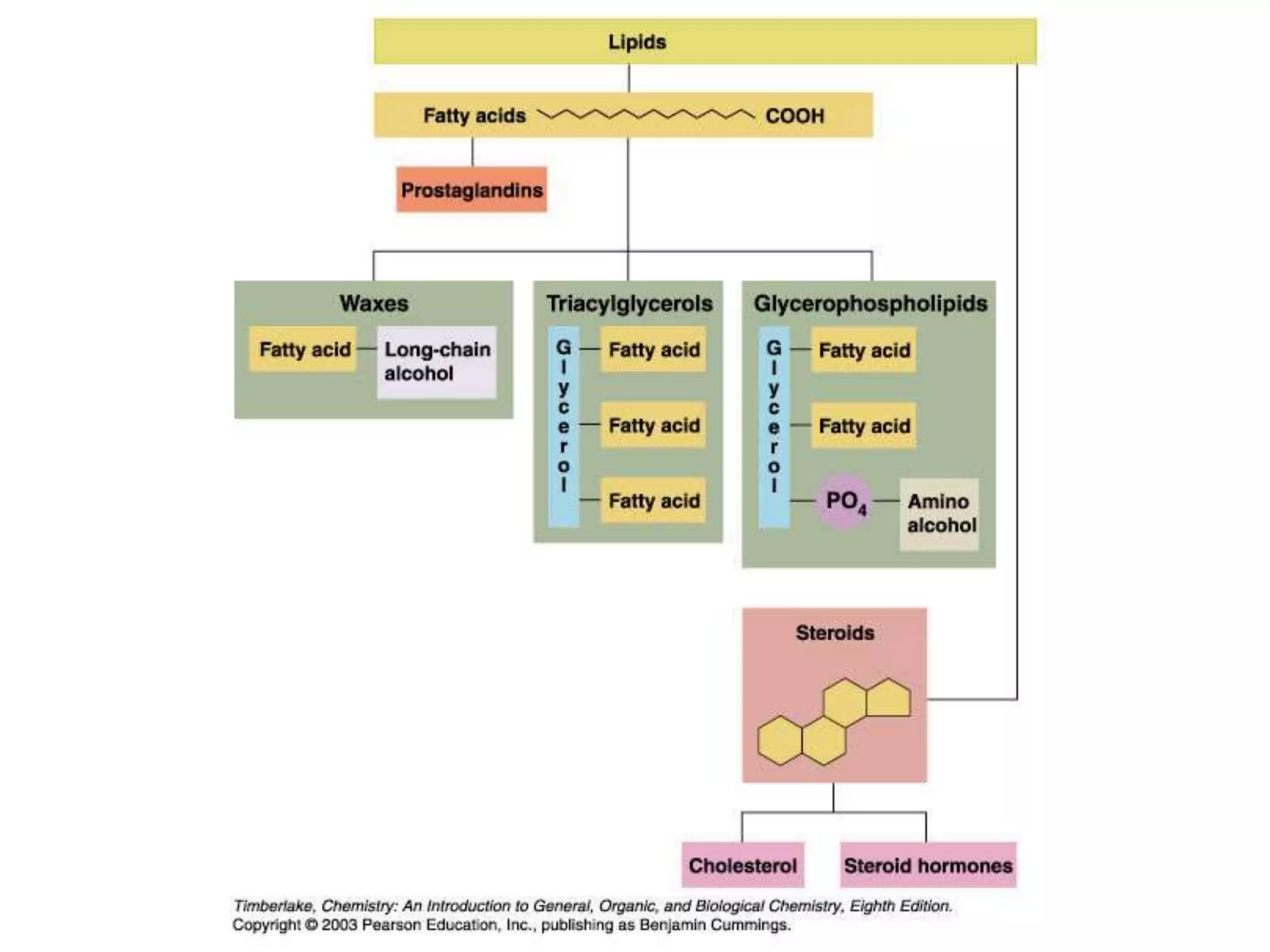
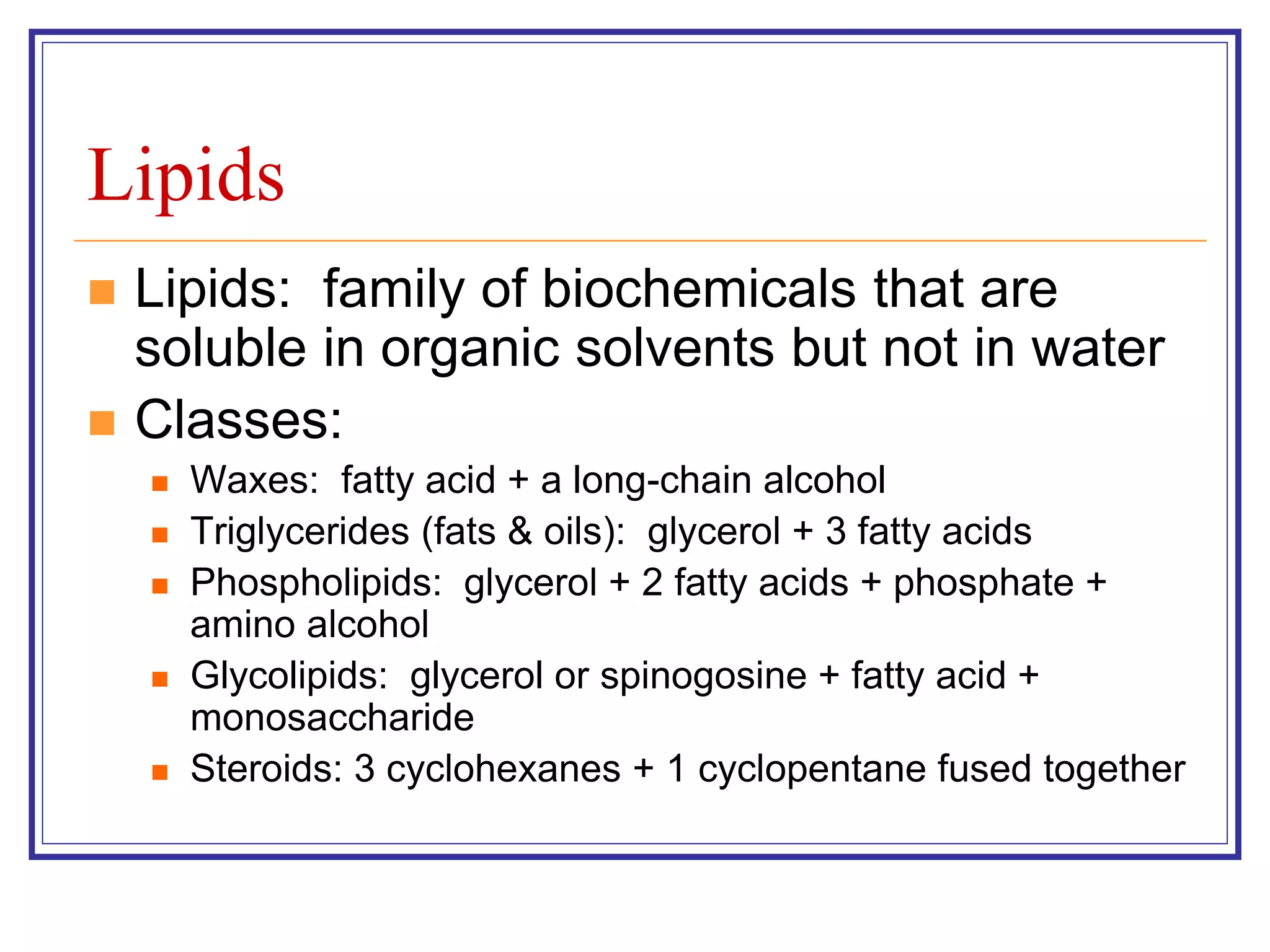
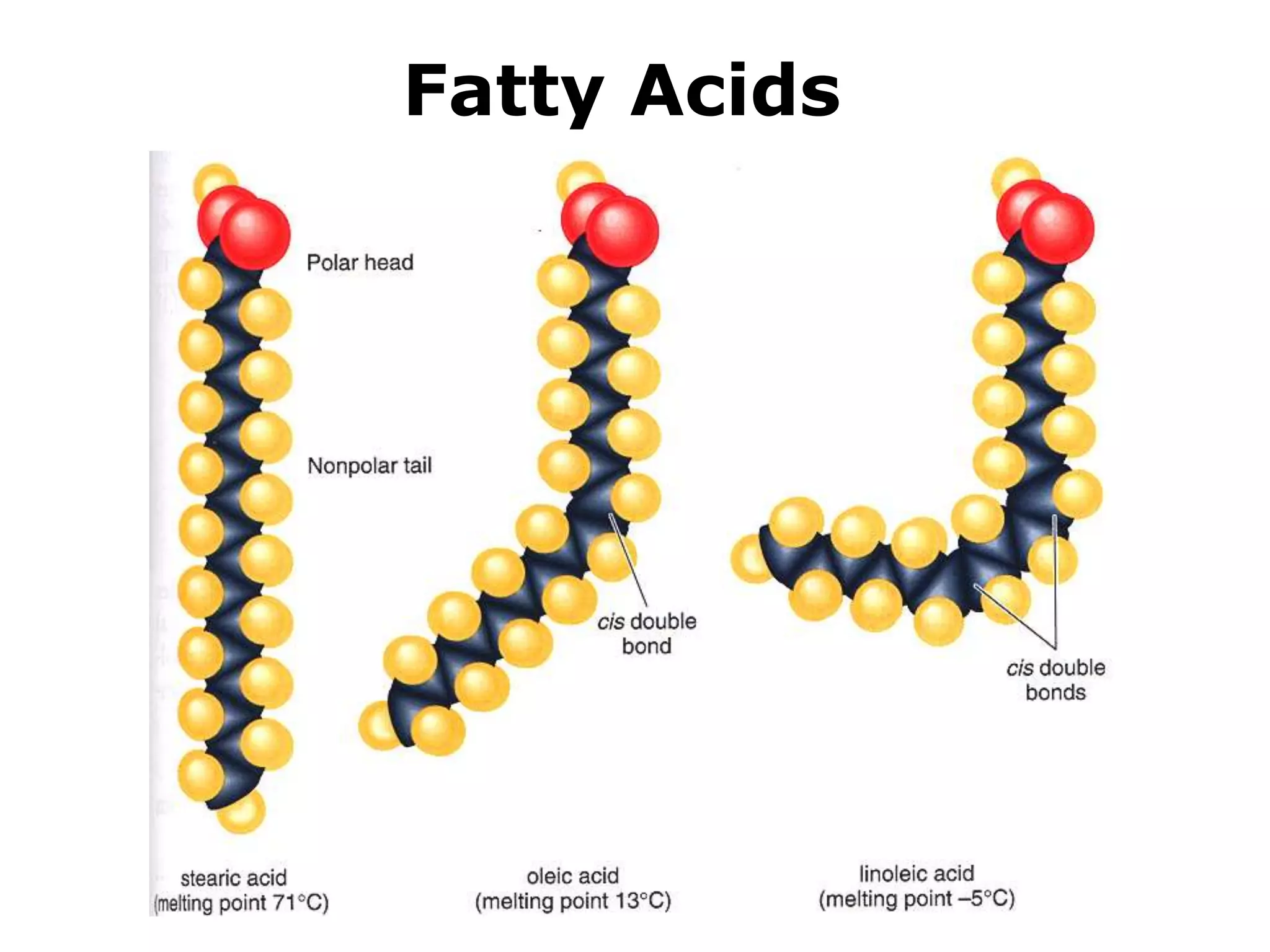
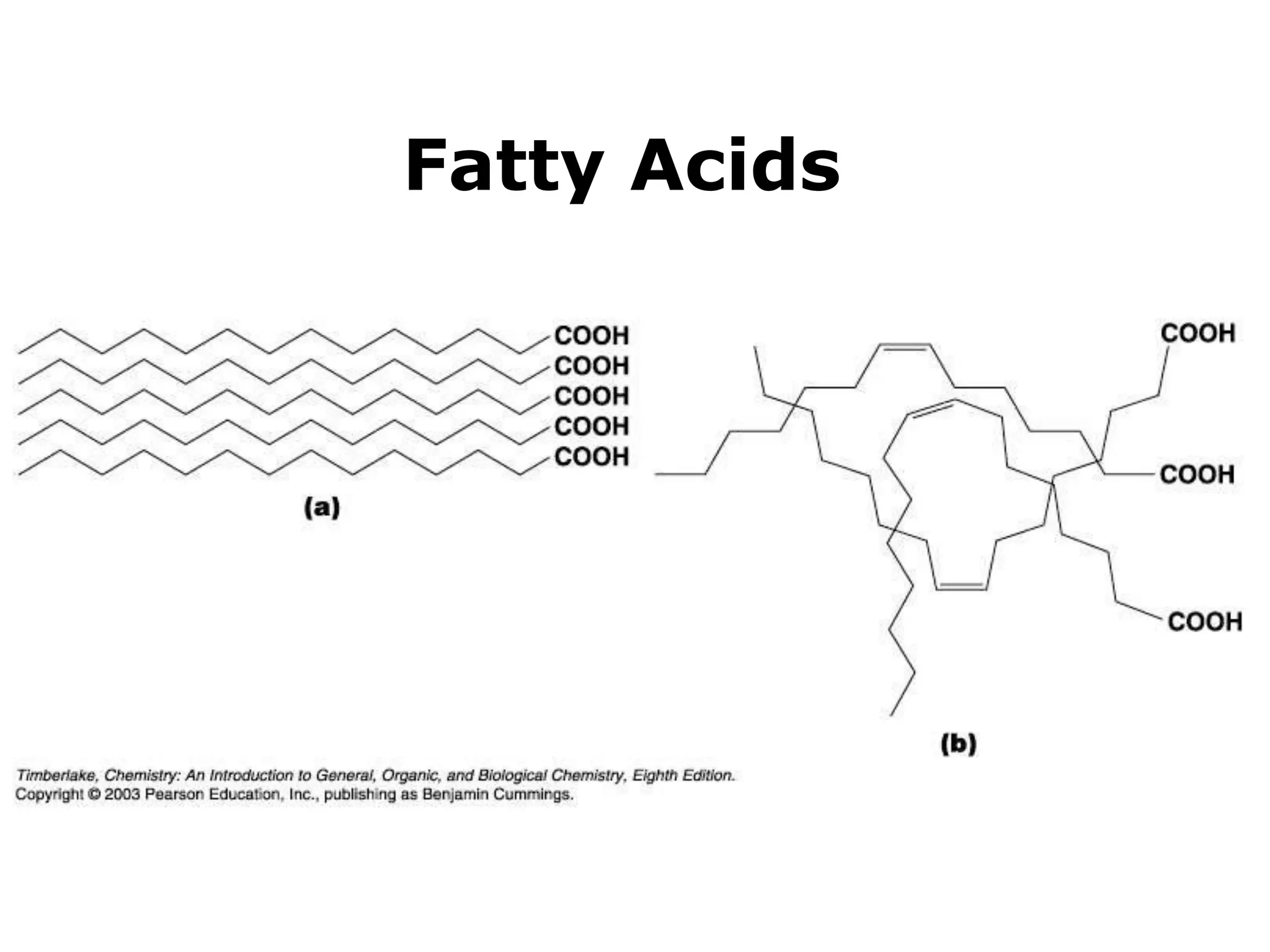
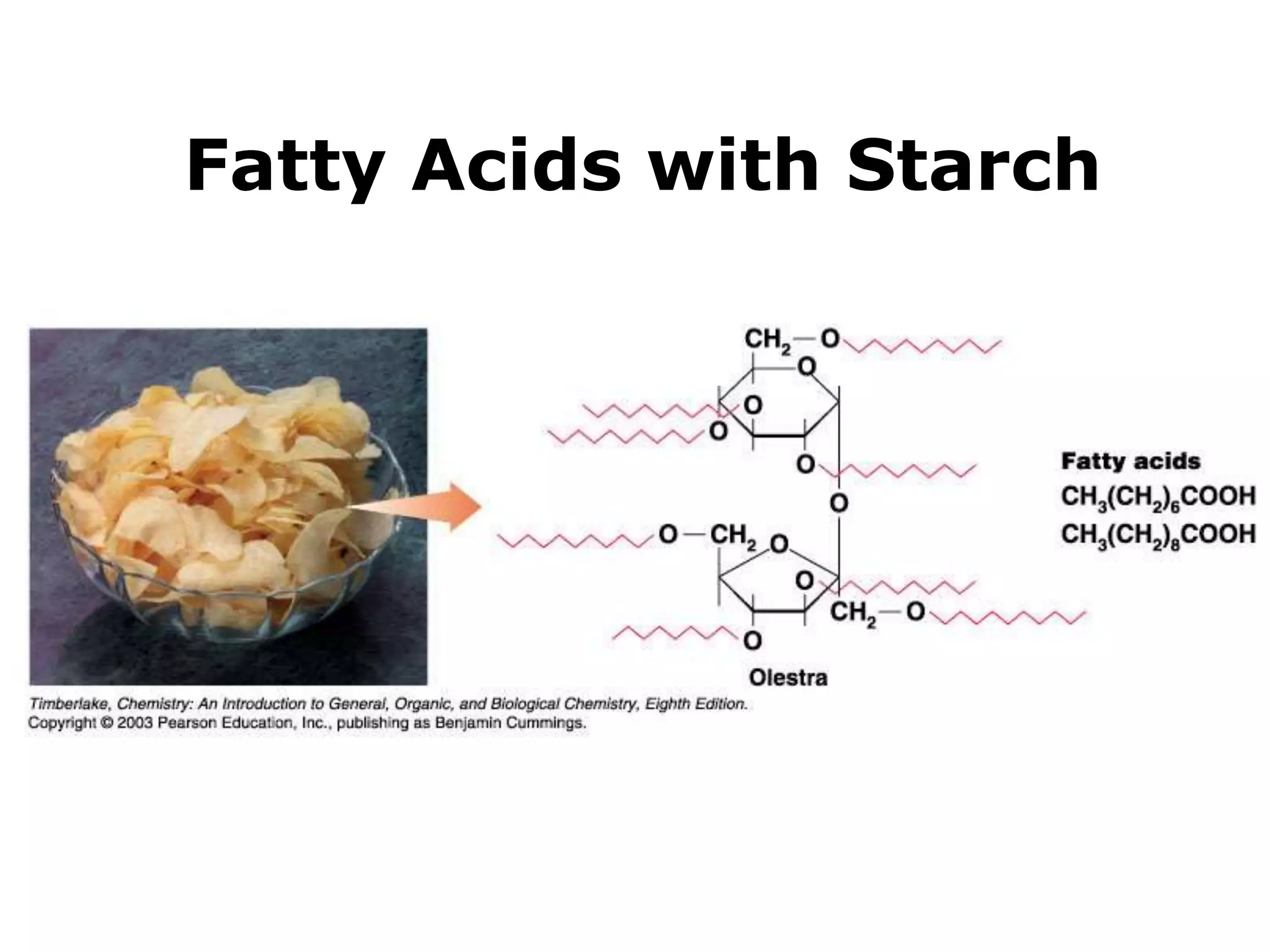
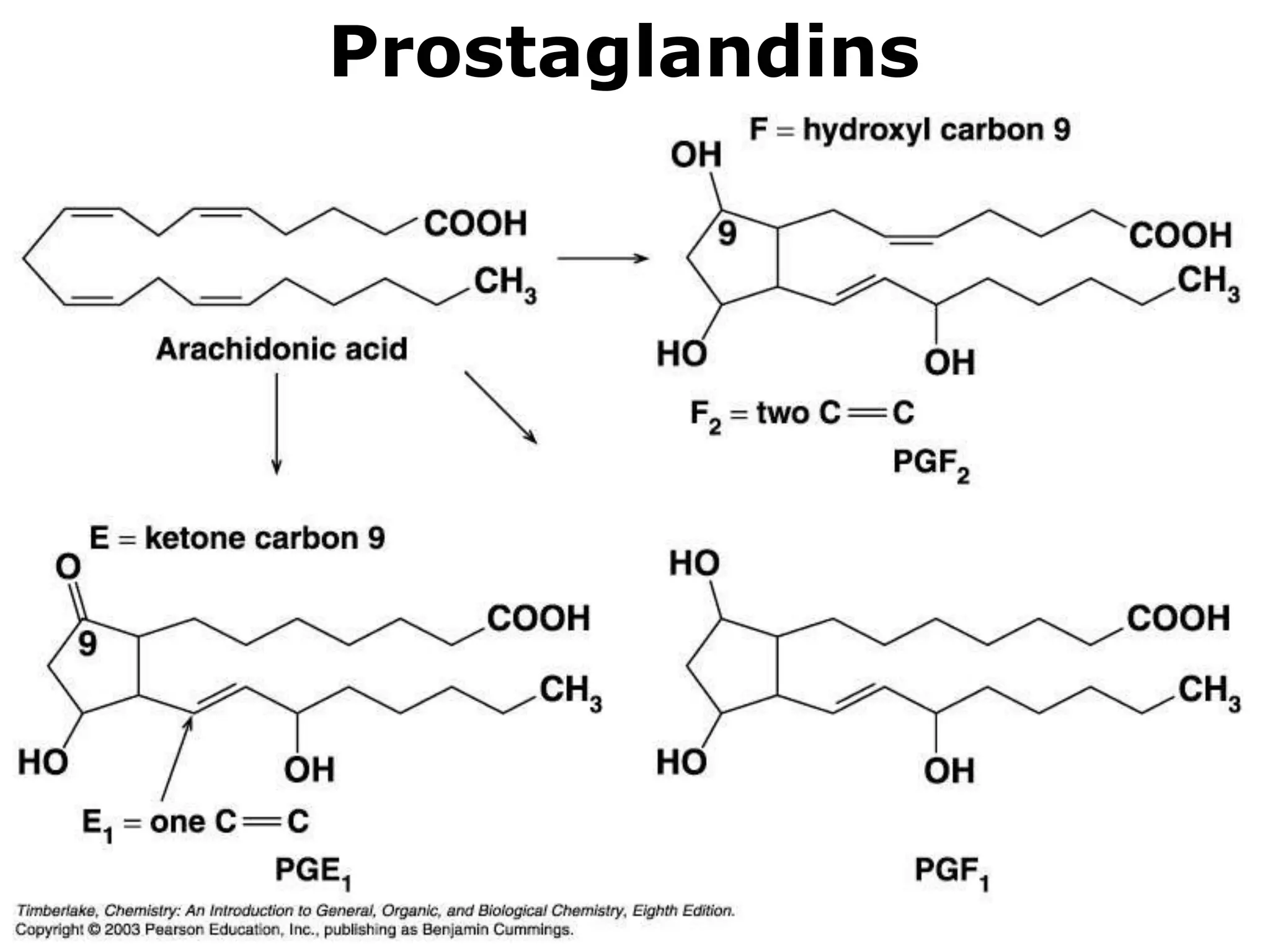
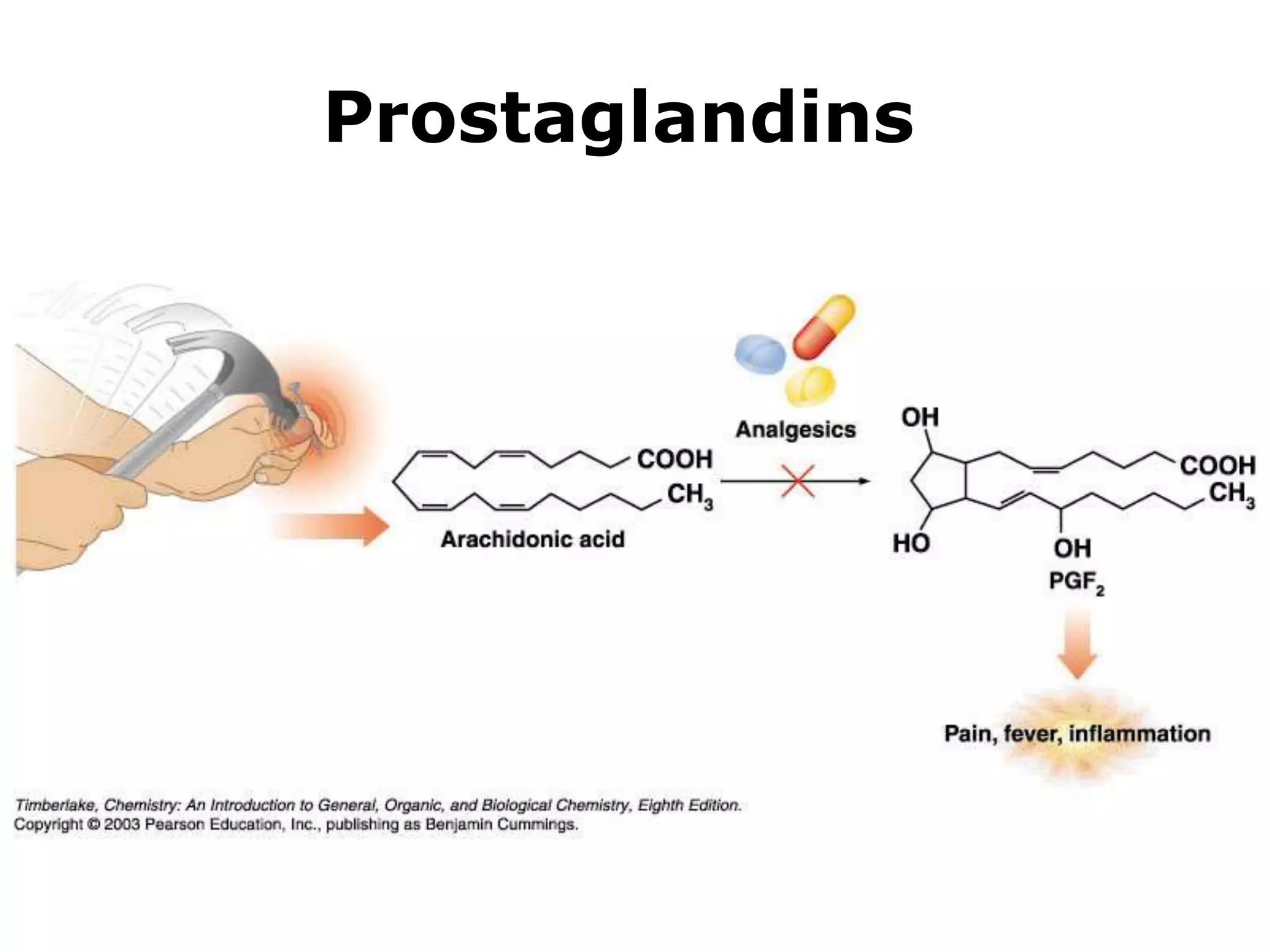
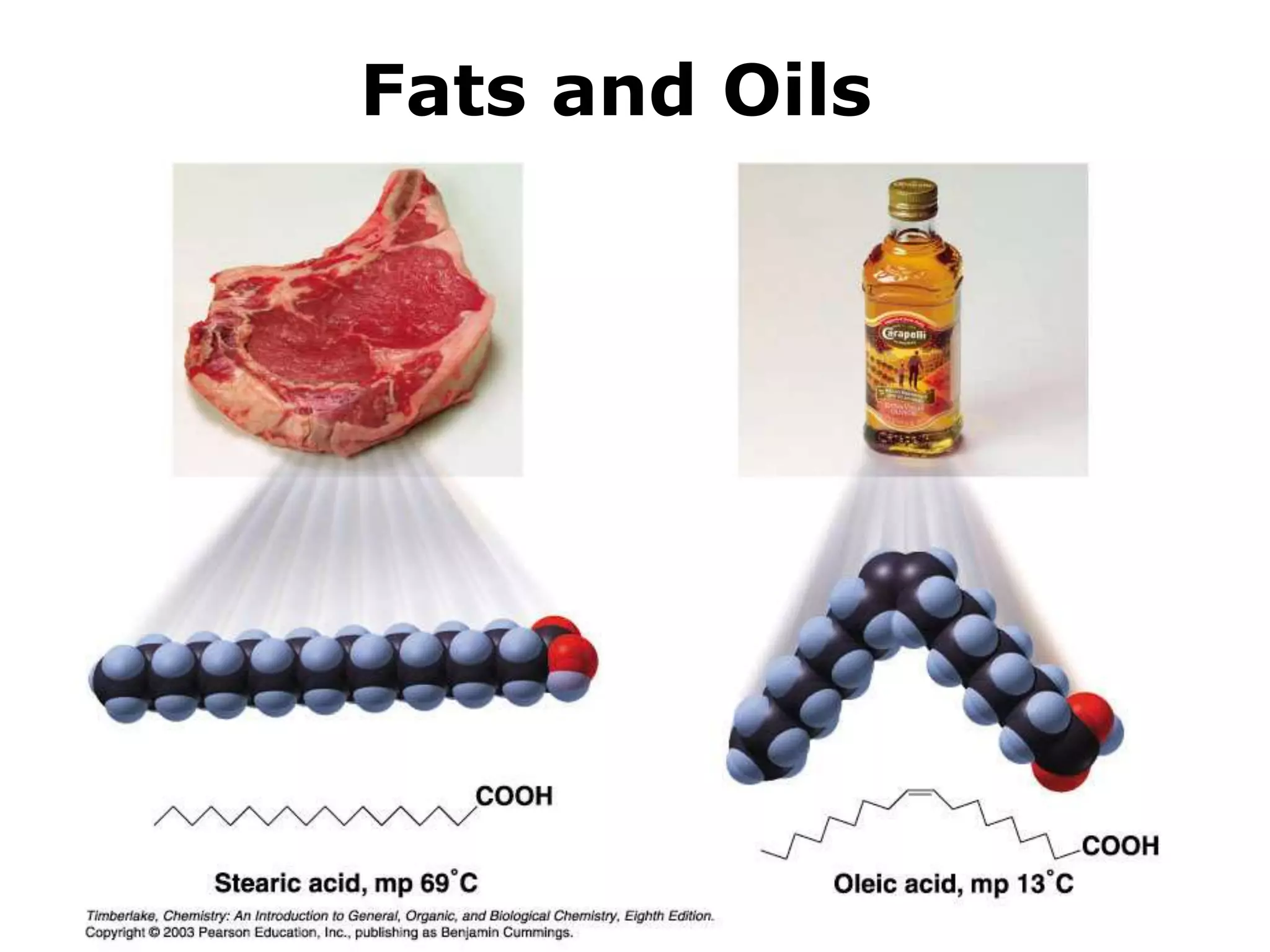
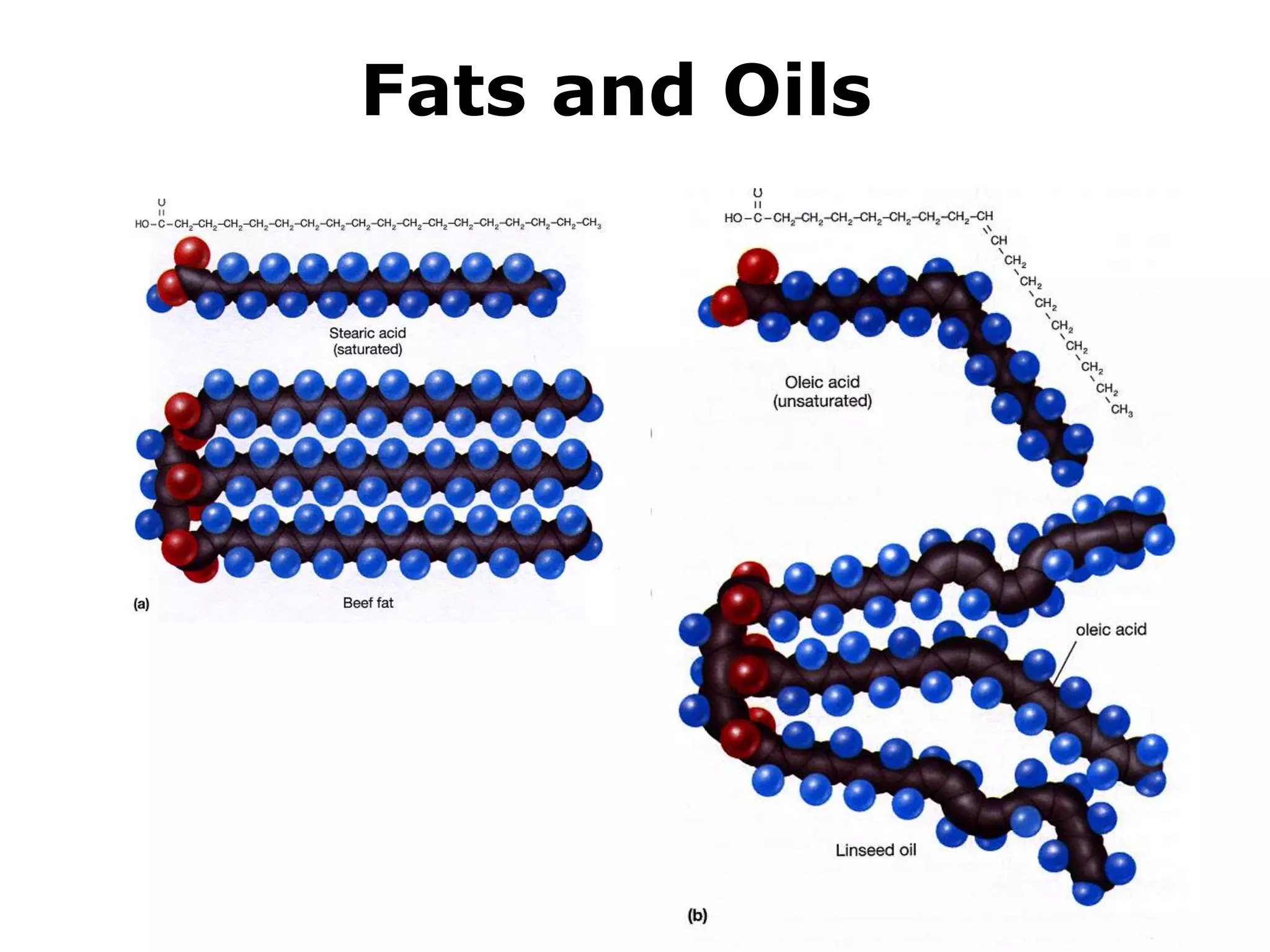
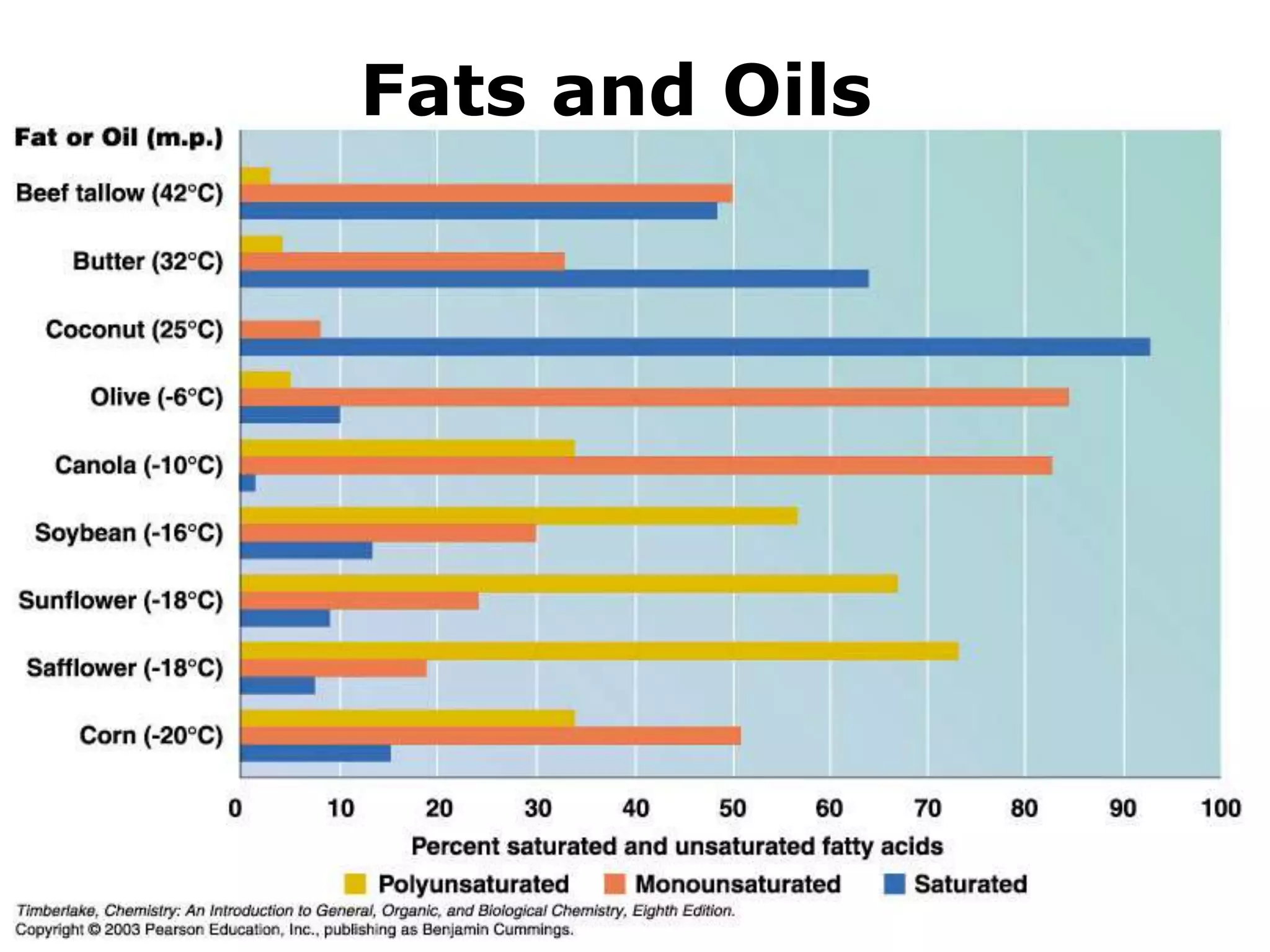
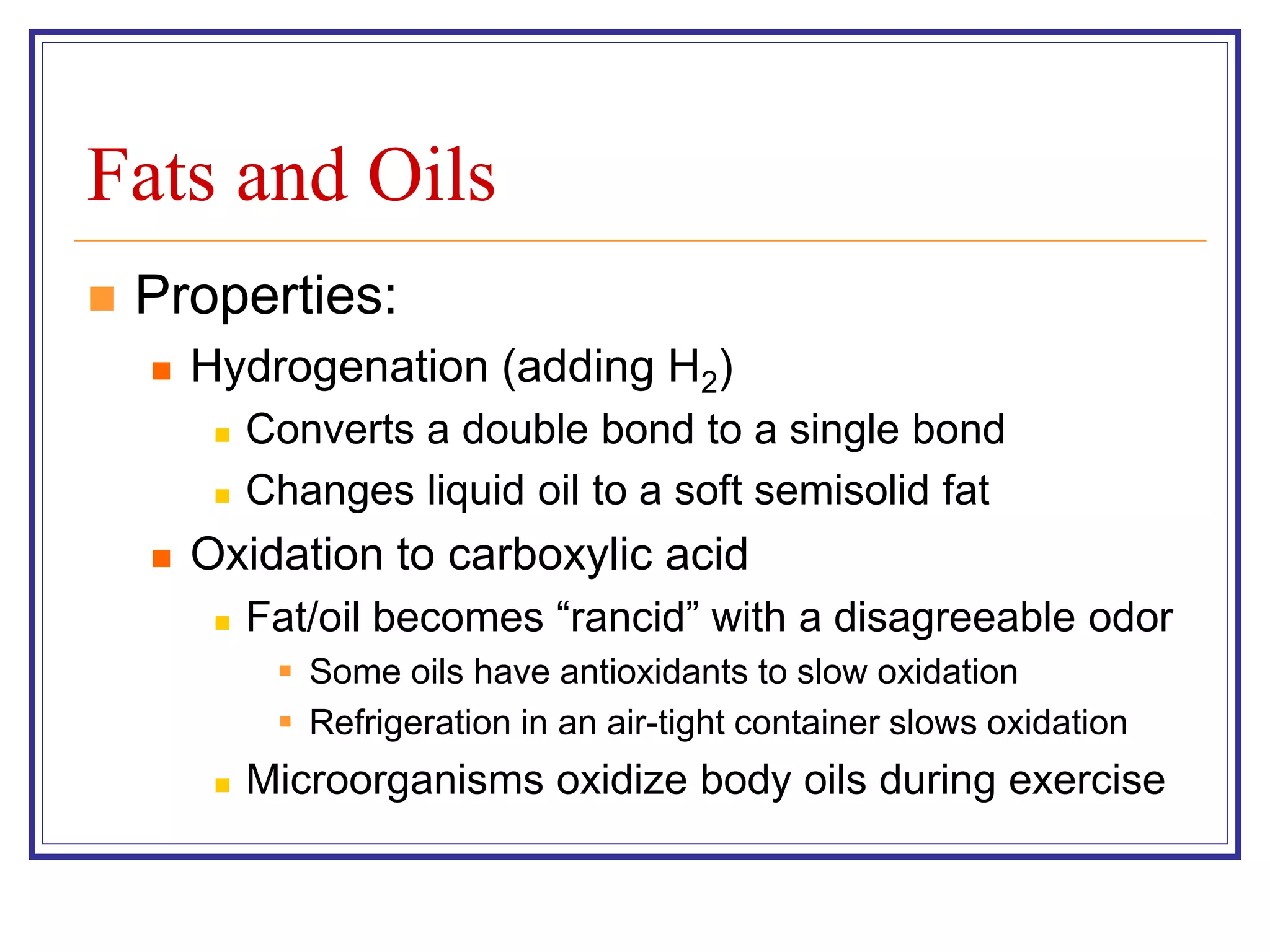
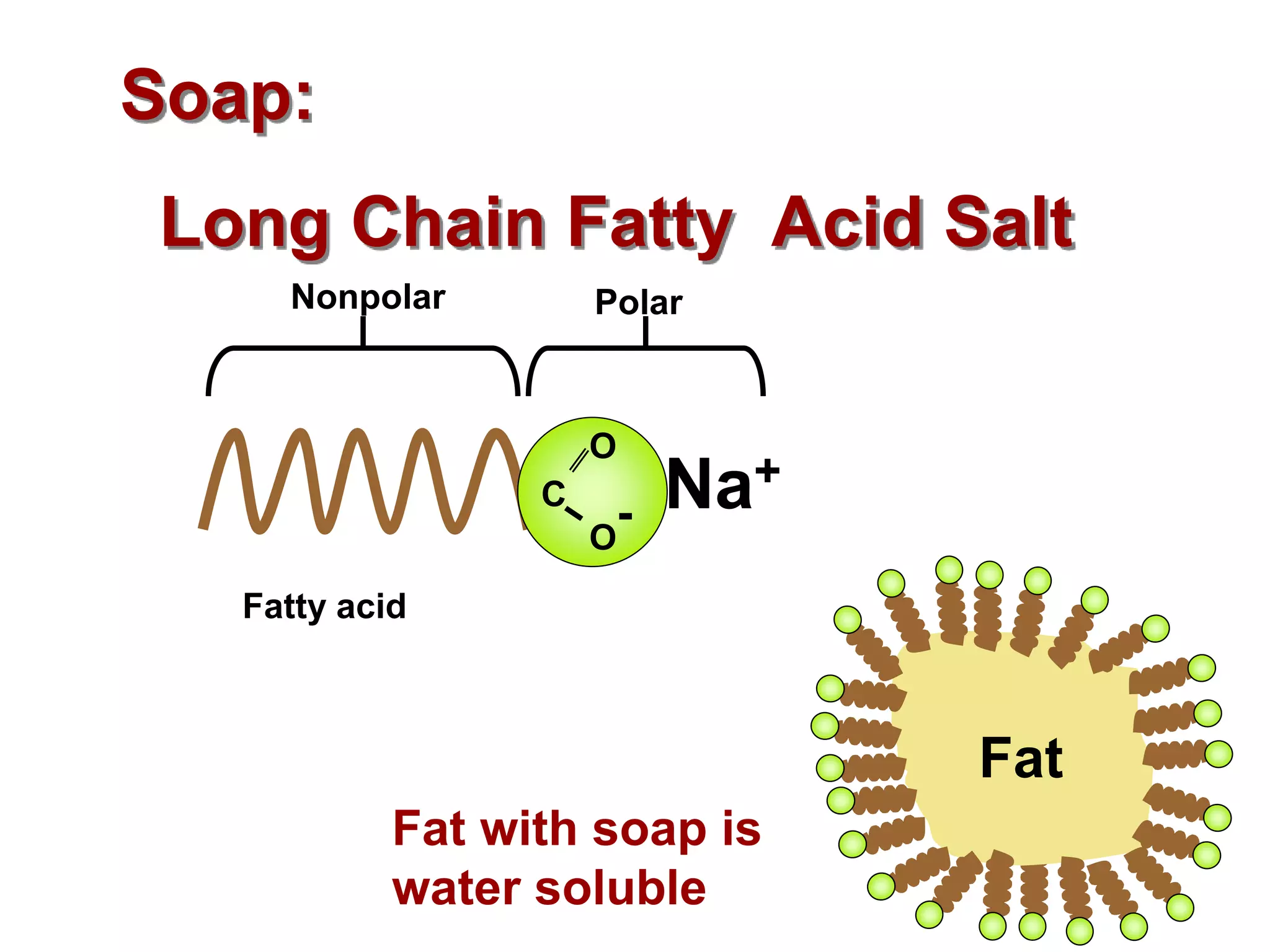
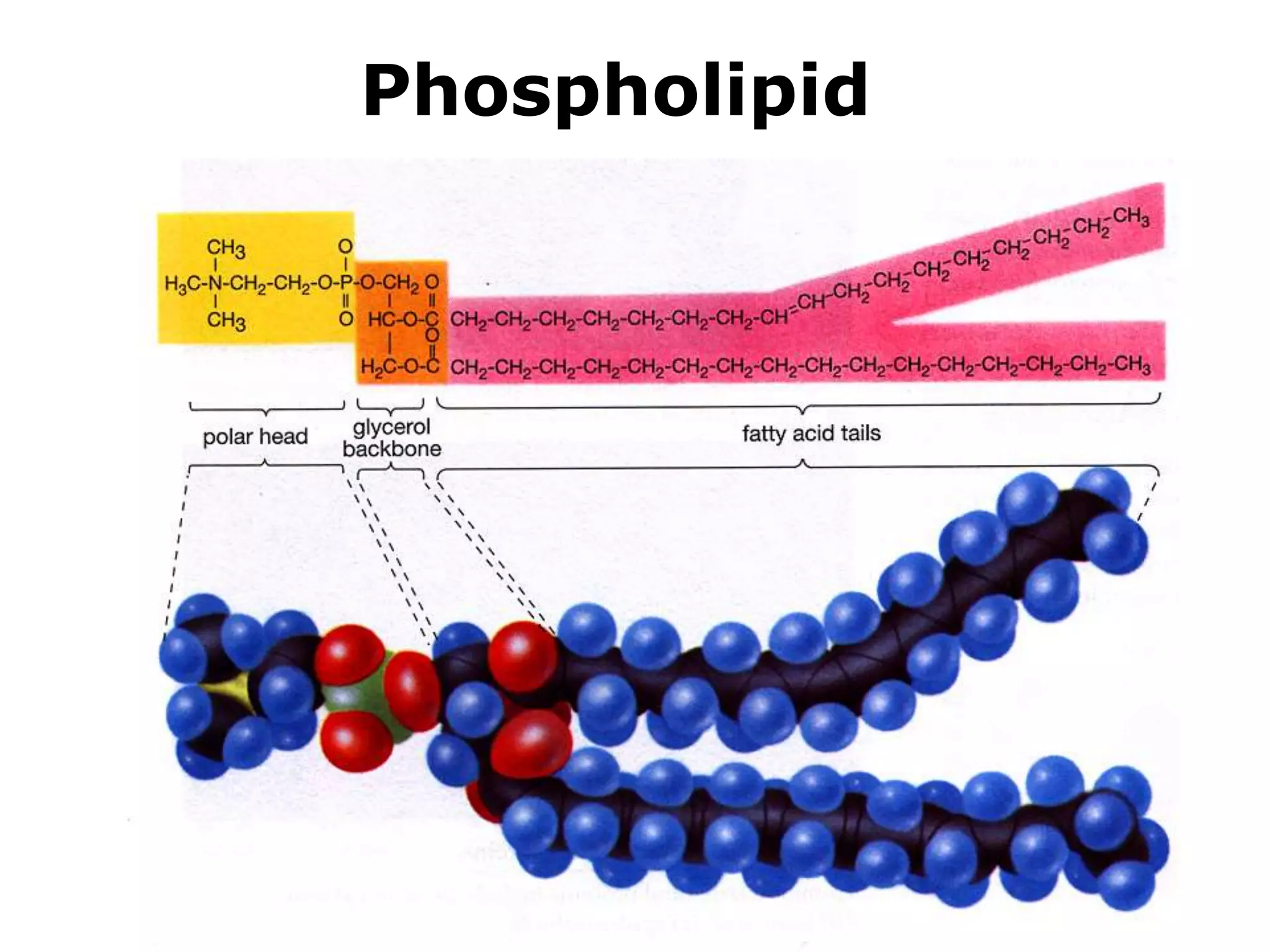
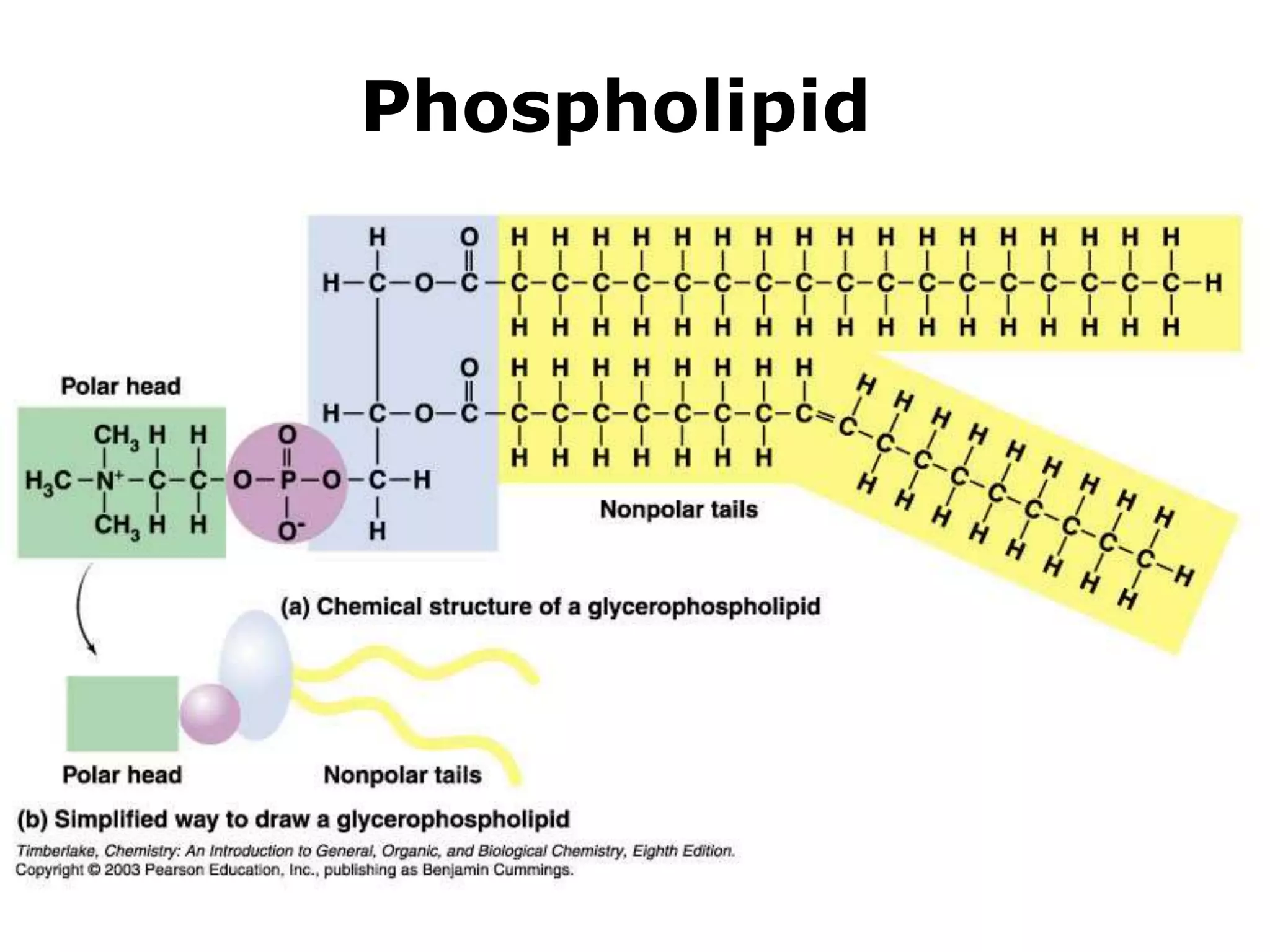
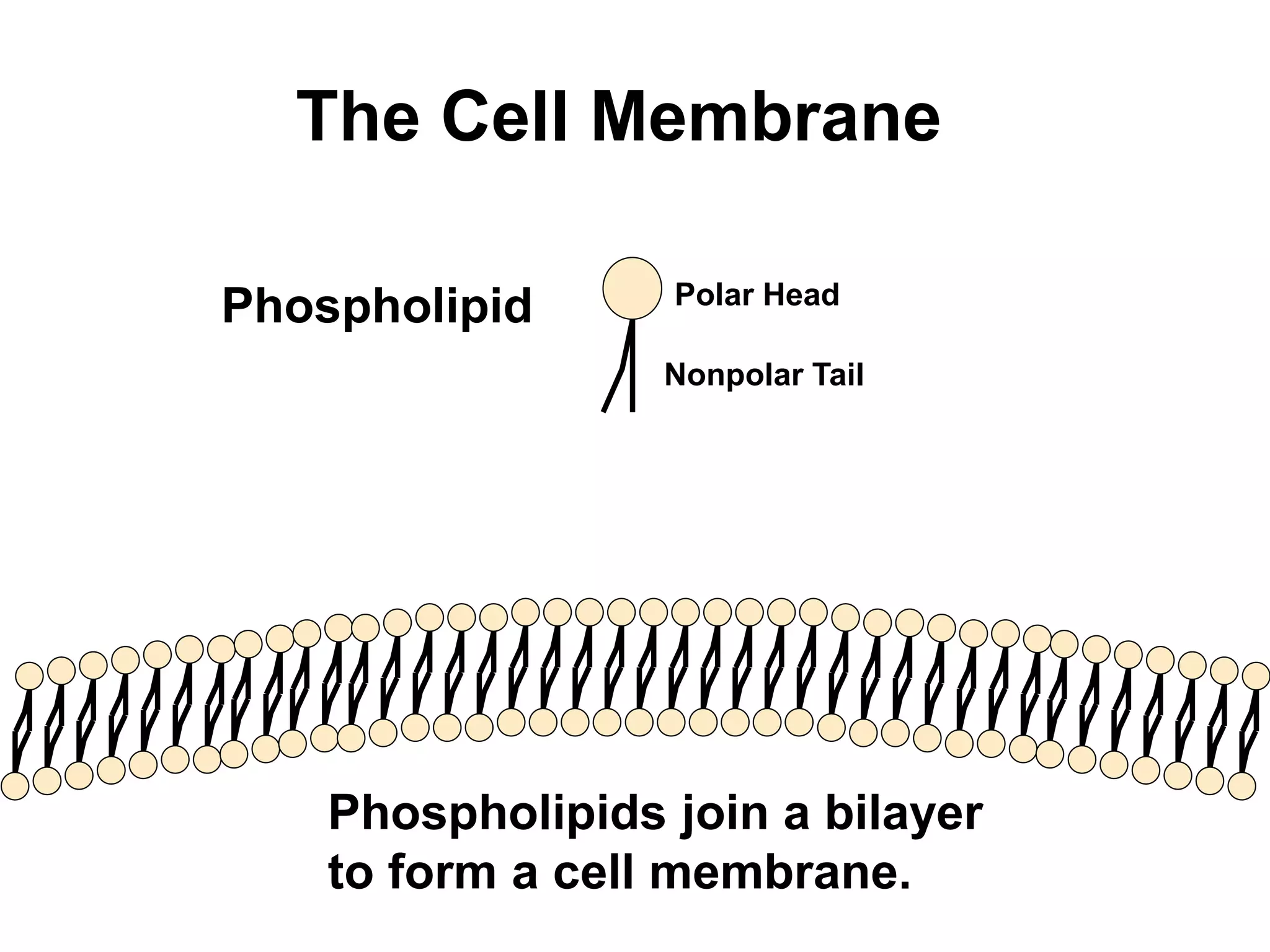
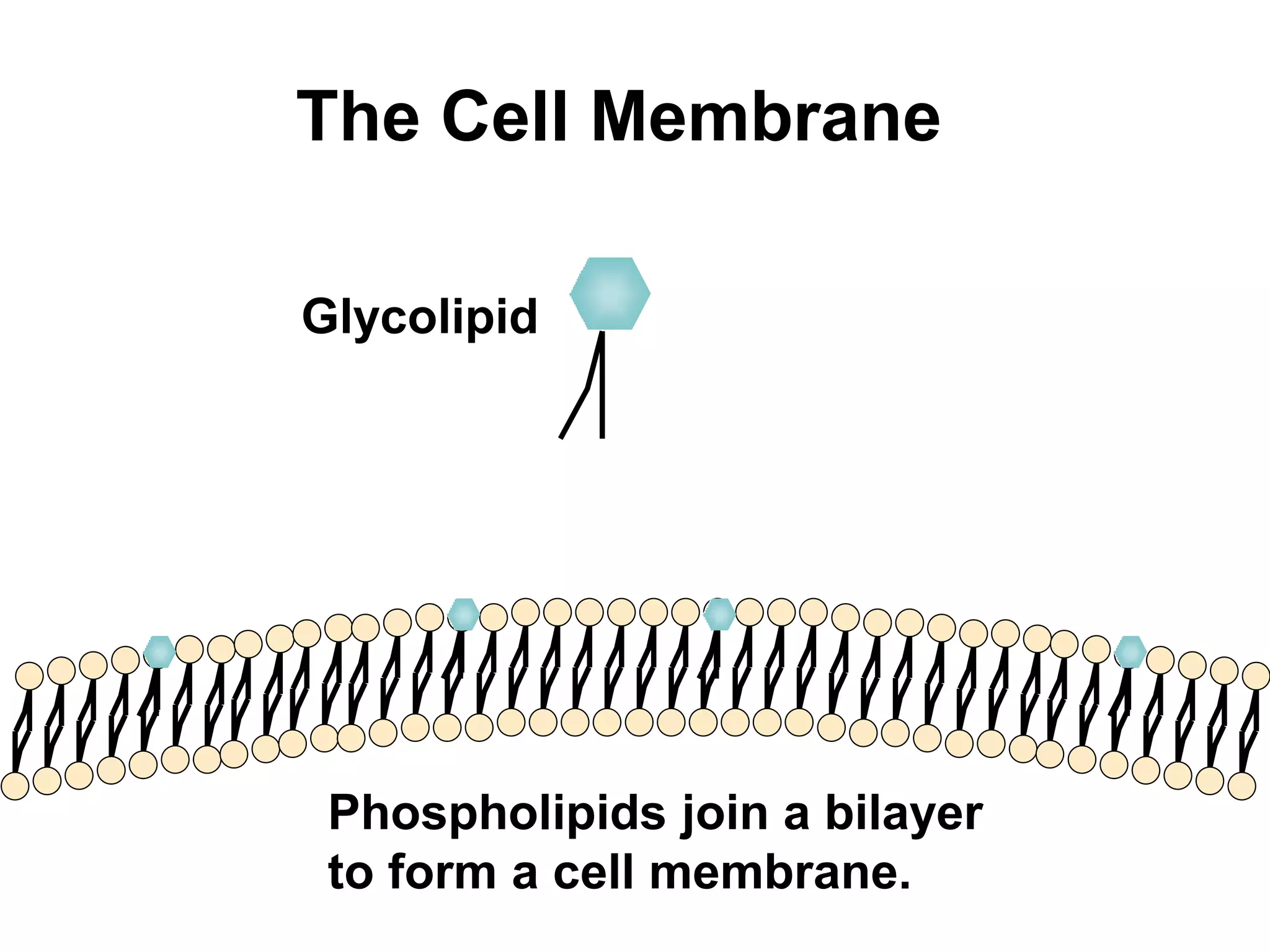
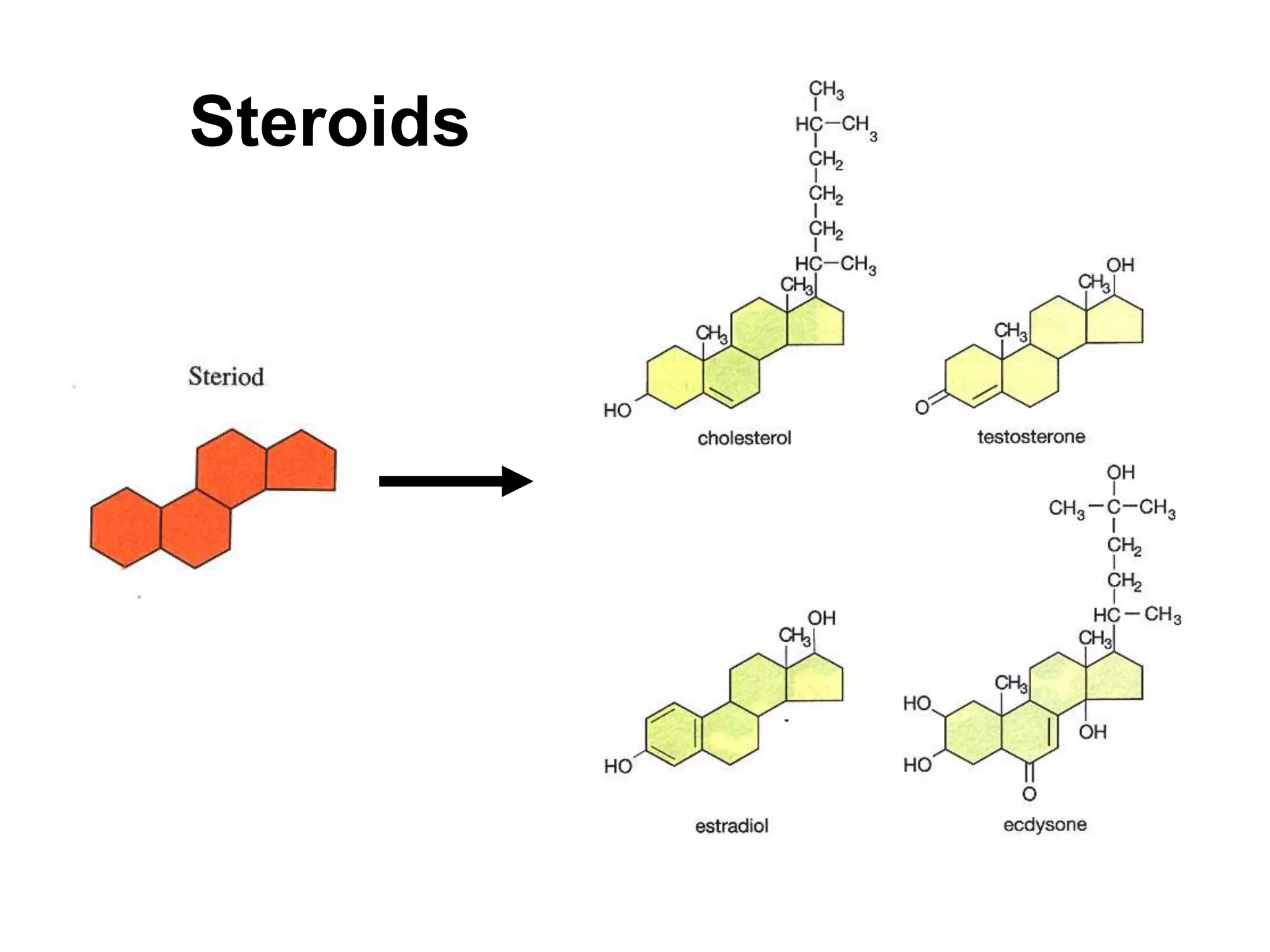
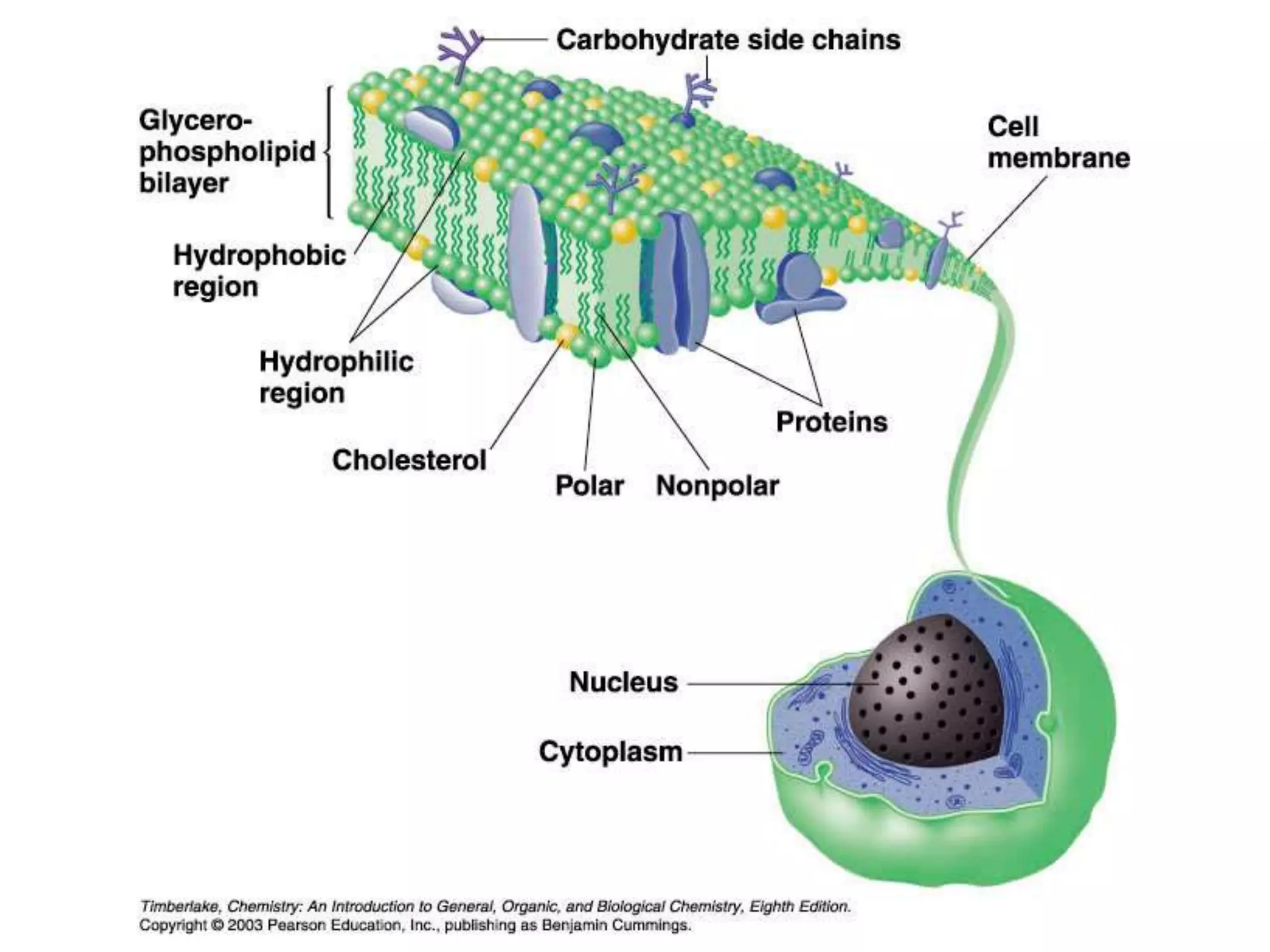
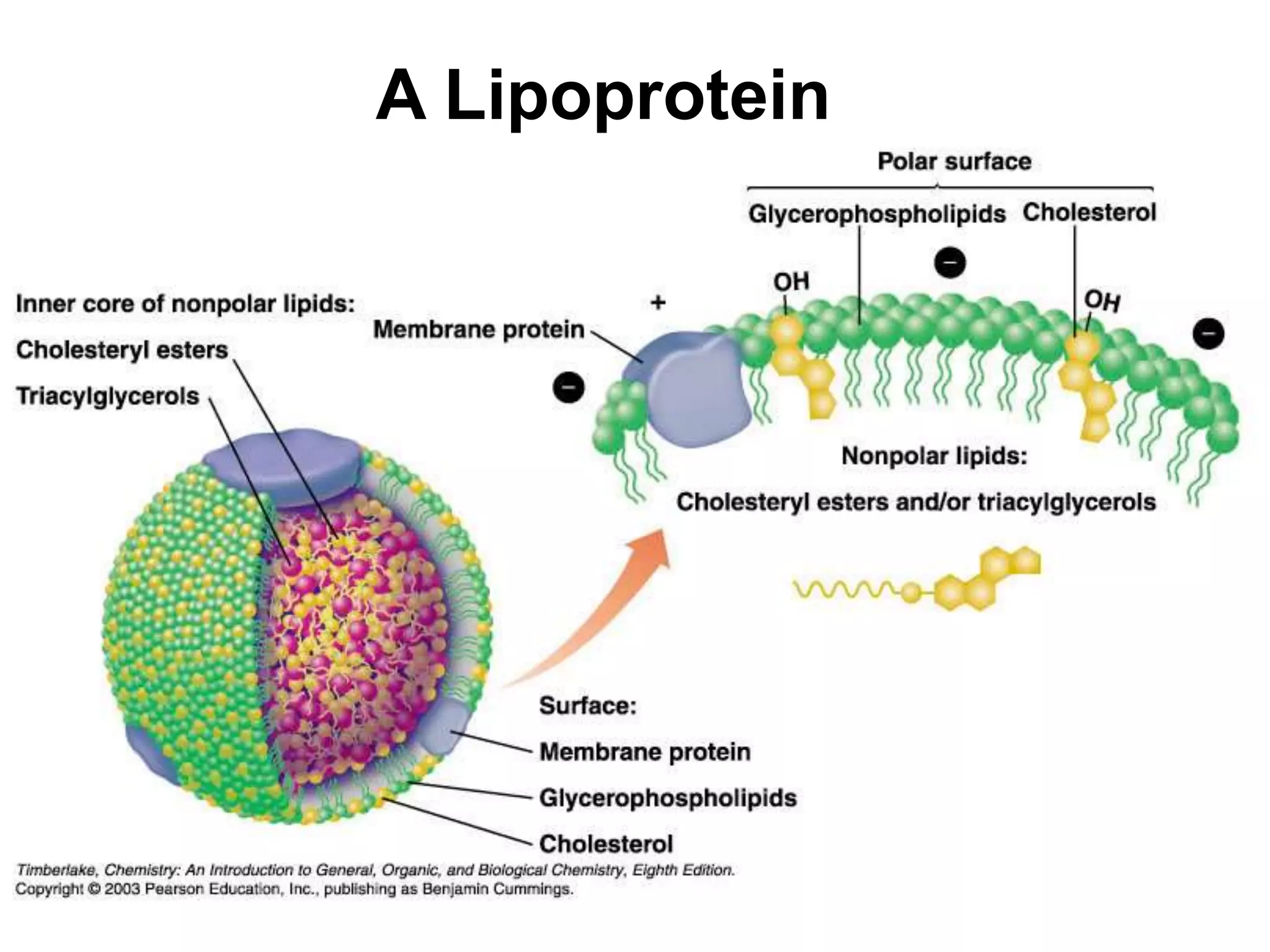
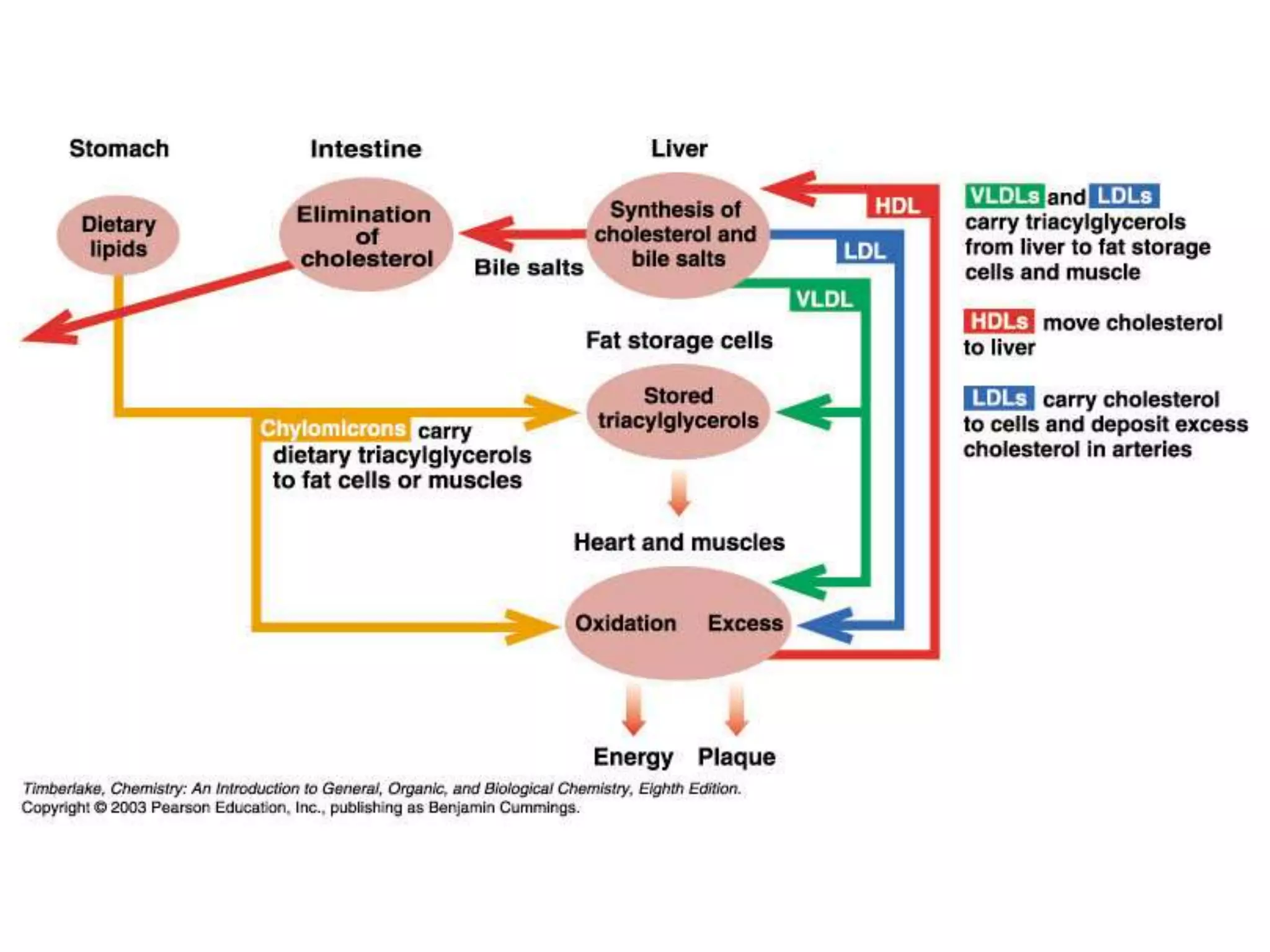
The document discusses various classes of lipids, their structures, and functions, including fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, glycolipids, and steroids. It highlights the importance of essential fatty acids, the properties of fats and oils, and the role of lipoproteins in transporting lipids in the body. Additionally, it touches on the health implications of certain lipids, such as cholesterol and its relation to gallstones and arterial plaque.