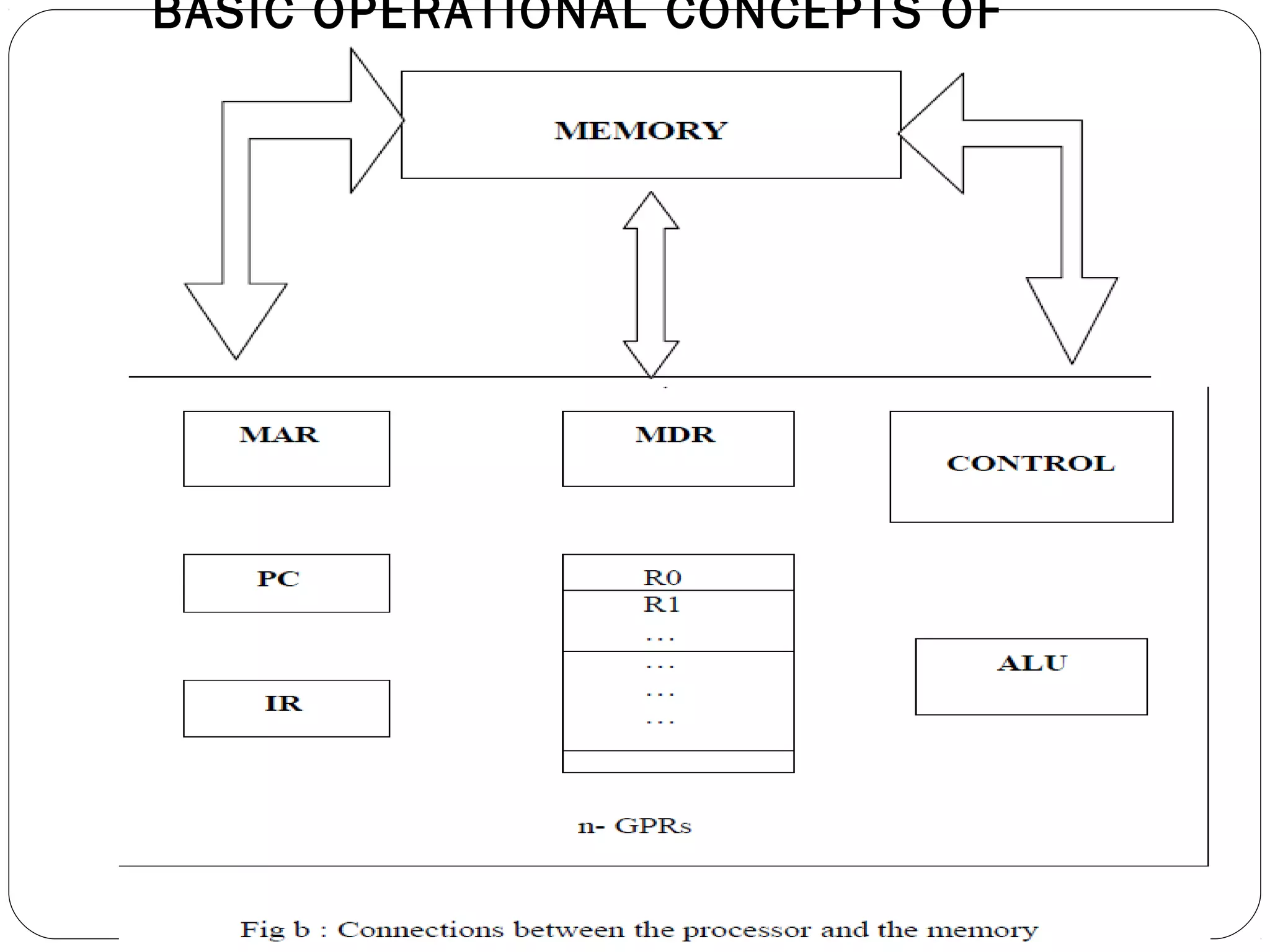
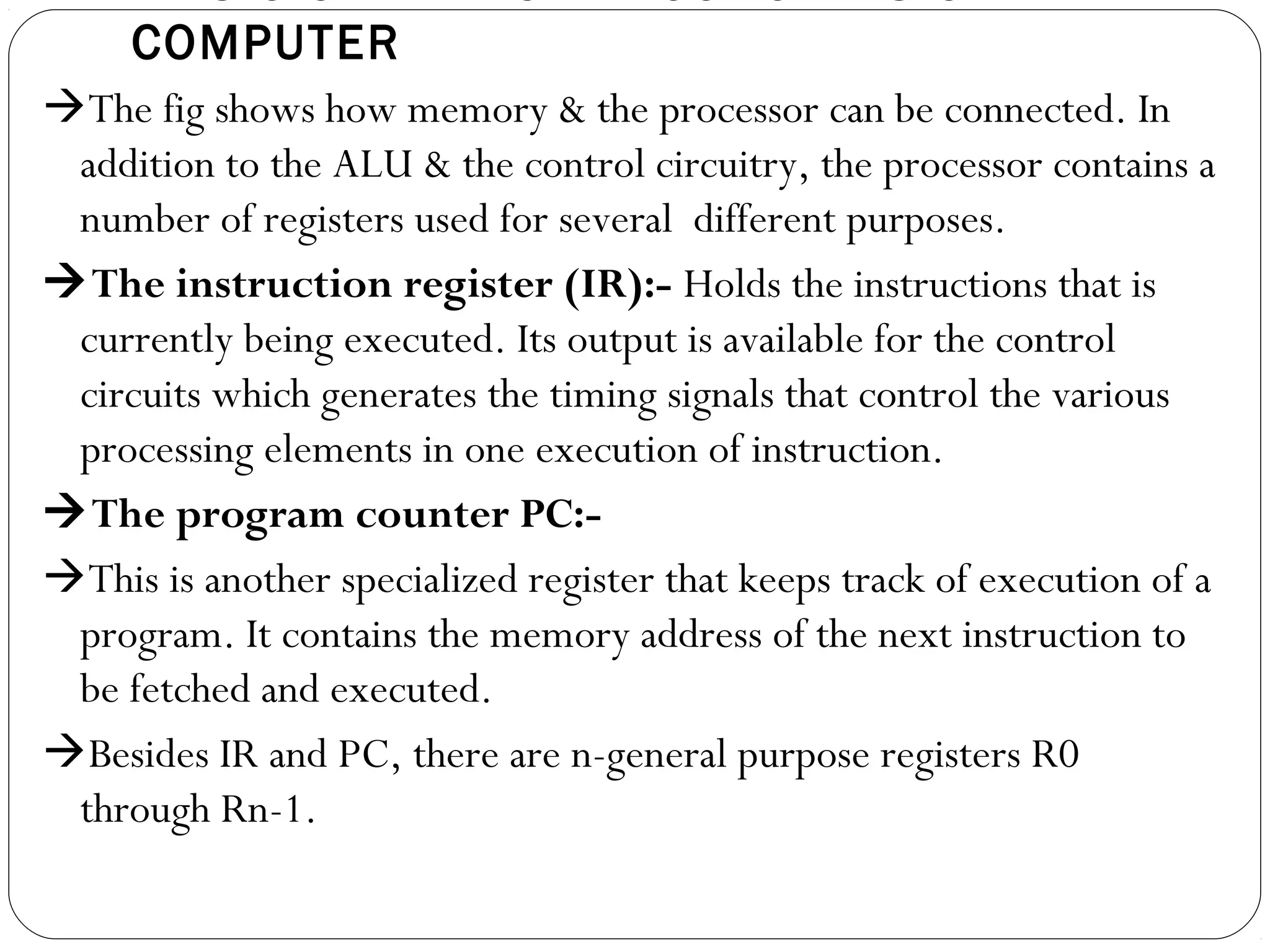
To perform tasks, programs consisting of instruction lists are stored in memory. Individual instructions are fetched from memory into the processor for execution. Data is also stored in memory. The processor contains an ALU, control circuitry, and registers like the instruction register (IR), program counter (PC), memory address register (MAR), and memory data register (MDR). Instructions are fetched from memory based on the PC, decoded and executed, potentially accessing operands from memory via the MAR and MDR and performing operations in the ALU. Results may be written back to memory using the same process.