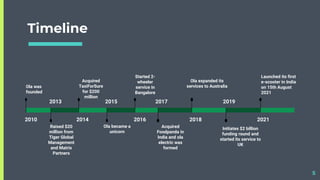
The document provides a case study of Ola Cabs, an Indian ride-hailing company. It discusses how Ola was founded in 2010 to address issues with India's fragmented and unorganized taxi market. Ola's co-founders worked tirelessly in the early days to build the business. Over time, Ola expanded its services, acquired competitors, raised funding, and became a unicorn valued at over $6.5 billion. However, the COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted Ola's core ride-sharing business initially. Ola adapted by focusing on financial stability and electric mobility. The case study outlines Ola's business model, timeline of growth, expansion into new services, valuation and effects of the pandemic.