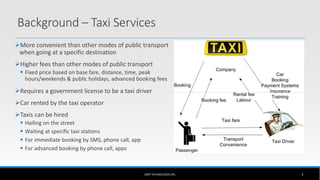
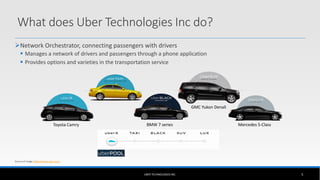
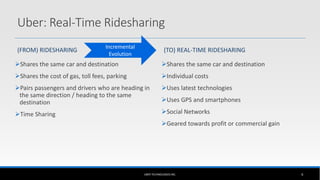
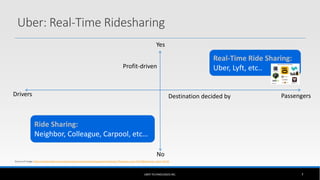
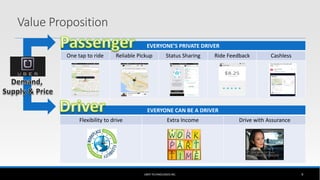
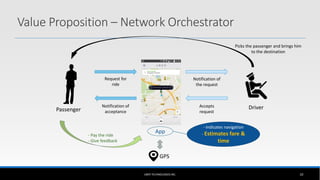
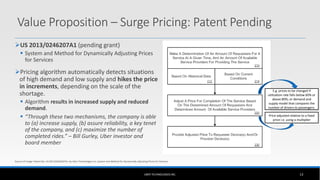
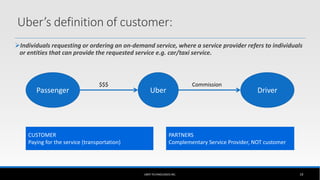
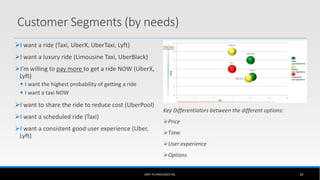
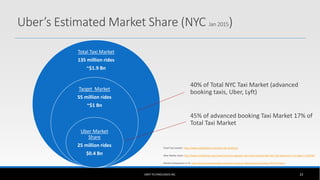
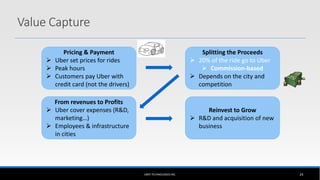
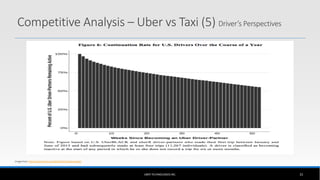
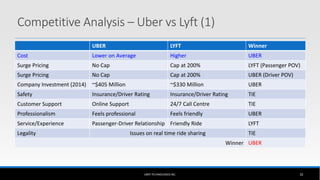
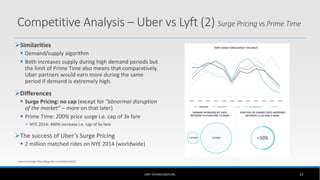
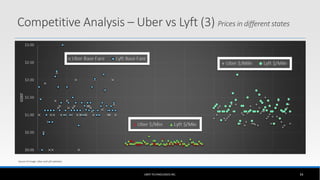
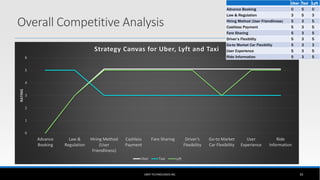
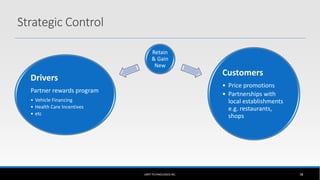
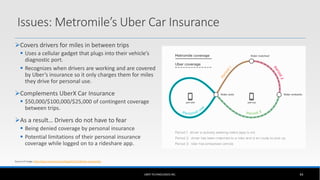
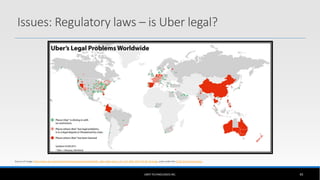
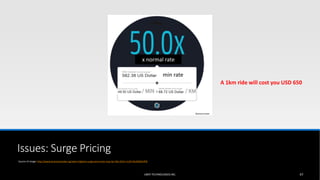
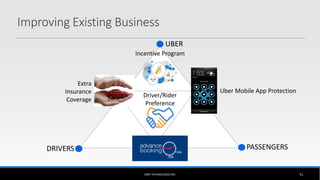
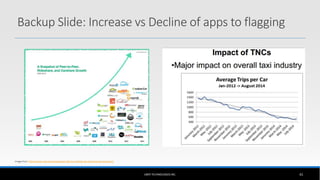
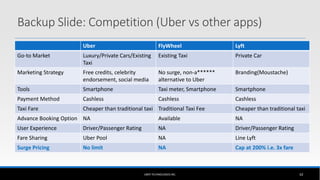
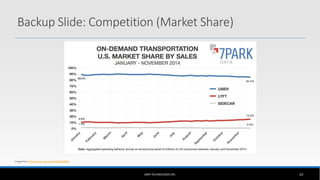
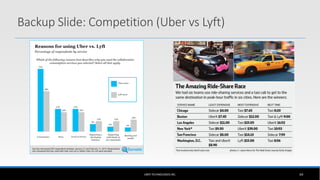
The document outlines the business model of Uber Technologies Inc., emphasizing its role as a network orchestrator that connects passengers with drivers through a mobile app. It discusses key aspects such as the value proposition, customer segments, pricing mechanisms, and competition. The document also addresses issues faced by Uber, including trust and safety concerns, and the impact of surge pricing on service demand.